Which of the following Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) uses a database of attacks, known system vulnerabilities, monitoring current attempts to exploit those vulnerabilities, and then triggers an alarm if an attempt is found?
Knowledge-Based ID System
Application-Based ID System
Host-Based ID System
Network-Based ID System
Knowledge-based Intrusion Detection Systems use a database of previous attacks and known system vulnerabilities to look for current attempts to exploit their vulnerabilities, and trigger an alarm if an attempt is found.
Source: KRUTZ, Ronald L. & VINES, Russel D., The CISSP Prep Guide: Mastering the Ten Domains of Computer Security, 2001, John Wiley & Sons, Page 87.
Application-Based ID System - "a subset of HIDS that analyze what's going on in an application using the transaction log files of the application." Source: Official ISC2 CISSP CBK Review Seminar Student Manual Version 7.0 p. 87
Host-Based ID System - "an implementation of IDS capabilities at the host level. Its most significant difference from NIDS is intrusion detection analysis, and related processes are limited to the boundaries of the host." Source: Official ISC2 Guide to the CISSP CBK - p. 197
Network-Based ID System - "a network device, or dedicated system attached to teh network, that monitors traffic traversing teh network segment for which it is integrated." Source: Official ISC2 Guide to the CISSP CBK - p. 196
In the process of gathering evidence from a computer attack, a system administrator took a series of actions which are listed below. Can you identify which one of these actions has compromised the whole evidence collection process?
Using a write blocker
Made a full-disk image
Created a message digest for log files
Displayed the contents of a folder
Displaying the directory contents of a folder can alter the last access time on each listed file.
Using a write blocker is wrong because using a write blocker ensure that you cannot modify the data on the host and it prevent the host from writing to its hard drives.
Made a full-disk image is wrong because making a full-disk image can preserve all data on a hard disk, including deleted files and file fragments.
Created a message digest for log files is wrong because creating a message digest for log files. A message digest is a cryptographic checksum that can demonstrate that the integrity of a file has not been compromised (e.g. changes to the content of a log file)
Domain: LEGAL, REGULATIONS, COMPLIANCE AND INVESTIGATIONS
References:
AIO 3rd Edition, page 783-784
NIST 800-61 Computer Security Incident Handling guide page 3-18 to 3-20
Which of the following usually provides reliable, real-time information without consuming network or host resources?
network-based IDS
host-based IDS
application-based IDS
firewall-based IDS
A network-based IDS usually provides reliable, real-time information without consuming network or host resources.
Source: KRUTZ, Ronald L. & VINES, Russel D., The CISSP Prep Guide: Mastering the Ten Domains of Computer Security, 2001, John Wiley & Sons, Page 48.
Who should measure the effectiveness of Information System security related controls in an organization?
The local security specialist
The business manager
The systems auditor
The central security manager
It is the systems auditor that should lead the effort to ensure that the security controls are in place and effective. The audit would verify that the controls comply with polices, procedures, laws, and regulations where applicable. The findings would provide these to senior management.
The following answers are incorrect:
the local security specialist. Is incorrect because an independent review should take place by a third party. The security specialist might offer mitigation strategies but it is the auditor that would ensure the effectiveness of the controls
the business manager. Is incorrect because the business manager would be responsible that the controls are in place, but it is the auditor that would ensure the effectiveness of the controls.
the central security manager. Is incorrect because the central security manager would be responsible for implementing the controls, but it is the auditor that is responsibe for ensuring their effectiveness.
Controls provide accountability for individuals who are accessing sensitive information. This accountability is accomplished:
through access control mechanisms that require identification and authentication and through the audit function.
through logical or technical controls involving the restriction of access to systems and the protection of information.
through logical or technical controls but not involving the restriction of access to systems and the protection of information.
through access control mechanisms that do not require identification and authentication and do not operate through the audit function.
Controls provide accountability for individuals who are accessing sensitive information. This accountability is accomplished through access control mechanisms that require identification and authentication and through the audit function. These controls must be in accordance with and accurately represent the organization's security policy. Assurance procedures ensure that the control mechanisms correctly implement the security policy for the entire life cycle of an information system.
Source: KRUTZ, Ronald L. & VINES, Russel D., The CISSP Prep Guide: Mastering the Ten Domains of Computer Security, 2001, John Wiley & Sons, Page 33.
In what way can violation clipping levels assist in violation tracking and analysis?
Clipping levels set a baseline for acceptable normal user errors, and violations exceeding that threshold will be recorded for analysis of why the violations occurred.
Clipping levels enable a security administrator to customize the audit trail to record only those violations which are deemed to be security relevant.
Clipping levels enable the security administrator to customize the audit trail to record only actions for users with access to user accounts with a privileged status.
Clipping levels enable a security administrator to view all reductions in security levels which have been made to user accounts which have incurred violations.
