Oracle Related Exams
1z0-1073-24 Exam







How Back-to-Back Fulfillment Works
The back-to-back process flow is one in which specific sales order demand triggers supply creation and a link is established between the sales order and the supply.
An organization procures goods from an internal or external supplier or source to a specific warehouse from where you can combine those goods with others to create a single shipment to the customer.
Back-to-back supply processes are similar to regular supply processes that deliver supply to a warehouse except for one difference; the back-to-back supply is always reserved to an order management fulfillment line.
At a high level, you can think of back-to-back fulfillment as a three-step process:
1.Creation of a customer sales order (source of demand).
2.Creation and fulfillment of supply document (source of supply) to the fulfillment warehouse.
3.Shipment of sales order from the fulfillment warehouse to the customer.
However, the back-to-back flow is truly a highly integrated process flow involving several Oracle Fusion Cloud applications. The following figure shows the back-to-back process flow in detail. An explanation for each number follows the figure.
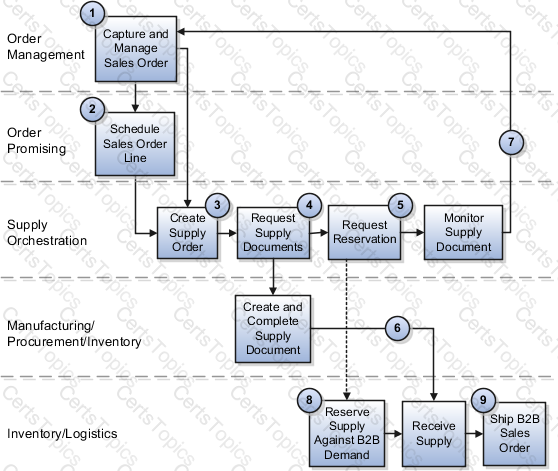
Back-to-Back Supply Creation Flows
You can set up Oracle Fusion Cloud applications that support back-to-back fulfillment to trigger supply creations flows (buy, make, transfer, and on hand) after a sales order is entered and scheduled.
Each variant of the back-to-back flow differs in the supply document that's created and the supply execution application in which the document is created. Depending on the source of the item, supply is provided from manufacturing, procurement, or inventory. Then, after the supply is received into the fulfillment warehouse, the back-to-back order is ready for shipment to your customer.
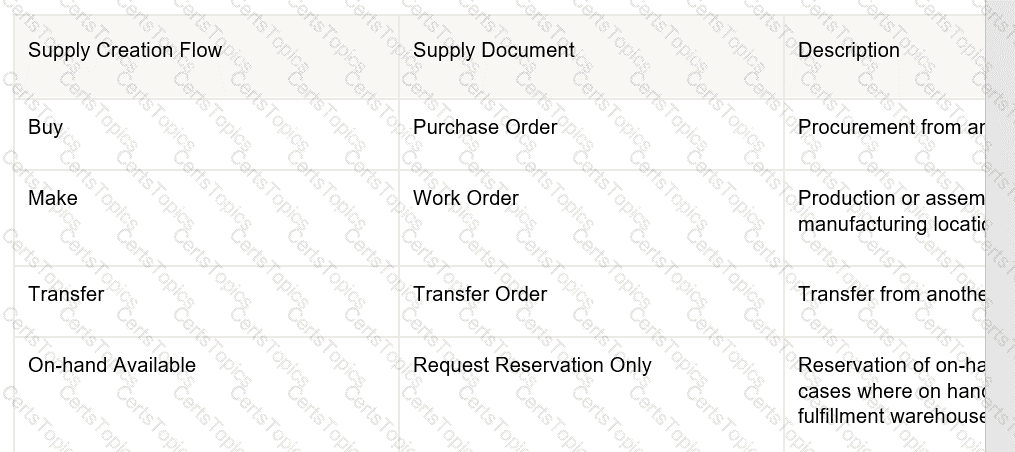
The following table describes the supply creation flows and associated supply document supported for each flow when using back-to-back fulfillment.
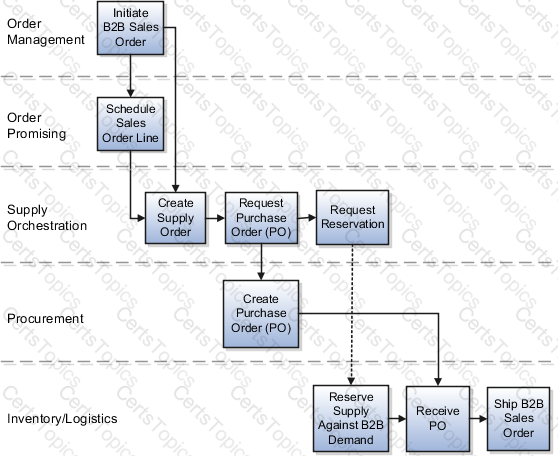
Back-to-Back Supply Creation Buy Flow
The supply document for a back-to-back buy flow is a purchase order. Based on supply recommendations from Oracle Global Order Promising, a purchase order is created and reserved against the sales order. When the purchase order is received by the supplier, on hand is created to ship out the back-to-back sales order.
The following figure shows the back-to-back supply creation buy flow.
Which two purposes can be achieved by using an item organization?