EMC Related Exams
D-PVM-OE-01 Exam







Data is written on a source track and the original data needs to be preserved for a snapshot. Which technology does TimeFinder SnapVX use to prevent a new write from being demoted to a lower tier?
Two PowerMax arrays have been configured for replication using SRDF During a disaster recovery operation production has been transferred to the R2 devices at the target site
Which operation allows the primary hosts to access the R1 devices without waiting for a data transfer to complete from the R2 devices'?
Refer to the exhibit.
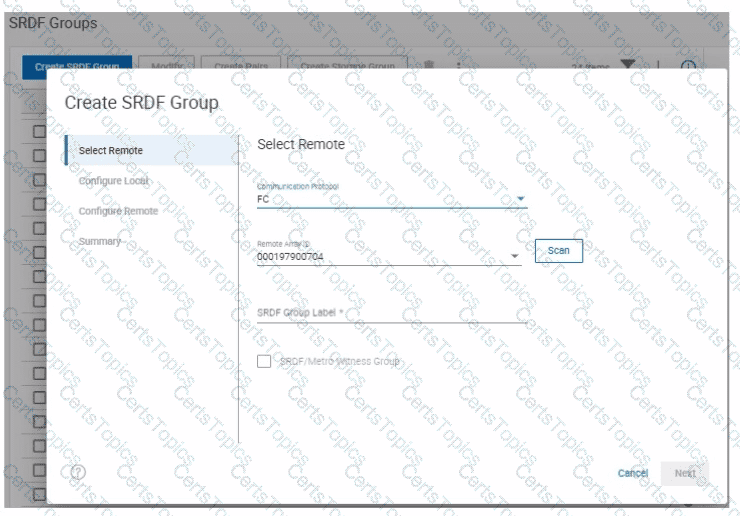
SRDF/Metro has been configured between two arrays using a physical witness.
When creating a new SRDF group for the configuration, why is the option to create an SRDF/Metro Witness Group greyed out?