Explain, with examples, the advantages of a Procurement Department using electronic systems (25 marks)
See the solution in Explanation part below.
- Mention of some of the following benefits with at least one example provided against each; cost savings, time savings, more efficient, higher levels of transparency, easier to access historical records to inform upon decision making, mitigates risks such as fraudulent spending, easier to track spend against budgets, ensures compliance with regulations, provides ‘real-time’ information, paperless communications (so more environmentally friendly), assists in Supply Chain Management and integration with supply partners.
- I’d suggest 5 is a good amount to aim for
Example Essay
Procurement stands to gain numerous benefits from the adoption of electronic systems. These electronic tools and systems bring efficiency, accuracy, transparency, and cost-effectiveness to the procurement process. Here are several compelling reasons why procurement should leverage electronic systems:
Cost savings – the use of electronic tools saves organisations money. Although there is an initial cost outlay, over time the systems will save the organisation money. For example the use of e-procurement tools can save money by accessing a wider pool of suppliers. For example, when using an e-sourcing portal, a tender may reach a larger number of suppliers- this makes the tender more competitive thus driving down prices. Compared to traditional methods such as phoning suppliers for prices, the use of electronic portals encourages suppliers to ‘sharpen their pencils’ and provide the best prices in order to win work. Money is also saved as communication is digital (so there is no costs for paper and postage).
Time savings – electronic tools automate a lot of processes which saves time. An example of this is e-requisitioning tools where orders can be placed automatically by a piece of technology when quantities of a material reach a certain level. For example, in a cake manufacturing organisation they may use an MRP system which calculates how many eggs are required per day. The machine knows that when the company only have 50 eggs left, a new order needs to be issued to the supplier. The MRP system (e-requisitioning system) therefore saves time as the Procurement department doesn’t have to manually pick up the phone to place the order with the supplier- it is done automatically.
Access to higher levels of information - e-Procurement gives you centralised access to all your data. You can access the system to look at historical purchases with ease compared to having to dig through folders and filing cabinets. For example, an electronic PO system will hold details of all historical POs, this means if someone has a question about a PO that was raised 4 months ago, finding the information is much easier and quicker. Some systems may also be able to provide analytical data such as changes to spend over time, or which suppliers a buyer spends the most money with. This higher level of information can help inform upon future decision making. For example, if the organisation wishes to consolidate its supplier base it would look through historical data provided by the electronic system to find out which suppliers are used the least and remove these from the ‘pre-approved supplier list’. This level of data might not be available in manual systems.
Better budget tracking – using electronic systems allows for real-time information to be collected which allows Procurement Managers to see where spend is compared to forecasts and budgets. An example of this is in the use of Pre-Payment Cards – rather than giving staff members petty cash to make transactions and having to chase this up and collect receipts and change, a pre-payment card usually comes with an online portal where a manager can see what has been purchased and the remaining budget on that card for the month. A manager may be able to see for example that a member of staff has spend £300 of their allotted £500 monthly allowance.
Higher levels of transparency and control – using E-procurement tools allows an organisation to track who is ordering what. For example, an e-requisitioning tool may allow Procurement Assistants to make purchases up to £500 but set an automatic escalation if they try to buy something of higher value. This allows for Management to have greater levels of visibility and more control over spending. Another example of transparency and control is in the use of e-sourcing tools to run a competitive tender exercise. All communication between the buyer and suppliers is tracked on the system and award letters can be sent via the system too. This reduces the risk of information being lost.
Environmental benefits- the use of e-procurement tools means that there is less paperwork involved. For example, rather than creating a physical PO which needs to be signed by a manager, an electronic system can allow a manager to sign-off the purchase by clicking a button. This means there is no requirement for the document to be printed. This saves paper and thus has a positive on the environment. Using electronic systems may help an organisation achieve their environmental targets.
In conclusion there are numerous benefits for procurement to adopt e-procurement tools. Depending on the sector and requirements of each individualised company, some advantages may be more pertinent than others, but it is undeniable that technology is helping to shape the industry into a value adding function of organisations.
Tutor Notes
- With an essay like this you could use subheadings and number the advantages if you like. It’s a good idea to do one advantage per paragraph and using formatting really helps the examiner to read your essay.
- study guide p.108
Describe the main characteristics of, and differences between, procuring goods, services and construction works (25 points)
See the solution in Explanation part below.
- there are a lot of components to this question so I would take a good 5 minutes to write out some bullet points on the characteristics of each one, and on some differences. Then from your notes make this into an essay. The mark scheme isn’t 100% clear on how many characteristics and differences you need to name, so try and keep an equal split between the two areas. You would probably need 2-3 characteristics of each, and 3 differences for a good score.
- Characteristics of goods: tangible, homogeneous, items tend not to perish quickly, can be stored
- Characteristics of services: intangible, heterogenous, inseparable (produced and consumed at the same time), no transfer of ownership, perish upon use (i.e. cannot be stored)
- Characteristics of construction work: project-based procurement, includes procuring both goods and services, complex procurement which has its own set of regulations (CDM2015).
- Differences between these
1) goods are not usually outsourced and services can be.
2) Complexity of the supply chain (goods and construction may have a complex supply chains, but service contracts usually only involve 2 parties).
3) Timescales – construction work has a designated timescale but procurement of goods could be a one off or long-term contract, services is usually a long-term contract.
Example Essay
Introduction:
Procurement is a multifaceted field, and understanding the nuances between procuring goods, services, and construction works is pivotal for effective management. This essay explores the main characteristics that differentiate these categories.
Tangible / Intangible:
Goods are tangible items that can be physically seen and touched. For instance, raw materials like wheat and sugar in a manufacturing organization are tangible goods. On the other hand, services are intangible—though the results can be observed, the service itself cannot be touched. An example is a cleaning contract for a factory; while the effects of the cleaning are visible, the service itself remains intangible. Construction is usually a mixture of tangible and intangible procurement; the tangible is the construction materials such as bricks and windows, and the intangible aspect is the labour to complete the project.
Heterogeneous / Homogeneous:
Goods are generally homogeneous, meaning they are always the same. For example, steel purchased for manufacturing purposes will always be the same. In contrast, services are heterogeneous, varying each time they are rendered. Customer service, for instance, is inherently different each time due to the dynamic nature of customer interactions. Construction could be either heterogeneous or homogeneous depending on the project – is it a one off unique building, or is it a large housing estate of same-build properties?
Transfer of Ownership:
When goods are procured, there is a transfer of ownership. The product becomes the property of the buyer upon delivery and payment. In contrast, services do not involve a transfer of ownership as there is no physical entity to transfer. In construction the transfer of ownership is extremely complex and varies depending on the project. Usually the buyer will retain ownership of the land throughout the project, but on some occasions the construction company may take ownership for insurance purposes.
Storable (Separable/ Inseparable):
Goods are storable, allowing for purchase on one day and use on another. For example a factory can buy in plastic to be used to manufacture toys and this is stored in inventory until the time comes to make the toys. However, services are consumed at the point of purchase, making them inseparable. The service is bought and utilized simultaneously. Services cannot be stored. This is the same for construction.
Ability to Outsource:
Goods are rarely outsourced, as they are typically purchased directly from suppliers. Services, on the other hand, can be easily outsourced—examples include outsourcing finance, cleaning, or security services. Construction works are commonly outsourced, with external companies hired to execute projects.
Complexity of the Supply Chain:
Service contracts often involve a simple two-party relationship between the buyer and the supplier. Goods and construction, however, may have complex supply chains. For example, procuring a pen involves a supply chain with various steps, including the raw material supplier, manufacturer, and possibly a wholesaler. Construction works often feature a tiered supply chain with subcontractors playing crucial roles.
