You need to connect Vnet2 and Vnet3. The solution must meet the virtual networking requirements and the business requirements.
Which two actions should you include in the solution? Each correct answer presents part of the solution.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
You need to prepare Vnet1 for the deployment of an ExpressRoute gateway. The solution must meet the hybrid connectivity requirements and the business requirements.
Which three actions should you perform in sequence for Vnet1? To answer, move the appropriate actions from the list of actions to the answer area and arrange them in the correct order.

You need to provide connectivity to storage1. The solution must meet the PaaS networking requirements and the business requirements.
What should you include in the solution?
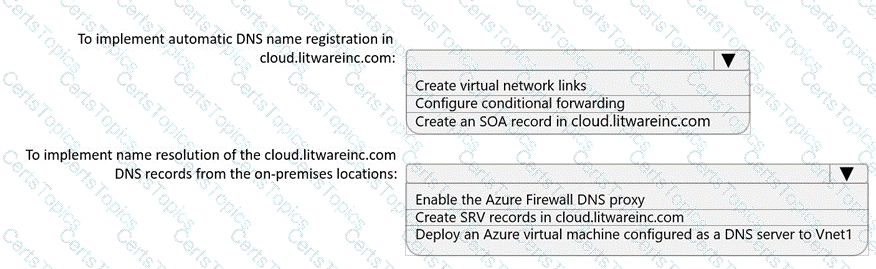
You need to implement name resolution for the cloud.liwareinc.com. The solution must meet the networking requirements.
What should you do? To answer, select the appropriate options in the answer area.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.