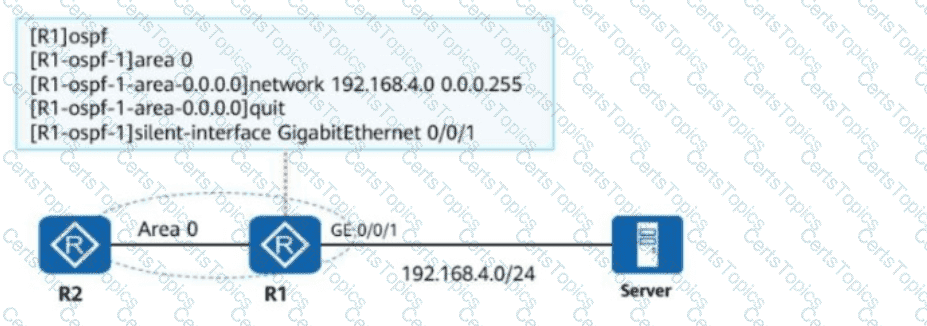
Silent Interface Explanation
Thesilent-interfacecommand is used to prevent OSPF from sending or receiving OSPF packets on the specified interface (GE 0/0/1). This disables OSPF adjacency establishment and stops route advertisement for that interface.
Network Observations
Statement A: R2 can access the server.This is correct, as the silent interface does not impact data traffic, only OSPF-related communication.
Statement B: GE 0/0/1 of R1 cannot send OSPF packets.Correct due to thesilent-interfaceconfiguration.
Statement C: The network segment to which GE 0/0/1 of R1 belongs cannot be advertised.This is correct, as the silent interface prevents route advertisement.
Statement D: GE 0/0/1 of R1 cannot accept OSPF packets.Correct, as the silent interface configuration blocks packet reception.
HCIP-Datacom-Core Reference
OSPF interface command behavior is outlined in the configuration and lab examples sections.