Admission Tests Related Exams
GRE Exam







The importance of the Bill of Rights in twentieth-century United States law and politics has led some historians to search for the "original meaning" of its most controversial clauses. This approach. known as "originalism." presumes that each right codified in the Bill of Rights had au independent history that can be studied in isolation from the histories of other rights, and its proponents ask how formulations of the Bill of Rights in 1791 reflected developments in specific areas of legal thinking at that time. Legal and constitutional historians, for example, have found originalism especially useful in the study of provisions of the Bill of Rights that were innovative by eighteenth-century standards, such as the Fourth Amendment's broadly termed protection against "unreasonable searches and seizures." Recent calls in the legal and political arena for a return to a "jurisprudence of original intention." however, have made it a matter of much more than purely scholarly interest when originalists insist that a clause's true meaning was fixed at the moment of its adoption, or maintain that only those rights explicitly mentioned in the United States Constitution deserve constitutional recognition and protection. These two claims seemingly lend support to the notion that an interpreter must apply fixed definitions of a fixed number of rights to contemporary issues, for the claims imply that the central problem of rights in the Revolutionary era was to precisely identity, enumerate, and define those rights that Americans felt were crucial to protecting their liberty.
Both claims, however, are questionable from the perspective of a strictly historical inquiry, however sensible they may seem from the vantage point of contemporary jurisprudence. Even though originalists are correct in claiming that the search for original meaning is inherently historical, historians would not normally seek.
It can be inferred that the author of the passage would be most likely to agree with which of the following statements about the Bill of Rights?
The cube root of which of the following integers is equal to 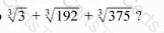
Recent studies of the gender gap in the history of United States politics tend to focus on candidate choice rather than on registration and turnout. This shift in focus away from gender inequality in political participation may be due to the finding in several studies of voting behavior in the United States that since 1980. differences in rates of registration and voting between men and women are not statistically significant after controlling for traditional predictors of participation. However. Fullerton and Stern argue that researchers have overlooked the substantial gender gap in registration and voting in the South. While the gender gap in participation virtually disappeared outside the South by the 1950s, substantial gender differences persisted in the South throughout the 1950s and 1960s, only beginning to decline in the 1970s.
The passage is primarily concerned with