Construction as a Hybrid:
Construction procurement represents a hybrid, incorporating elements of both goods and services. It involves hiring a service, such as a bricklayer for laying bricks, while also procuring the tangible goods—bricks. Separating goods from services in construction is challenging, as they are often intertwined, and both aspects are paid for simultaneously.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, distinguishing between the procurement of goods, services, and construction works is essential for effective supply chain management. The tangible or intangible nature, heterogeneity, transfer of ownership, storability, outsourcing potential, and supply chain complexities offer a comprehensive framework for understanding the unique characteristics of each category. Recognizing these distinctions empowers organizations to tailor their procurement strategies to the specific challenges and dynamics associated with goods, services, and construction works.
Tutor Notes
- What a characteristic is can also be a difference. So for example you can say tangible is a characteristic of goods but tangibility is also the main difference between goods and services. So don’t worry too much about which order to write stuff in, or doing clear sections for this type of essay. It all comes out in the wash.
- Other differences in procuring these include:
- Costs: procuring goods such as stationary for an office will be low-cost so may not require approval, but a service contract may require management sign off. Procuring construction projects tend to be huge sums of money
- Where the budget comes from: goods and services may be operational expenditure and construction works capital expenditure.
- The level of risk involved in the procurement: goods tends to be quite low risk and construction high risk.
- Types of contract involved: procuring goods may be very simple and just require a PO, services is more complex so may require a formal contract or Deed of Appointment. Construction projects will require a contract due to the high value and high risk of the purchase
- Legislation – Goods = Sale of Goods Act, Construction - CDM Regulations 2015. Construction is much more heavily regulated than services or goods. Note CDM regulations isn’t part of CIPS. It’s occasionally referenced in various modules but you don’t have to really know what it is. Just know it’s the main legislation governing the construction industry. Construction - Construction Design and Management Regulations 2015 (hse.gov.uk)
- Study guide LO 1.3.1 p. 40, but mainly p. 52 for services. NOTE the title of this learning outcome includes construction and it is hardly mentioned in the study guide. Most of the above information on construction comes from my own knowledge rather than the book.
Examine FIVE ways in which procurement activities can contribute to achieving BrightAid's organisational objectives. (25 marks)
BrightAid
BrightAid is a medium-sized charity (not-for-profit) with 20 permanent employees and it uses 400 volunteers to deliver aid and services to the individuals and groups it serves. Its main aims are to raise awareness of its cause and bring issues to people's minds to prompt them to donate and/or join campaign activities. The charity depends on these voluntary donations, as without them, it would not be able to function. It also aims for this support to be continued on a regular basis and must engage with a wide range of stakeholders (both internal and external). BrightAid is also considering joining a buying group with several other charities and aims to extend the member's purchasing power and obtain competitive prices for the group members. Recognising that there is increasing competition in the amount and frequency of donations, the charity is now looking at several ways to increase the amount or frequency of donations and make its internal processes more efficient and effective. Up to this point, any procurement activities have been undertaken ad-hoc with no formalised processes.
See the solution in Explanation part below.
Five Ways Procurement Activities Can Contribute to BrightAid’s Organisational Objectives
Procurement plays a critical role in supporting the operational efficiency and sustainability of a not-for-profit organization like BrightAid. Given its reliance on donations and volunteers, a structured and strategic procurement approach can help maximize resources, reduce costs, and enhance the charity’s impact. Below are five key ways in which procurement can contribute to BrightAid’s organisational objectives.
1. Cost Reduction and Financial Efficiency
How Procurement Helps:
Implementing a formal procurement strategy ensures that goods and services are sourced at the most cost-effective prices.
Joining a buying group with other charities can enhance BrightAid’s purchasing power, securing bulk discounts and reducing overhead costs.
Supplier negotiations and competitive tendering can help maximize value for money on every purchase.
Impact on BrightAid:
More funds can be allocated to core aid and campaign activities.
Lower operational costs mean greater financial sustainability and improved service delivery.
2. Enhancing Transparency and Accountability
How Procurement Helps:
Implementing clear procurement policies and procedures ensures fair supplier selection, minimizing risks of fraud or inefficiencies.
Establishing a procurement audit process ensures compliance with ethical and legal standards.
Open and fair supplier engagement strengthens stakeholder trust (donors, volunteers, and partners).
Impact on BrightAid:
Increases donor confidence, encouraging repeat and larger donations.
Ensures resources are used efficiently and ethically, enhancing the charity’s reputation.
3. Improving Supply Chain Reliability and Efficiency
How Procurement Helps:
Strategic supplier selection ensures consistent delivery of essential goods and services.
Developing long-term supplier relationships can reduce risks of supply disruptions.
Procurement can introduce supplier performance reviews to ensure that services meet BrightAid’s needs effectively.
Impact on BrightAid:
More efficient aid distribution, ensuring beneficiaries receive timely support.
Reduced operational disruptions, allowing volunteers and staff to focus on charitable work instead of supply issues.
4. Supporting Ethical and Sustainable Procurement
How Procurement Helps:
Ethical sourcing policies ensure that supplies (e.g., food, clothing, medical aid) come from responsible and sustainable sources.
Procurement can help BrightAid select suppliers that align with its mission and values (e.g., fair trade suppliers, environmentally friendly packaging).
Working with ethical suppliers enhances CSR (Corporate Social Responsibility) partnerships, attracting more donors.
Impact on BrightAid:
Increases public trust and donor support, strengthening brand reputation.
Aligns procurement decisions with the charity’s core mission and sustainability goals.
5. Enhancing Operational Effectiveness and Stakeholder Engagement
How Procurement Helps:
A structured procurement process ensures timely and cost-effective delivery of goods and services, reducing inefficiencies.
Procurement professionals can engage stakeholders (staff, volunteers, donors) to understand their needs and improve sourcing decisions.
Implementing procurement technology or e-procurement systems can streamline purchasing and reduce administrative burdens.
Impact on BrightAid:
Staff and volunteers can focus more on core charitable activities rather than administrative tasks.
Better stakeholder engagement ensures that procurement aligns with donor expectations, strengthening long-term relationships.
Conclusion
By implementing a structured and strategic procurement function, BrightAid can significantly improve its financial efficiency, supply chain reliability, and ethical standards, ultimately enhancing its ability to deliver aid effectively and attract continued donor support. With growing competition for donations, a well-managed procurement process ensures cost savings, improved transparency, and stakeholder trust, directly contributing to the charity’s long-term sustainability and success.
Explain, with examples, the three different ways one can categorise procurement spend: direct vs indirect, capital expenditure vs operational expenditure and stock vs non-stock items. (25 points)
See the solution in Explanation part below.
The knowledge to remember:
 A table with text on it
Description automatically generated
A table with text on it
Description automatically generated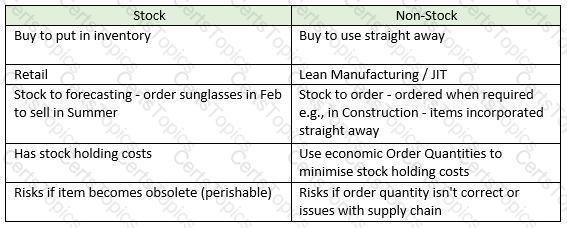
Essay Plan :
Remember to include examples for each of the six categories of spend. This is specifically asked for in the question so it’s important to include as many examples as you can. To do this you could take an example organisation such as a cake manufacturer and explain which of their purchases would fall into each category and why.
