A security analyst has determined that a security breach would have a financial impact of $15,000 and is expected to occur twice within a three-year period. Which of the following is the ALE for this risk?
Which of the following practices would be best to prevent an insider from introducing malicious code into a company's development process?
A company is developing a business continuity strategy and needs to determine how many staff members would be required to sustain the business in the case of a disruption. Which of the following best describes this step?
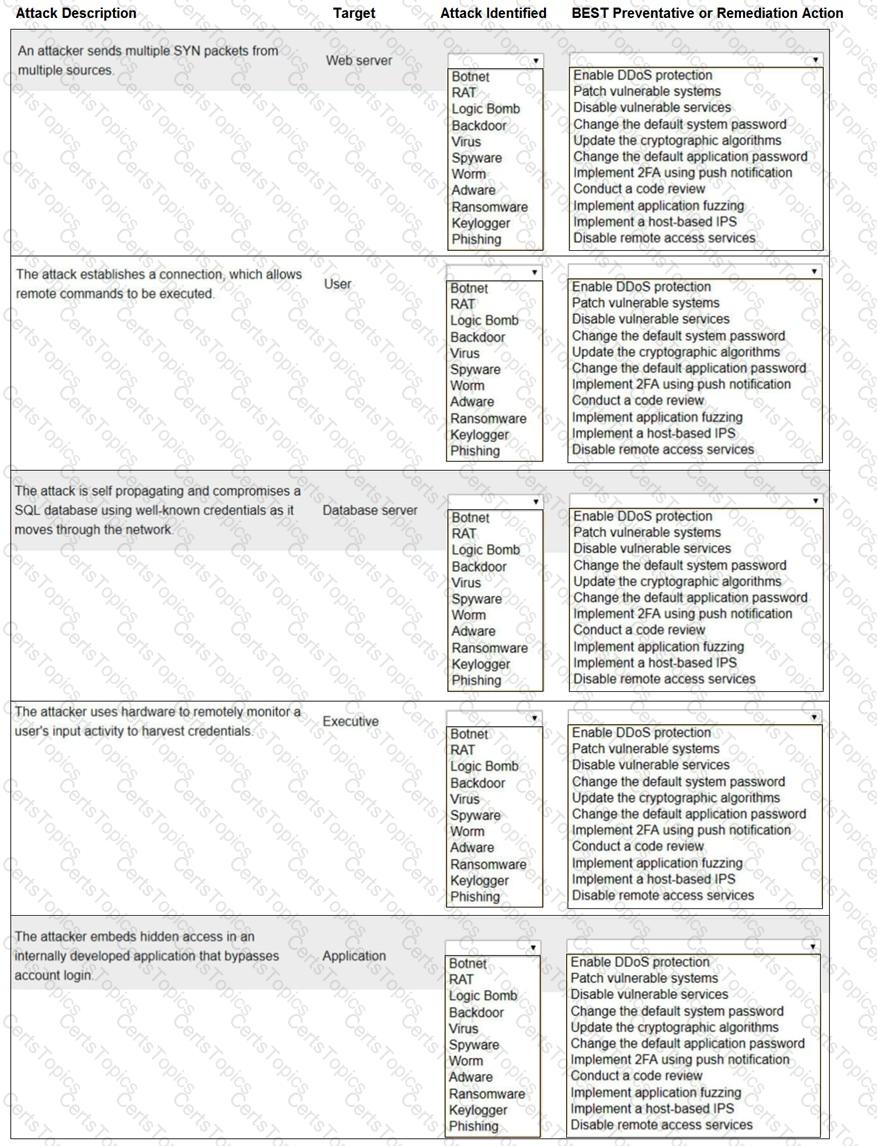
Select the appropriate attack and remediation from each drop-down list to label the corresponding attack with its remediation.
INSTRUCTIONS
Not all attacks and remediation actions will be used.
If at any time you would like to bring back the initial state of the simulation, please click the Reset All button.