EMC Related Exams
D-ISM-FN-23 Exam







Refer to the Exhibit:
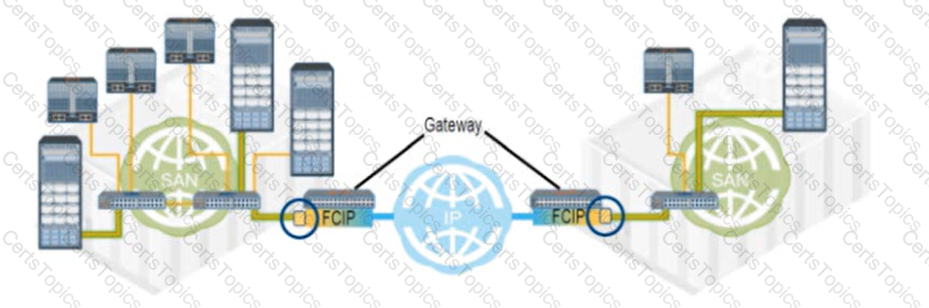
What type of FC port connects each FCIP gateway to each FC SAN?
What is the functionality of the application server in a Mobile Device Management?