Introduction – explain why procurement categorises spend
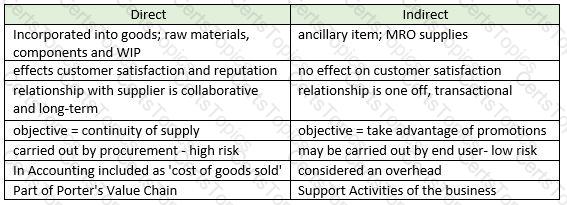
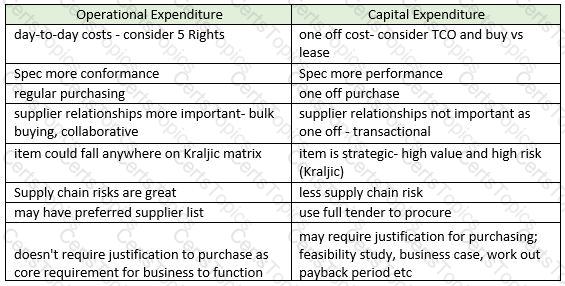
- Direct – these are items that are incorporated into the final goods (the cakes) so would include raw materials such as flour, eggs, sugar etc
- Indirect – these are items that the company needs, but don’t go into the end product. For example, cleaning products and MRO supplies for the machines
- Capital Expenditure- these are large one-off purchases, such as buying a new piece of equipment such as a giant oven to cook the cakes.
- Operational Expenditure – these are purchases that are required to ensure the business can function day-to-day. They may include PPE for the workers in the factory and cleaning equipment
- Stock items – these are items procured in advance and held in inventory until they are needed. In a cake manufacturing factory this could be PPE for staff such as hairnets and gloves. The organisation will buy these in bulk and keep them in a stock cupboard, using these as and when they are required
- Non- stock items - items that are not stored and used right away. An example would be eggs- these will need to be put directly into the cakes as they would go off if bought in advance.
Conclusion – the categories are not mutually exclusive – an item can be direct and operational, or indirect and stock. Different companies may use different systems to classify items of spend.
Example Introduction and Conclusion
Introduction
Procurement categorizes spend to efficiently manage resources and make strategic decisions. Three primary ways of categorizing procurement spend include distinguishing between direct and indirect spend, classifying expenditures as capital or operational, and categorizing items as stock or non-stock. These distinctions aid organizations in optimizing their procurement strategies for better resource allocation.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, categorizing procurement spend into direct vs. indirect, capital vs. operational, and stock vs. non-stock items is essential for strategic resource management. While these categories provide a structured framework, they are not mutually exclusive, as an item can fall into multiple categories. For example, an item may be both direct and operational or indirect and stock. The flexibility of these categories allows organizations to tailor their procurement strategies based on their specific needs, ensuring efficient resource allocation and effective supply chain management. Different companies may adopt varying categorization approaches depending on their industry, size, and operational requirements.
Tutor notes:
- Because you’ve got 6 categories of spend to talk about you’re only going to need 3-4 sentences for each. Providing you’ve said the category, explained what it is and given one example, you’ll absolutely fly through this type of question
- You could also mention that it is useful to use categories of spend as this helps with budgeting. Different categories may also have different processes to follow for procuring the item (this could form part of your introduction or conclusion).
- This subject is LO 1.3.2 it’s quite spread out in the text book but the main info is on p.49
- Note- different companies/ industries classify items of spend differently. Particularly packaging and salaries. Some say they’re direct costs and some say they’re indirect costs. Honestly, it’s a hotly debated subject and I don’t think there is a right or wrong. I’d just avoid those two examples if you can and stick to ones that aren’t as contentious like eggs and PPE.
What is a Code of Ethics? What should an Ethical Policy Contain? What measures can an organisation take if there is a breach of their Ethical Policy? (25 points)
See the solution in Explanation part below.
- Firstly give a short definition of Code of Ethics: a document that sets out moral principles or values about what is right and wrong.
- What an Ethical Policy should contain: Condition of workers, Environment, H+S, Discrimination, Gift / Bribery Policy, Whistleblowing, Confidentiality, Fair Dealings, Declaration of Conflict of Interests. You won’t have time to go into depth on all of these, so pick a few where you want to give an example.
- Measures to take if there is a breach: depending on what the breach is and who breached it this could include: education/ training, sanctions, blacklisting, reporting to authorities, publicise the issue, use a performance improvement plan, issue warnings, dismissal.
Example Essay:
A code of ethics is a formal document or set of principles that outlines the values, ethical standards, and expected conduct for individuals within an organization. It serves as a guide for employees and stakeholders, shaping their behaviour and decision-making to align with the organization's ethical framework. It may take the form of a Mission Statement, Core Values, Specific Guidelines or established reporting mechanisms. The purpose of the Code is to establish standards, promote integrity, mitigate risks and build trust- with both internal and external stakeholders.
A Code of Ethics may contain the following:
- Condition of workers – stating what the company will provide to the employees to make sure the environment is safe. This could include the physical environment but also hours worked, opportunities for breaks etc. Depending on the sector it could detail shift patterns, expectations regarding overtime and compensation.
- Environment – this section would discuss compliance with legislation regarding pollution, disposal of waste materials etc. Depending on the company’s goals- they may have higher commitments to the environment than those imposed by the government. Additional commitments may include NetZero targets or the use of renewable sources of energy.
- H+S- Health and Safety. Ensuring that the working environment is free of hazards and that workers have the training and equipment they need to complete the work safely. E.g. PPE
- Discrimination- a promise not to discriminate based on any characteristic. Aligns with the Equalities Act. Policy should include how the company would handle situations, for example if an employee reports an issue of discrimination or harassment. This may involve the use of a whistleblowing hotline or details on how to contact HR.
- Gift / Bribery Policy – this area of the code of conduct would explain whether the company allows staff members to receive gifts (e.g. from suppliers) and the processes to complete if they do (e.g. return the item, complete an internal document, donate the gift to charity). Different companies and industries will have different rules surrounding this, the Public Sector is much more likely to reject gifts from suppliers for example.
- Declaration of conflict of interests- this explains what staff should do if there is a conflict. For example if they are running a tender and their father owns one of the suppliers who is bidding for the work. The conflict of interest policy will explain what the person should do, how to report it and have mechanisms in place to ensure that nothing untoward could come of the situation. This may be having another member of staff mark the tender to ensure unbiasedness.
Measures to take in case of a breach
A response to a breach will depend on who breached the policy – whether this is an employee or a supplier. It will also depend on the severity of the breach.
Remedies for a supplier breach could include: education / training if the breach is minor. Supplier development if the relationship with the supplier is very important (for example if there are no other suppliers the buyer could turn to) and the breach is minor. If the breach is major such as fraud or misappropriation of funds, a buyer could look to issue sanctions, claim damages and dismiss the supplier. There could be options to claim liquidated damages if this is included in the contract. For very serious offenses the buyer may blacklist the supplier- never use them ever again and could also report the issue to the police if the breech is also criminal (e.g. modern slavery or fraud).
Remedies for an employee breach could include: for minor breaches training may be required, particularly if it was a junior member of the team and it was an innocent mistake like forgetting to fill out a form when they received a Gift. The employee could be carefully monitored and put on an Improvement Plan. If internal issues are found, such as several staff are breaching the Code of Ethics, senior management could look to review policies to make sure issues are being flagged and responded to in the best way. Employees who fail to follow the Ethical Policy, either through routinely failing to adhere to it or through a major breach could be dismissed from the organisation. There would need to be strong evidence of this.
In conclusion it is important for all organisations regardless of size of industry to have an Ethics Policy. Sharing the code of ethics with staff is a fundamental step in embedding ethical principles into the organizational culture. Regular communication and training reinforce these principles, fostering a shared commitment to ethical behaviour across all levels of the organization.
Tutor Notes
- In an essay like this it’s always a good example to use examples. They can be hypothetical – you don’t have to know any company’s Ethics policy off by heart. E.g. If a supplier breached a buyer’s Ethical Policy by employing Child Labour in their factories, an appropriate measure for the buyer to take would be to cancel the contract and find another supplier. This is because not only is Child Labour illegal, the buyer will not want to be associated with this supplier as it will have negative repercussions on their image. The best response would therefore be to distance themselves from the supplier.
