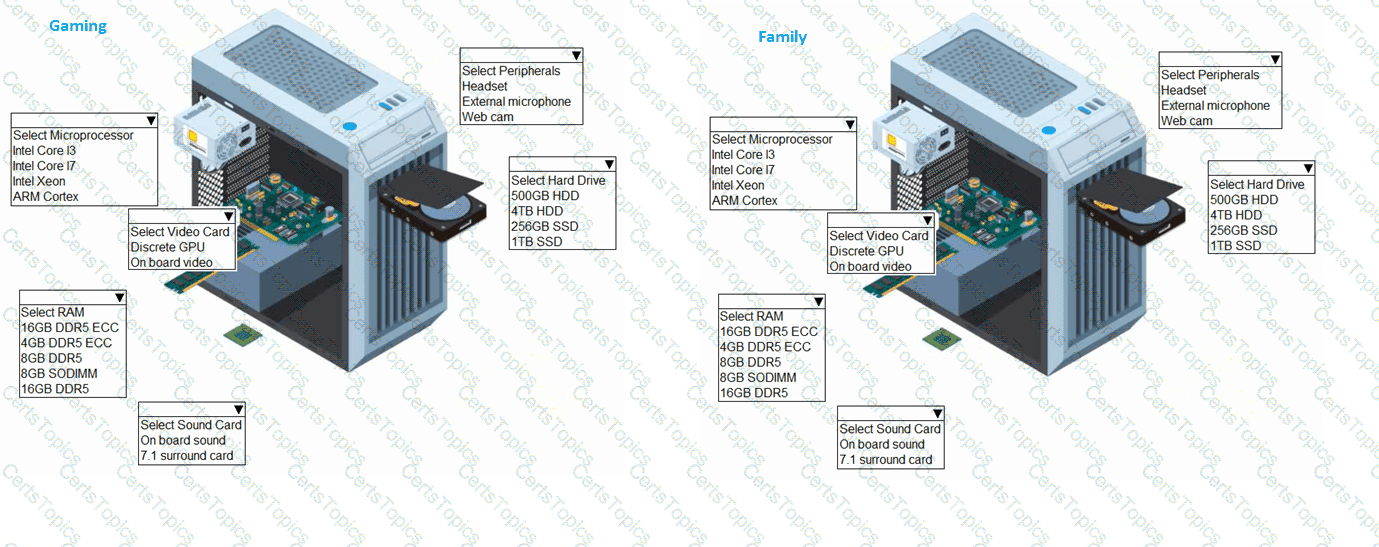
A customer has contacted you about building two new desktops. The first desktop will be a gaming workstation. The customer requirements include:
Playing the newest games at a high frame rate
Fast game load times
Enough storage to have several games installed at once
High-end audio
No concern about cost
Running the current Windows OS
The second workstation will be a family workstation. The requirements include:
Capability for word processing, videoconferencing, and basic web surfing
Minimal cost, as long as it meets the requirements
Running the current Windows OS
A drive failed on a server that was leveraging a RAID disk configuration. The server administrator would like to rebuild the array so it can withstand a potential multidrive failure in the future. Which of the following RAID configurations will the administrator MOST likely select?
A technician is troubleshooting a laptop that has a blank LCD panel. The technician shines a flashlight into the LCD and sees a faint image. Which of the following BEST describes the issue?
A technician connects a new computer to the internet and then opens the wiring closet. Even though all of the wires are terminated, nothing in the wring closet is labeled. Which of the following tools should the technician use to complete the task?