VMware Related Exams
2V0-72.22 Exam







Refer to the exhibit.
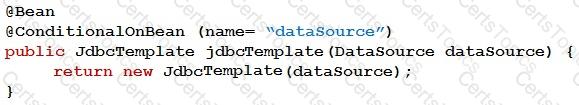
The above code shows a conditional @Bean method for the creation of a JdbcTemplate bean. Which two statements correctly describe the code behavior? (Choose two.)
Which two mechanisms of autowiring a dependency when multiple beans match the dependency's type are correct? (Choose two.)
Which two statements are true regarding bean creation? (Choose two.)