- Code of Ethics and an Ethics Policy are the same thing. Just different language. The terms can be used interchangeably
- Study guide p. 128
Discuss 3 areas of regulation relating to competition that a procurement professional should be aware of (25 points)
See the solution in Explanation part below.
How to approach this question
- This question is very vague. Sometimes CIPS do this. It allows for you to be a bit more free in your response, but can also be quite stressful because you don’t 100% know what they’re after.
- For this question we’re looking at competitions, so full tenders where lots of suppliers are invited to bid for an opportunity. This means the type of things we could be discussing include; IP, cartels, merger controls and monopolies.
Example Essay
Procurement professionals operate within a legal framework that regulates competition, aiming to ensure fair business practices and prevent anti-competitive behaviour. Three critical areas of regulation related to competition that procurement professionals should be aware of include intellectual property, cartels, and merger controls.
Intellectual Property (IP):
Intellectual property encompasses creations of the mind, such as inventions, designs, and brand names, protected by law. In the context of procurement, understanding intellectual property is essential when dealing with suppliers' products, technologies, or services that may involve intellectual property rights.
Procurement professionals must be aware of the intellectual property rights associated with the goods or services they are procuring. This includes respecting patents, trademarks, copyrights, and trade secrets owned by suppliers. Due diligence is crucial to ensure that the products or services being procured do not infringe on the intellectual property rights of others, requiring verification of legal ownership and legitimacy. An example of something procurement should look out for include ensuring goods are authentic and not counterfeit.
Cartels:
Cartels involve agreements between competitors to control prices, manipulate markets, or restrict competition. For procurement professionals, it is imperative to be vigilant and avoid engaging in or unintentionally supporting cartel activities. Procurement professionals should refrain from participating in anti-competitive behaviour, such as bid-rigging or price-fixing, which are common cartel activities. This involves not colluding with suppliers or competitors to manipulate procurement processes. Maintaining open and fair competition is essential, ensuring that procurement processes remain transparent, competitive, and free from attempts to distort market dynamics, thereby preventing the formation of cartels and promoting a level playing field.
One notable example involved the construction industry in the UK. In 2019, the Competition and Markets Authority (CMA) fined three major suppliers to the construction industry for participating in a cartel. The companies, which supplied concrete drainage products, were found to have coordinated their behaviour to share markets, fix prices, and rig bids. The investigation revealed that these companies had breached competition law by engaging in anti-competitive practices that limited competition and negatively impacted customers. The fines imposed were part of the CMA's efforts to deter and penalize such cartel behaviour, emphasizing the importance of fair competition in procurement. The Directors of the companies have also been banned from undertaking the role of Director of any company for 12 years.
Merger Controls:
Merger controls are regulations overseeing the consolidation of companies, mergers, and acquisitions to prevent monopolistic practices and protect fair competition. Procurement professionals need to be aware of these regulations, especially when dealing with suppliers undergoing mergers or acquisitions.
Staying informed about mergers and acquisitions within the supplier base is crucial. If a key supplier undergoes such changes, it may impact the stability of the supply chain or alter market dynamics. Procurement professionals need to be aware of potential changes in supplier relationships, pricing structures, or product/service availability resulting from mergers. Engaging in proactive risk management and contingency planning is necessary to mitigate any negative impacts on procurement operations.
Mergers are actively watched in the UK by the Competition and Markets Authority, and where rules are broken, the CMA can intervene and even prevent mergers from happening. A notable example of this was the attempted merger between JD Sports and Footasylum – the companies were fined millions of pounds for exchanging information and attempting to collude and distort the marketplace.
In conclusion, procurement professionals play a crucial role in navigating these regulatory landscapes effectively. Understanding intellectual property, avoiding cartel activities, and staying informed about merger controls contribute to fostering fair and transparent competition within the marketplace.
Tutor Notes
- The construction example of a cartel can be found here Supply of precast concrete drainage products: civil investigation - GOV.UK but feel free to use your own!
- The JD/ Footasylum one is here: JD Sports and Footasylum fined £4.7m for competition breach - BBC News. Basically, the CMA got involved because the two firms were sharing private information and having secret meetings, with the intention that they could combine. The CMA thought it was super dodgy and that it would distort the trainer / footwear market in the UK so they fined the companies and told them to stop it.
- The study guide is a bit light on this topic, so I would do a bit of extra research and have an example in your back pocket for if you need it. P. 142
If you want an example of IP issues- Shein is a great company to look at- ‘They took my world’: fashion giant Shein accused of art theft | Art and design | The Guardian
Describe the main stages of the CIPS Procurement and Supply Cycle (25 points)
See the solution in Explanation part below.
How to respond to this question:
- Include as many of the stages as you can, but it’s not vital to remember them all. You should aim to remember at least 8 of the 13 steps.
- The steps are; Define Business Need, Market Analysis + Make vs Buy, Develop Strategy and Plan, Pre-Procurement Market Testing, Develop Documents and Specification, Supplier Selection, Issue Tender, Bid Evaluation, Contract Award and Implementation, Warehouse Logistics, Contract performance and Improvement, Supplier Relationship Management and Asset Management
Essay Plan:
Introduction - Explain what the CIPS Procurement and Supply Cycle is- a tool to be used by procurement professionals which tracks a procurement exercise from inception to close. It’s helpful as it ensures procurement exercises are done correctly and steps are completed in the right order.
- Describe (briefly) what happens at each stage of the cycle, giving examples. You should put each stage into a separate paragraph. It’s also a good idea to name the stages in chronological order. Some ideas of things you could mention include:
1) Define Business Need and Develop Specification - Identify what the need is, what type of purchase, put together a business case and outline the requirements
2) Market Analysis and Make vs Buy Decision – analyse the market using market segmentation (e.g. by buyer, product, geography etc) or use Porter’s 5 Forces (buyer and supplier power, threat of new entrants, threat of substitutions, supplier rivalry). Looks at if what you want to procure is actually available.
3) Develop Strategy / Plan – you could use a STEEPLE and SWOT analysis. Consider if this is the right time to procure. Create timelines and budgets.
4) Pre-Procurement Market Testing - consider stakeholder engagement, supplier engagement, new / upcoming legislation, currency fluctuations, market, competitor actions. Is this the best time to procure? Will it be successful?
5) Develop Documentation / Creation of Contract terms- firm up the requirements and create the formal documents for the tender exercise. This may be a RFQ or ITT. Define the offer. Include KPIs.
6) Supplier Selection – May not be required for rebuys but an important step for new buys. May use a list of pre-approved suppliers or this may be going out to the open market. You can shortlist suppliers by sending out a pre-qualification questionnaire.
7) Issue Tender - Electronically, consider whether to use an open vs closed procurement exercise
8) Bid / Tender Evaluation – Very flexible for companies in the private sector but there are guiding principles for doing this for public procurement; transparency, equal treatment, proportionality. Often considers both price and quality.
9) Contract Award and Implementation- Organisations may have different processes for different values (e.g. large purchases may need senior management approval, but under £500 just needs a manager’s signature). May require post-award negotiation. Contract is drafted and signed.
10) Warehouse Logistics and receipt – includes POs and Invoices. Battle of the Forms. Goods Inwards = receiving and inspecting goods- may use quality control.
11) Contract performance review - ensuring contract obligations are fulfilled includes P2P procedures, database management, budgeting / costs monitoring, reporting and dispute resolution.
12) Supplier Management – will depend on the relationship but includes; contact / meetings with the supplier, motivating / incentivising the supplier, working with them on performance issues, ensuring KPIs are met.
13) Asset Management / End of Life- considers TCO, ongoing maintenance and costs, insurance and warrantees and disposal of the item once it has reached the end of its life.
