An insurance company wants to increase sales by 15% and customer retention by 10% within 1 calendar year.
Various strategies to achieve this were considered and a restructure to the existing pricing model is selected to help achieve these goals.
A business analyst (BA) works with stakeholders such as actuaries, product specialists, sales staff, risk managers, and underwriters who agree to applying varying levels of discounts to customers based on:
•Total annual premium the customer has with the company (Financial worth)
•Time with the insurance company (Loyalty)
Various financial models are considered but the stakeholders agree that an initial applicable discount is determined based on the customer's overall premium:
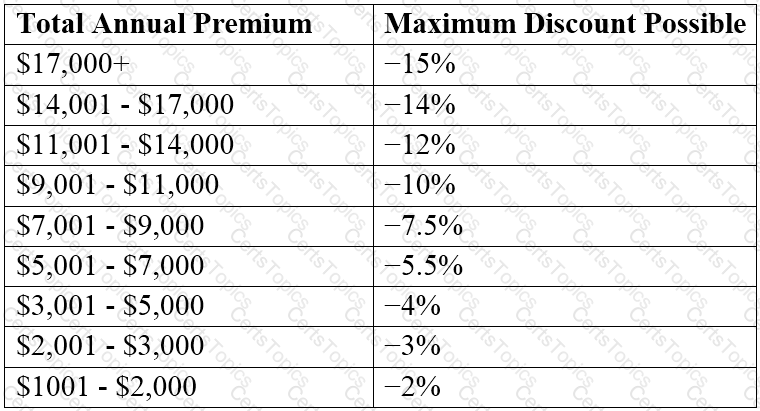
The percentage of the maximum possible discount available to the customer is adjusted based on time with the company:
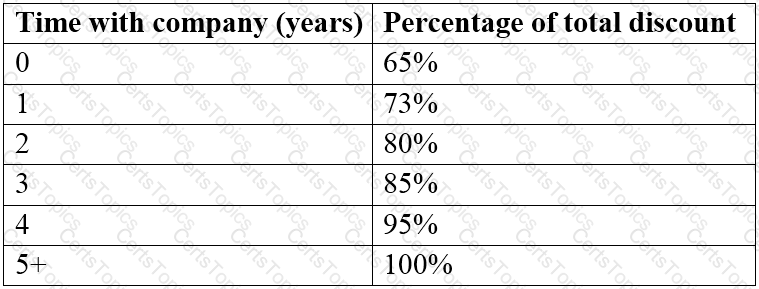
Which technique would the BA use to validate the desired outcomes?
A company has a process improvement initiative that is projected to increase revenue by $150,000 USD non- compounded per year. The budgeted cost of the initiative is $200.000 and supporting the initiative will cost
$30.000 for years two and three.
What is the projected return on investment over the first 3 years?
A company that specialized in manufacturing vending machines for books has been in business for 10 years. As the e-book and online retailing grow, the company perceived that a change is required to respond to the new emerging market forces. However, the change should focus on reusability as much as possible to reduce expenses. After analyzing the current state with the business subject matter experts, the business analyst
(BA) proposed investing in a new business line of vending machines that sell pay per use mobile device phone fast charging stations.
Due to the urgency of this change, the BA was asked to finalize requirements elicitation in the shortest possible time.
By proposing this change, what type of view did the BA use to analyze the current manufacturer's state?
A non-profit utility company has 900 employees, a majority of whom are hourly employees and must track their time using a paper based process A few years ago, the Director of Human Resources purchased a software system to eliminate the current paper-based time reporting process. No requirements specific to the utility company were defined prior to the purchase. A team was formed to implement the software During implementation process, the team discovered the software lacked functionality and was not robust enough to support the general ledger requirements The company stopped the effort and incurred a $500,000 USD loss on the cost of the software.
This year, the Director of Finance requested that a team investigate the current paper based time reporting process and recommend solutions. The Director of Finance feels that the Director of Human Resources must be involved as a critical stakeholder. The Director of Human Resources is still bitter about the last effort because the process stopped'.
During a brainstorming session on improvement opportunities, the Director of Human Resources repeatedly interrupts the group and states why the proposed ideas will not work.
Which approach should the business analyst (BA) take to refocus the group?