Explanation
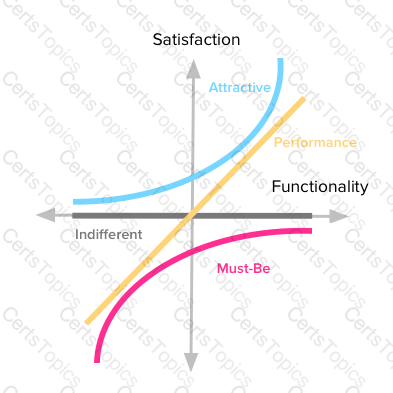
Kano model of excitement and basic quality (Kano et al, 1984; Berger et al, 1993; Matzler et al, 1996) brings a different perspective for the analysis of improvement opportunities in products and services because it takes in consideration the asymmetrical and non-linear relationship between performance and satisfaction. The Kano model classifies customers requirements in three categories (figure 3):
a) Basic Requirements (or Must-be requirement). The basic requirements fulfill the basic func-tions of a product. If they are not present or their performance is insufficient, customers will be extremely dissatisfied. On the other hand, if they are present or have sufficient performance, they don't bring satisfaction. Customers see them as prerequisites. For instance, for luxury automobiles, "air bags" are considered basic. A customer won't feel satisfied if the automobile has "air bag", however he/she will not buy it if “air bag” is not present.
b) Performance Requirements (or One-dimensional requirements). As for these requirements, satisfaction is proportional to the performance level – the higher the performance, the higher the customer's satisfaction will be and vice-versa. Gas consumption in automobiles is an example of these requirements. Usually customers explicitly demand performance requirements.
c) Excitement Requirements (or Attractive requirements). These requirements are key to cus-tomer satisfaction. If they are present or have sufficient performance, they will bring superior satisfaction. On the other hand, if they are not present or their performance is insufficient, customers will not get dissatisfied. For instance, a surprise gift at the end of a dinner in a restaurant will certainly bring satisfaction, but it will not cause dissatisfaction if not offered. These requirements are not demanded nor expected by customers.
Two other types of requirements may be identified in the Kano model: neutral and reverse ones. Neutral requirements do not bring either satisfaction or dissatisfaction. Reverse require-ments bring more satisfaction if absent than if present.
 Diagram
Description automatically generated
Diagram
Description automatically generated
[Reference:, - Integrating Kano model and QFD for Designing New Products, - CIPS study guide page 171-172]