Conclusion – The CIPS Procurement Cycle is cycle rather than process as it is a continuous loop and needs constantly emerge. It never ends. New buys are more likely to follow all the stages of the cycle, rebuys may skip steps
Tutor Notes:
- Often steps 11 and 12 are confused or merged together but they are different. It’s possible to have great contract management and a poor supplier relationship i.e. the contract is working effectively and the supplier is delivering in line with the contract BUT the relationship may be fraught with tension and the buyer and supplier don’t like each other.
- To get a high score I would include examples of all of the stages, but remember you only have 45 minutes to answer the question, so balance detail with timing so you don’t overwrite
- The procurement cycle is on p. 70 or you can download it here: Procurement Supply Cycle | CIPS
Explain FIVE ways conflicts of interest could be managed by effective corporate governance. (25 marks)
See the solution in Explanation part below.
Five Ways to Manage Conflicts of Interest Through Effective Corporate Governance
Conflicts of interest arise when an individual or entity has competing personal and professional interests that could compromise their judgment or decision-making in business transactions. Effective corporate governance ensures that such conflicts are identified, managed, and mitigated to uphold transparency, integrity, and accountability within an organization. Below are five ways corporate governance can help manage conflicts of interest:
1. Establishing Clear Policies and Codes of Conduct
Organizations should implement formal policies that outline what constitutes a conflict of interest and how employees and stakeholders should handle such situations.
Effectiveness:
Provides clear guidelines on ethical behavior.
Ensures employees disclose conflicts before engaging in business transactions.
Sets disciplinary actions for non-compliance.
2. Mandatory Disclosure of Interests
Employees, board members, and executives should be required to declare financial, personal, or business interests that may conflict with their duties.
Effectiveness:
Enhances transparency in procurement and business dealings.
Prevents individuals from unduly influencing decisions for personal gain.
Enables proactive identification of potential conflicts before they escalate.
3. Implementing Independent Oversight and Decision-Making Structures
Establishing independent committees such as audit, risk, and procurement committees to oversee critical decision-making.
Effectiveness:
Ensures decisions are made objectively, reducing the risk of favoritism or unethical influence.
Promotes accountability by having multiple parties involved in key transactions.
Prevents a concentration of power in one individual or department.
4. Whistleblowing Mechanisms and Ethical Reporting Channels
Organizations should provide anonymous reporting mechanisms for employees to report unethical behavior or conflicts of interest.
Effectiveness:
Encourages a culture of transparency and ethical behavior.
Protects whistleblowers from retaliation.
Allows management to address conflicts before they result in financial or reputational damage.
5. Regular Audits and Compliance Monitoring
Conducting periodic internal and external audits to detect and investigate potential conflicts of interest.
Effectiveness:
Helps identify patterns of unethical behavior.
Ensures continuous improvement in governance practices.
Reinforces a compliance-driven corporate culture.
Conclusion
By implementing these governance strategies, organizations can effectively manage conflicts of interest, reduce risks associated with unethical practices, and ensure decisions are made in the best interest of stakeholders. Effective corporate governance fosters trust, accountability, and long-term business sustainability.
What is meant by a structured procurement process? (10 marks) Why is this important? (15 marks).
See the solution in Explanation part below.
- Definition of ‘structured procurement process’ – when an organisation provides a sequence of actions / steps to take to get the outcome (the procurement of an item). This involves an organisation providing guidelines and instructions of how things should be done. Basically following a step-by-step process.
- Why this is important – Ensures all tasks that need to be done are done, maintains consistency, prevents conflict and suboptimal behaviour, improves efficiency, better managerial control, compliance (with laws and standards), assists with continuous improvement, may result in time/ cost savings, reduces risks such as fraudulent spending.
Example essay:
The first part of the question is worth 10 points, so you could include a few of the following points. It would also be good to include examples:
- Structured procurement involves creating rules on how procurement should be done
- This is in contrast to reactive / maverick spending
- May come about due to company policy, external regulations or through trying to achieve Competitive Advantage
- Examples include an organisation having set procedures for ordering items of different spend- e.g. Procurement Assistants can purchase items up to £500. Items between £500-£1000 require a manager’s approval and anything over £1000 requires a written Business Case in order to procure
- Structures Procurement Processes will usually also include the use of a designated e-procurement tool. E.g. an organisation may insist that all tenders use a certain online system and that invoices are sent via X system within 30 days.
The second part of the question is worth slightly more points, so spend more time on this. You could put each of the reasons why it is important in a separate paragraph. Also use examples where you can;
- Ensures all tasks that need to be done are done- having structured processes means having a step-by-step guide to how to procure. This means activities are well co-ordinated and there are no gaps, no duplications of effort and no conflicting efforts. It may involve assigning different people in the team different roles e.g. someone makes the requisition and someone else approves it. It also means that nothing is forgotten.
- Maintains consistency- having standardised processes means each procurement exercise follows the same process. This may include using a standard template for a requisition or ITT. Where there is consistency, this results in time being saved and less mistakes being made as everyone (including supply partners) is familiar with the processes.
- Prevents conflict and suboptimal behaviour- in organisations that use structured procurement processes everyone does the same. This means there is no conflict (e.g. one person doing things one way and another person does it differently and arguing which way is best). It also means no one can do procurement ‘wrong’ – there are written guides and procedures to follow. This is particularly helpful for new starters.
- Efficiency – time and money can be saved where there are standard procedures as people don’t have to plan each procurement activity individually. Structured Procurement Processes may also involve completing bulk orders and co-ordinating activity within the organisation which means less orders are placed over the year and efficiency savings can be made. For example, a factory may create an order of cleaning products once a quarter, compared to ordering products just as and when they are required. This will save time of the procurement department overall throughout the year and allows them to focus on other more value-adding tasks.
- Better managerial control – Managers have more oversight when using structured procurement. There are clear rules as to when managers need to be involved and provide sign-off. This visibility makes it easier for managers to make decisions and allows for early intervention where someone needs assistance. It will reduce maverick spending and fraudulent spending. For example, it is much harder to provide kick-backs to suppliers when there are clear processes and audit trails and managers have visibility over all processes.
- Compliance (with laws and standards) – particularly in the Public Sector there are rules and regulations regarding procurement practices. Using standardised processes allows organisations to demonstrate compliance with appropriate legislation. It also protects them from ‘challenge’. This is when a bidder who is unsuccessful challenges the decision to award a contract to someone else. Using a structured procurement process allows the organisation to demonstrate that they procured the item correctly and the challenge is unfounded.
Tutor Notes
- This topic isn’t as well explained in the new study guide as it used to be. It’s all pretty obvious stuff but the language is slightly different. The guide now talks about ‘compliance with processes’ and the benefits this brings. Which is exactly the same as why do you follow a structured process. This is on p. 114.
- If you’re feeling clever, you could mention the difference between Public and Private Sector- e.g. a private organisation may use standardised processes for efficiency and cost savings, whereas a public sector organisation may use it more for compliance purposes.
Describe 3 stages of the sourcing cycle that occur in the post-contract award stage (25 marks)
See the solution in Explanation part below.
How to approach the question
Your answer should provide details on 3 of the following:
- Contract Award and Implementation
- Warehouse Logistics
- Contract performance and Improvement
- Supplier Relationship Management
- Asset Management
Because the question is only asking for 3 stages, you’re going to have to go much more into detail for each stage, giving lots of information about why each stage is important and examples. You could consider thinking of an example procurement you have done recently and explaining the stages for that. Or you could take a hypothetical procurement too. Either will get you the same marks. Pick the three that you can write the most about.
Essay Plan
Introduction – explain that sourcing of goods and the role of Procurement doesn’t end once a contract is signed. There is ongoing management and processes which must be carried out to ensure success.
