Refer to the exhibit.
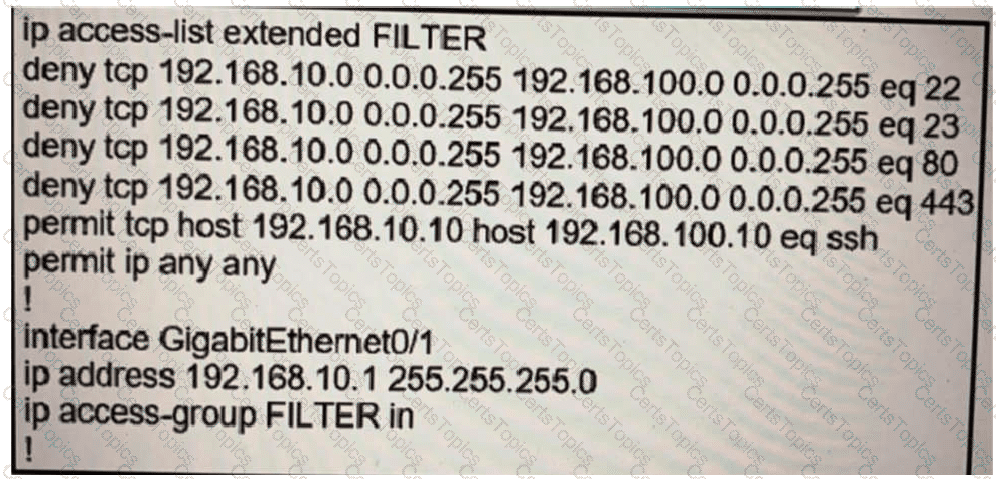
The ACL is placed on the inbound Gigabit 0/1 interface of the router. Host
192.168.10.10cannot SSH to host 192.168.100.10 even though the flow is permitted. Which action
resolves the issue without opening full access to this router?
Refer to the exhibit.
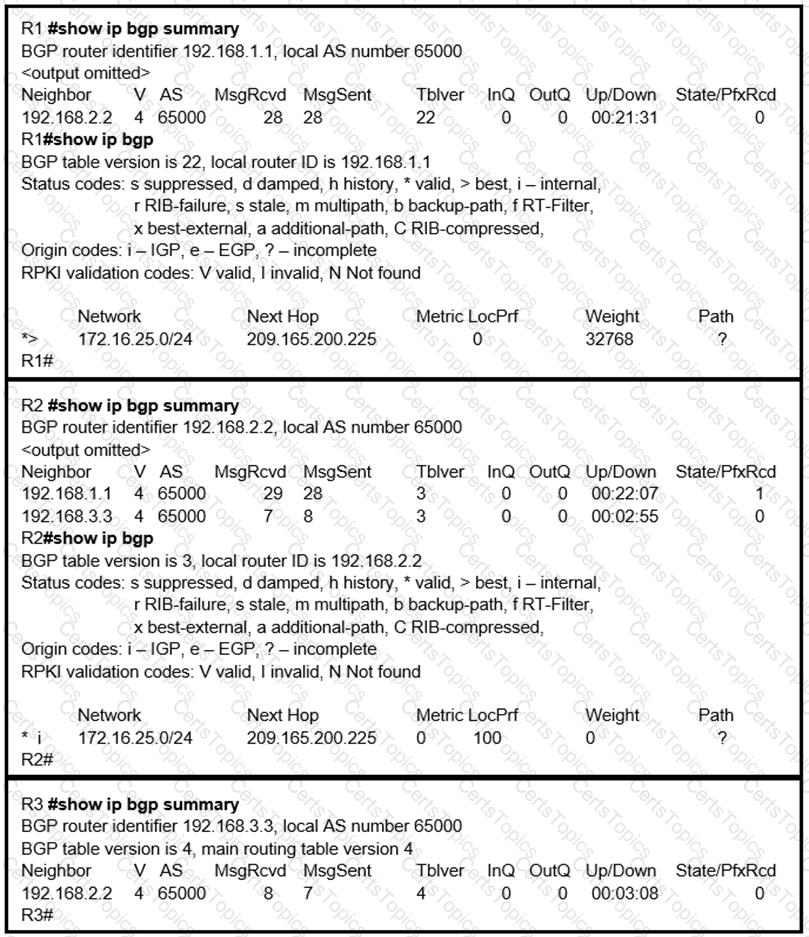
R2 is a route reflector, and R1 and R3 are route reflector clients. The route reflector learns the route to 172.16.25.0/24 from R1, but it does not advertise to R3. What is the reason the route is not advertised?
Refer to the exhibit.
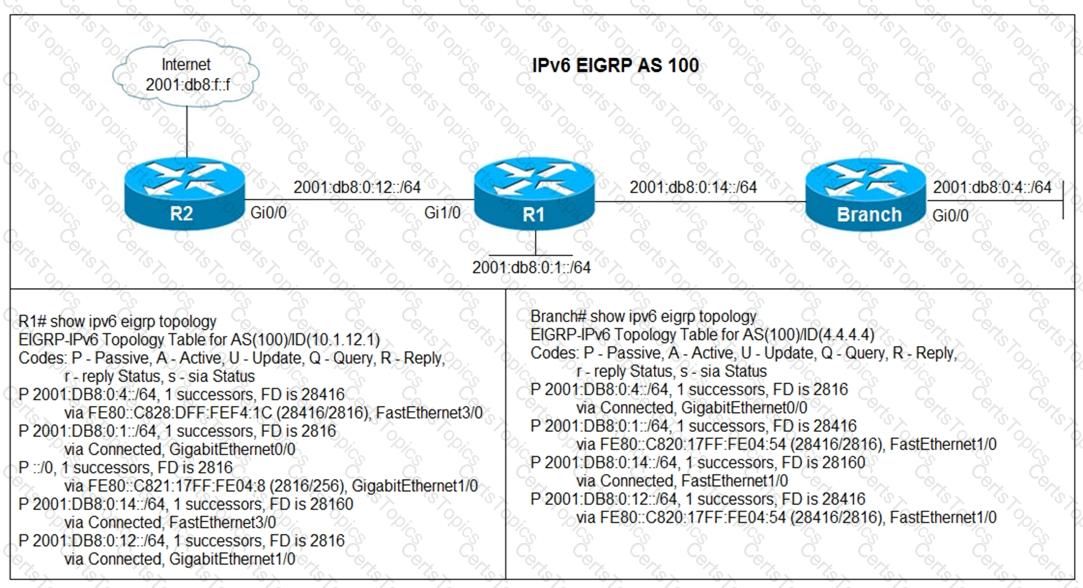
Users in the branch network of 2001:db8:0:4::/64 report that they cannot access the Internet. Which command is issued in IPv6 router EIGRP 100 configuration mode to solve this issue?
What is a function of IPv6 ND inspection?