Paragraph 1 – Contract Performance and Improvement
· This is about ensuring contract obligations are fulfilled. Contract administration includes P2P procedures, database management, budgeting / costs monitoring, reporting and dispute resolution
· Procurement’s role may be in managing contract performance through the use of SLAs and / or KPIs. This can be done via reporting, using a Supplier Scorecard and meeting regularly to discuss.
· It’s important KPIs are measured and that there are consequences for failing to meet them. An example of consequences could be using a Performance Improvement Plan.
· Contract Management also includes updating the contract where required – e.g. issuing variations to contract and updating the change control log
· Another important aspect of this is ensuring the costs remain within scope of the budget
· Contract performance can be compared if you have several suppliers delivering the same goods- could use a Factor Rating Method.
· Performance could be measured against several criteria such as on time deliveries, response time of supplier, number of complaints.
Paragraph 2 – Supplier Relationship Management
· There is a difference between managing the contract and managing the supplier relationship. It’s possible to have excellent contract performance and a terrible relationship. However, the two are generally linked- where there is a good relationship, the contract often performs well.
· The supplier management approach depends on where the relationship falls on the relationship spectrum (e.g. transactional or collaborative)
· This involves; maintaining regular contact with the supplier, motivating the supplier, working collaboratively with them (e.g. on performance issues or resolving any disputes)
· Incentivising the supplier leads to collaboration and mutual support
· To assess or rank suppliers you could use a vendor rating method or supplier evaluation forms
· Supplier relationship management may involve investing in the supplier- e.g. through training or technology sharing
Paragraph 3 – Asset Management
· Includes creating a post contract ‘lessons-learned’
· Assessments should be carried out to determine if business requirements have changed, whether the agreement is still required and fit for purpose, what can be learnt from the process and how improvements can be incorporated next time.
· This is the final stage of the Procurement Cycle and takes us back to the start of cycle, which begins again when the item needs to be reprocured
· Whole life costing should be considered at this stage: this is the total cost of ownership over the life of an asset. The concept is also known as life-cycle cost (LCC) or lifetime cost, and is commonly referred to as "cradle to grave" or "womb to tomb" costs.
· Generally used on large purchases such as machinery and vehicles. Full Asset Management may not necessary for direct cost items such as raw materials incorporated into final goods.
· Considerations may include; costs of running the asset, how long it will perform, insurance, maintenance, opportunity costs, disposing of the asset.
· Also consider environmental and social impacts of the procurement.
Conclusion – it is important that procurement are involved at every stage of the cycle, not just in the pre-award stages. Procurement can add value at every stage.
Tutor Notes
- Depending on the examples you choose to use, you could talk about how the type of item procured could impact on the different stages. For example, high risk purchases may require more contract management than low risk purchases, and capital expenditure items such as new machinery may require more attention to the Asset Management stage.
- You could also think about how procurement adds value at each of the stages.
- Study guide p. 79
Provide a definition of a stakeholder (5 points) and describe 3 categories of stakeholders (20 points).
See the solution in Explanation part below.
Essay Plan:
Definition of Stakeholder- someone who has a ‘stake’ or interest in the company. A person or organisation who influences and can be influenced by the company.
Categories of stakeholders:
1) Internal Stakeholders- these people work inside the company e.g. employees, managers etc
2) Connected- these people work with the company e.g. suppliers, mortgage lenders
3) External Stakeholders – these people are outside of the company e.g. the government, professional bodies, the local community.
Example Essay:
A stakeholder is an individual, group, or entity that has a vested interest or concern in the activities, decisions, or outcomes of an organization or project. Stakeholders are those who can be affected by or can affect the organization, and they play a crucial role in influencing its success, sustainability, and reputation. Understanding and managing stakeholder relationships is a fundamental aspect of effective organizational governance and decision-making and there are several different types of stakeholders.
Firstly, internal stakeholders are those individuals or groups directly connected to the daily operations and management of the organization. Internal stakeholders are key to success and are arguably more vested in the company succeeding. They may depend on the company for their income / livelihood. Anyone who contributes to the company's internal functions can be considered an internal stakeholder for example:
This category includes
1) Employees: With a direct influence on the organization's success, employees are critical internal stakeholders. Their engagement, satisfaction, and productivity impact the overall performance.
2) Management and Executives: The leadership team has a significant influence on the organization's strategic direction and decision-making. Their decisions can shape the company's future.
Secondly, connected stakeholders are those individuals or groups whose interests are tied to the organization but may not be directly involved in its day-to-day operations. Connected stakeholders work alongside the organisation and often have a contractual relationship with the organisation. For example, banks, mortgage lenders, and suppliers. These stakeholders have an interest in the business succeeding, but not as much as internal stakeholders. It is important to keep these stakeholders satisfied as the organisation does depend on them to some extent. For example, it is important that the organisation has a good relationship with their bank / mortgage provider/ supplier as failing to pay what they owe may result in the stakeholders taking legal action against the organisation.
This category includes:
1) Shareholders/Investors: Holding financial stakes in the organization, shareholders seek a return on their investment and have a vested interest in the company's financial performance.
2) Suppliers and Partners: External entities providing goods, services, or collaboration. Their relationship with the organization impacts the quality and efficiency of its operations.
Lastly external stakeholders are entities outside the organization that can influence or be influenced by its actions. This category includes anyone who is affected by the company but who does not contribute to internal operations. They have less power to influence decisions than internal and connected stakeholders. External stakeholders include the government, professional bodies, pressure groups and the local community. They have quite diverse objectives and have varying ability to influence the organisation. For example, the government may be able to influence the organisation by passing legislation that regulates the industry but they do not have the power to get involved in the day-to-day affairs of the company. Pressure groups may have varying degrees of success in influencing the organisation depending on the subject matter. This category includes:
1) Customers: With a direct impact on the organization's revenue, customers are vital external stakeholders. Their satisfaction and loyalty are crucial for the company's success.
2) Government and Regulatory Bodies: External entities overseeing industry regulations. Compliance with these regulations is crucial for the organization's reputation and legal standing.
In conclusion, stakeholders are diverse entities with a vested interest in an organization's activities. The three categories—internal, connected and external —encompass various groups that significantly influence and are influenced by the organization. Recognizing and addressing the needs and concerns of stakeholders are vital for sustainable and responsible business practices.
Tutor Notes
- The above essay is pretty short and to the point and would pass. If you want to beef out the essay you can include some of the following information for a higher score:
- Stakeholders can be harmed by, or benefit from the organisation (can affect and be affected by the organisation). For example a stakeholder can be harmed if the organisation becomes involved in illegal or immoral practices- e.g. the local community can suffer if the organisation begins to pollute the local rivers. The local community can also benefit from the organisation through increased employment levels.
- CSR argues organisations should respect the rights of stakeholder groups
- Stakeholders are important because they may have direct or indirect influence on decisions
- The public sector has a wider and more complex range of stakeholders as they’re managed on behalf of society as a whole. They’re more likely to take a rage of stakeholder views into account when making decisions. However, these stakeholders are less powerful – i.e. they can’t threaten market sanctions, to withdraw funding, or to quit the business etc.
- The essay doesn’t specifically ask you to Map Stakeholders, but you could throw in a cheeky mention of Mendelow’s Stakeholder Matrix, perhaps in the conclusion. Don’t spend time describing it though- you won’t get more than 1 point for mentioning it. You’d be better off spending your time giving lots and lots of examples of different types of stakeholders.
- Study guide p. 58
Explain what is meant by the term Inventory Management System? Describe MRP and ERP systems explaining when they are used and the advantages and disadvantages of using them (25 points)
See the solution in Explanation part below.
How to approach this question:
- Definition of Inventory Management System – a system, usually a piece of digital software, that helps an organisation manage their inventory. It oversees the process of ordering stock, receiving it, storing it and converting it into finished goods. Used predominantly in manufacturing organisations. MRP and ERP are types of IMS.
- MRP - Material Requirements Planning- this is a planning, scheduling, and inventory control system used to manage manufacturing processes. Most MRP systems are software-based. The aim is to automate and improve the efficiency of ordering and processing raw materials.
- ERP – Enterprise Resource Planning – this system uses MRP but also includes other operations such as finance, so allows for budgeting and forecasting, and customer relations. ERP gives an organisation a more holistic overview compared to MRP which just focuses on manufacturing.
- When they are used – predominantly in the manufacturing industry for the ordering of goods. Not used for services. Used when there is a lot of maths involved in figuring out how much of something to order and when e.g. a chocolate manufacturer who needs to produce 50,000 chocolate bars a day. MRP / ERP helps the organisation know what to order, how much and when. It helps achieve the 5 Rights of Procurement.
- Advantages – the advantages of MRP and ERP are very similar and in most cases the same: more accurate than manual processes, quicker response times, automated process frees up people to complete more added value tasks, flexibility, has real time information to inform on decision making, improved responsiveness to customers, improved supply chain management, reduction in costs.
- Disadvantages - expensive, complicated, can break down or be hacked (as they're digital systems), only as good as the information put into them. training required to use.
Example Essay:
IMS
An Inventory Management System (IMS) is a software application or set of tools designed to oversee and optimize the management of a company's inventory. The primary goal of an inventory management system is to maintain an accurate record of stock levels, streamline the procurement process, and ensure efficient order fulfilment. This system plays a crucial role in supporting businesses by helping them avoid stockouts, reduce excess inventory, and enhance overall supply chain efficiency.
Inventory Management Systems have the following functions: demand management (which assists with forecasting, and helps the avoidance of overstocking), helps to control stock levels (by stating minimum and maximum levels), replenishment of stock in line with policies, allows automatic reordering when stock levels get low, tracks stock movements (e.g. around a warehouse), allows communication with suppliers and end users, and helps increase safety by ensuring stock isn’t damaged or deteriorating.
MRP
MRP stands for Material Requirements Planning, and it is a computer-based inventory management and production planning system used by businesses to optimize the management of materials, components, and finished products in the manufacturing process. MRP is a key component of Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems, focusing specifically on the planning and control of materials and production resources.
MRP systems uses 3 main modules: 1. Master Production Schedule- information on customer orders, forecast orders, customer requirements and stock orders 2. Bill of Materials – the recipe / breakdown of components of the finished product and 3. Inventory Status File – tells you the current stock levels.
How MRP works- For example, a customer wants to order a new sofa. 1. input the customer order into MRP 2. Check finished stock and if there’s a sofa, give the customer that sofa. If there isn’t a sofa in stock, the MRP system will look at the Bill of Materials- looking at individual materials needed to make the sofa and will order these, factoring in lead times 3. confirm to customer what the lead time is on getting their new sofa, based on delivery time of materials and time to make it.
MRP is a simple system – it doesn’t take into account other business processes and can go wrong due to inaccurate or outdated information.
Advantages of the MRP process include the assurance that materials and components will be available when needed, minimised inventory levels, reduced customer lead times, optimised inventory management, and improved overall customer satisfaction.
Disadvantages to the MRP process include a heavy reliance on input data accuracy (garbage in, garbage out), the high cost to implement, and a lack of flexibility when it comes to the production schedule.
ERP
This is business management software which is used to collect, store, manage, and interpret data from many business activities. It uses MRP but also includes other operations such as finance, HR and customer services. Therefore it’s more powerful than MRP. Where MRP can tell you how much of something to order and what the lead times are, ERP can also consider how many staff are available each day (by looking at holidays and sickness) and factor this into the manufacturing process. It can also produce accurate financial data, manage customer and supplier relationships.
ERP facilitates information flow between all business functions and manages connections to outside stakeholders. SAP and Oracle are examples of ERP systems. There is also ERP II – this extends the system to include links with suppliers and supply chain stakeholders
One of the primary advantages of implementing an ERP system is the integration of information across various departments. By providing a unified view of an organization's operations, an ERP system ensures that different functions work with synchronized and consistent data, fostering improved decision-making and collaboration.
Operational efficiency is another significant benefit of ERP systems. Through the automation of routine tasks and streamlined processes, organizations can achieve greater efficiency, reduce manual errors, and enhance overall productivity.
However, one of the primary disadvantages is the high initial implementation costs. Organizations must invest in software licenses, training programs, and customization to align the ERP system with their specific needs. The complexity of ERP systems and potential customization challenges can pose difficulties, requiring expertise and resources for successful implementation.
Resistance to change among employees is a common hurdle when introducing ERP systems. Employees may be hesitant to adopt new processes and technologies, leading to a slower transition period and potential inefficiencies during the learning curve. Organizations also become dependent on ERP vendors for updates, support, and maintenance, and switching vendors can be disruptive and costly.
In conclusion, while MRP and ERP systems offer numerous advantages in terms of operational efficiency, data integration, and strategic planning, organizations must carefully weigh these benefits against the associated challenges. A well-planned and effectively implemented system can contribute significantly to an organization's success, but the decision to adopt such a system should be approached with a thorough understanding of both its advantages and potential drawbacks.
Tutor Notes
- This is a really hard topic if you don’t have a manufacturing background. The way I think about it is this- imagine you’re Cadbury’s and you’re coming up to Easter. How much sugar do you need to buy and when do you need to buy it in order to make all your Easter Eggs? Hard question right? Well MRP / ERP is the clever software that figures that all out for you. It will tell you how much sugar needs to be bought on what day, in order for the delivery time to be right for manufacturing. It will consider storage costs and how quickly Easter Eggs get made in the factory. It’s honestly so clever. Feel free to use that example in your essay. Examples like that show the examiner you understand the topic.
- Although they’re fabulous systems, using MRP and ERP systems doesn’t guarantee success- at the end of the day they’re just software- the key to success is in the accuracy of the data that’s inputted into the systems and how the systems are used. That would make a strong conclusion.
- This is a good simple video that explains the topic: What is Materials Requirement Planning (MRP)? (youtube.com) I also like watching How Its Made – a documentary series about factory life. You can find it on BBC Iplayer. If you don’t have a manufacturing background it helps give context to some of these dry subjects like MRP and Just-in-Time manufacturing.
- LO 3.4 p. 175
Bob is a procurement manager at ABC Ltd. He has been asked to ensure all future purchases achieve ‘value for money’ for the organisation. What is meant by ‘value for money’? (5 points). Describe 4 techniques that Bob could use to achieve this (20 points)
See the solution in Explanation part below.
1) A definition of Value for Money: ensuring a purchase is cost effective. This may be that the purchase achieves the 5 Rights of Procurement or that the purchase achieves the 4Es: Economy, Efficiency, Effectiveness and Equity. – this is only worth 5 points, so don’t spend too long on this
2) 4 techniques Bob can use to achieve VFM: this is the bulk of your essay. Each of the 4 will be worth 5 points, so remember to give a thorough Explanation: and example. Pick 4 from the list below: complete a value analysis to eliminate non-essential features, minimise variety/ consolidate demand, avoid over specification, pro-active sourcing, whole life costing methodologies, eliminate / reduce inventory, use electronic systems, international sourcing, sustainability / environmental policies, currency/ exchange rate considerations, negotiating good payment terms, packaging, warrantees.
Example Essay:
"Value for money" (VFM) is a concept that refers to obtaining the best possible return on investment or benefits relative to the cost incurred. It involves assessing whether the goods, services, or activities provided offer an optimal balance between their cost and the quality, benefits, or outcomes they deliver. Value for money is not solely about choosing the cheapest option; instead, it considers the overall efficiency, effectiveness, and long-term value derived from an expenditure. For Bob, the Procurement Manager at ABC Ltd there are four key ways that he can achieve this for all future purchases.
Value Engineering
This is looking at the components of a product and evaluating the value of each component individually. You can then eliminate any components that do not add value to the end product. To do this Bob would choose a product to review and determine whether any parts of this can be omitted (thus saving the company money) or could be replaced by components that are of a higher quality at the same price (thus providing added value to the customer). For example, Bob could complete a Value Engineering exercise on the new mobile phone prototype ABC plan to release next year. His findings may discover a way to provide a higher quality camera at no additional cost or that some components don’t add value and can be eliminated.
Consolidate demand
Bob can achieve value for money by consolidating demand at ABC ltd. This would mean rather than each individual person/ department ordering what they want when they need it, Bob creates a centralised process for ordering items in bulk for the departments to share. For example, if each department require stationary to be ordered, Bob can consolidate this demand and create one big order each quarter. This will likely result in cost savings for ABC as suppliers often offer discounts for large orders. Moreover, consolidating demand will allow for saving in time (one person does the task once, rather than lots of people doing the same task and duplicating work).
International sourcing
Bob may find there is value for money in changing suppliers and looking at international sourcing. Often other countries outside of the UK can offer the same products at a lower cost. An example of this is manufactured goods from China. By looking at international supply chains, Bob may be able to make cost-savings for ABC. He should be sure that when using this technique there is no compromise on quality.
Whole Life Costing methodology
This is a technique Bob can use for procuring capital expenditure items for ABC. This involves looking at the costs of the item throughout its lifecycle and not just the initial purchase price. For example, if Bob needs to buy a new delivery truck he should consider not only the price of the truck, but also the costs of insurance for the truck, how expensive it is to buy replacement parts such as tyres and the cost of disposing of the truck once it reaches the end of its life. By considering these factors Bob will ensure that he buys the truck that represents the best value for money long term.
In conclusion Bob should ensure he uses these four techniques for all items he and his team procures in the future. This will ensure ABC Ltd are always achieving value for money, and thus remain competitive in the marketplace.
Tutor Notes
- This case study is really short, and the ones you’ll receive in the exam are often longer and give you more guidance on what they’re expecting you to write. With case study questions, you have to make your entire answer about Bob. So don’t bring in examples from your own experience, rather, focus on giving examples for Bob.
- A good rule of thumb for case study questions is make sure you reference the case study once per paragraph.
- Value for Money is a really broad topic and you can pretty much argue anything that procurement does is helping to achieve value for money. There’s a large table of stuff that’s considered VFM on p.38 but that table isn’t exhaustive. So feel free to come up with your own ideas for this type of essay.
Some additional tidbits of information on VFM:
- The ‘academic’ definition of Value for Money is ‘the optimum combination of whole life cost and the quality necessary to meet the customer’s requirement’
- Value for Money is an important strategic objective for most organisations but particularly in the public sector. This is because the public sector is financed by public money (taxes), so they must demonstrate that the organisation is using this money wisely. This might be an interesting fact to put into an essay on VFM.
- Value can often be hard to quantify, particularly in the service industry. E.g. in customer service it can be difficult to quantify the value of having knowledgeable and polite employees delivering the service.
Discuss the importance and role of an organisation’s branding in procurement and supply operations (25 marks)
See the solution in Explanation part below.
How to approach the question
- This is a very open question so your essay could discuss
o the functions of a brand; e.g. advertising, marketing, creating trust, identity
o What is effective branding? Strong image, convincing people to purchase, shared values with customers, offering a solution to a problem.
o The impact for procurement and supply chain isn’t explained in the study guide so tailor this however you like. The best thing to do would be to think about some companies where branding is important, such as luxury goods, cars, or the brand is synonymous with a particular aspect such as Apple being associated with innovative technology. From there you could argue the importance of selecting the right suppliers to work with in order to keep up the brand image. Another example could be an ethical company needing to ensure their supply chain is ‘clean’, so as not to damage their branding. Possibilities are endless with this one.
Example Essay
In the contemporary business landscape, the significance of branding extends far beyond marketing and consumer perception. In procurement and supply operations, an organization's brand plays a pivotal role in shaping relationships with suppliers, determining the quality of goods and services that are procured, and influencing overall supply chain efficiency. This essay delves into the importance of branding in procurement and supply, exploring how a strong brand image can drive competitive advantage, foster trust and collaboration, and impact an organization's bottom line.
Building Competitive Advantage Through Brand Reputation:
The reputation of an organization's brand is a key determinant in attracting and retaining high-quality suppliers. A strong brand often correlates with financial stability, market presence, and business ethics, making such organizations more appealing to work with. This advantage is critical in procurement as it can lead to preferential treatment, such as priority access to scarce resources, better payment terms, and opportunities to collaborate on innovative products. For example, a well-regarded technology company might receive early access to cutting-edge components from suppliers eager to be associated with a market leader.
Enhancing Supplier Relationships and Negotiations:
Branding extends into the realms of trust and reliability, essential components in building long-term relationships with suppliers. A well-respected brand often implies a history of fair dealings, prompt payments, and mutual respect, which can make suppliers more willing to negotiate favourable terms. This trust can be particularly vital in times of supply chain disruptions or market volatility. Suppliers are more likely to extend credit or expedite orders for trusted partners, which can be invaluable for maintaining uninterrupted operations.
Influencing Quality and Sustainability Standards:
An organization's brand also communicates its commitment to quality and sustainability, which are increasingly crucial in procurement decisions. Suppliers aligning with brands that emphasize high-quality standards are often more diligent in maintaining these standards in their products and services. Additionally, a strong brand committed to sustainability can drive supply chain practices that align with environmental and social governance (ESG) principles. This commitment can lead to long-term cost savings, risk mitigation, and enhanced brand loyalty among environmentally conscious consumers.
Brand Image and Consumer Perception:
The procurement function directly impacts the final product quality, which in turn affects consumer perception of the brand. An organization's ability to procure high-quality, ethically sourced materials can significantly enhance its brand image and appeal to a broader customer base. For instance, a fashion brand's commitment to ethical sourcing and procurement of sustainable materials can bolster its image as an environmentally responsible brand, appealing to a growing demographic of eco-conscious consumers. The reverse is also true, brands associated with child or forced labour where this is found to be in their supply chains can suffer from loss of customers, revenue and reputation as well as potentially even legal consequences.
Internal Branding and Employee Engagement in Procurement:
Internal branding, the way an organization's values and culture are perceived by its employees, plays a crucial role in procurement. Employees who are proud of their organization's brand are more likely to engage deeply with their work, leading to better performance in procurement roles. This engagement can result in more innovative procurement strategies, improved vendor management, and a greater focus on aligning procurement practices with the organization’s overall strategic goals.
Conclusion:
The role of an organization's branding in procurement and supply operations is deeply impactful. A strong brand can create competitive advantages, foster better supplier relationships, influence quality and sustainability standards, enhance consumer perception, and drive employee engagement. In the modern business world, where supply chains are complex and consumer expectations are high, branding is not just a marketing tool but a strategic asset in procurement and supply operations. Organizations that recognize and leverage the power of their brand within these operations are poised to achieve greater efficiency, sustainability, and overall success.
Tutor Notes
- This is a really random section of the study guide and doesn’t really relate to the rest of the content. Branding comes up on p.226 – 228. It therefore can come up as a question, but because it’s such as small part of the syllabus, don’t focus too much effort on this subject.
- If you remember one line from this topic it’s this: “branding is not just a marketing tool but a strategic asset in procurement and supply operations”
- This type of question could come up as a scenario / case study. E.g. How does the branding of X Company impact upon their supply chain.
Copyright © 2021-2026 CertsTopics. All Rights Reserved