Companies can set predefined thresholds for the number of certain types of errors that will be allowed before the activity is considered suspicious. The threshold is a baseline for violation activities that may be normal for a user to commit before alarms are raised. This baseline is referred to as a clipping level.
The following are incorrect answers:
Clipping levels enable a security administrator to customize the audit trail to record only those violations which are deemed to be security relevant. This is not the best answer, you would not record ONLY security relevant violations, all violations would be recorded as well as all actions performed by authorized users which may not trigger a violation. This could allow you to indentify abnormal activities or fraud after the fact.
Clipping levels enable the security administrator to customize the audit trail to record only actions for users with access to user accounts with a privileged status. It could record all security violations whether the user is a normal user or a privileged user.
Clipping levels enable a security administrator to view all reductions in security levels which have been made to user accounts which have incurred violations. The keyword "ALL" makes this question wrong. It may detect SOME but not all of violations. For example, application level attacks may not be detected.
Reference(s) used for this question:
Harris, Shon (2012-10-18). CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide, 6th Edition (p. 1239). McGraw-Hill. Kindle Edition.
and
TIPTON, Hal, (ISC)2, Introduction to the CISSP Exam presentation.
Attributes that characterize an attack are stored for reference using which of the following Intrusion Detection System (IDS) ?
signature-based IDS
statistical anomaly-based IDS
event-based IDS
inferent-based IDS
Source: KRUTZ, Ronald L. & VINES, Russel D., The CISSP Prep Guide: Mastering the Ten Domains of Computer Security, 2001, John Wiley & Sons, Page 49.
Who can best decide what are the adequate technical security controls in a computer-based application system in regards to the protection of the data being used, the criticality of the data, and it's sensitivity level ?
System Auditor
Data or Information Owner
System Manager
Data or Information user
The data or information owner also referred to as "Data Owner" would be the best person. That is the individual or officer who is ultimately responsible for the protection of the information and can therefore decide what are the adequate security controls according to the data sensitivity and data criticality. The auditor would be the best person to determine the adequacy of controls and whether or not they are working as expected by the owner.
The function of the auditor is to come around periodically and make sure you are doing what you are supposed to be doing. They ensure the correct controls are in place and are being maintained securely. The goal of the auditor is to make sure the organization complies with its own policies and the applicable laws and regulations.
Organizations can have internal auditors and/ or external auditors. The external auditors commonly work on behalf of a regulatory body to make sure compliance is being met. For example CobiT, which is a model that most information security auditors follow when evaluating a security program. While many security professionals fear and dread auditors, they can be valuable tools in ensuring the overall security of the organization. Their goal is to find the things you have missed and help you understand how to fix the problem.
The Official ISC2 Guide (OIG) says:
IT auditors determine whether users, owners, custodians, systems, and networks are in compliance with the security policies, procedures, standards, baselines, designs, architectures, management direction, and other requirements placed on systems. The auditors provide independent assurance to the management on the appropriateness of the security controls. The auditor examines the information systems and determines whether they are designed, configured, implemented, operated, and managed in a way ensuring that the organizational objectives are being achieved. The auditors provide top company management with an independent view of the controls and their effectiveness.
Example:
Bob is the head of payroll. He is therefore the individual with primary responsibility over the payroll database, and is therefore the information/data owner of the payroll database. In Bob's department, he has Sally and Richard working for him. Sally is responsible for making changes to the payroll database, for example if someone is hired or gets a raise. Richard is only responsible for printing paychecks. Given those roles, Sally requires both read and write access to the payroll database, but Richard requires only read access to it. Bob communicates these requirements to the system administrators (the "information/data custodians") and they set the file permissions for Sally's and Richard's user accounts so that Sally has read/write access, while Richard has only read access.
So in short Bob will determine what controls are required, what is the sensitivily and criticality of the Data. Bob will communicate this to the custodians who will implement the requirements on the systems/DB. The auditor would assess if the controls are in fact providing the level of security the Data Owner expects within the systems/DB. The auditor does not determine the sensitivity of the data or the crititicality of the data.
The other answers are not correct because:
A "system auditor" is never responsible for anything but auditing... not actually making control decisions but the auditor would be the best person to determine the adequacy of controls and then make recommendations.
A "system manager" is really just another name for a system administrator, which is actually an information custodian as explained above.
A "Data or information user" is responsible for implementing security controls on a day-to-day basis as they utilize the information, but not for determining what the controls should be or if they are adequate.
References:
Official ISC2 Guide to the CISSP CBK, Third Edition , Page 477
Schneiter, Andrew (2013-04-15). Official (ISC)2 Guide to the CISSP CBK, Third Edition : Information Security Governance and Risk Management ((ISC)2 Press) (Kindle Locations 294-298). Auerbach Publications. Kindle Edition.
Harris, Shon (2012-10-25). CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide, 6th Edition (Kindle Locations 3108-3114).
Information Security Glossary
Responsibility for use of information resources
Which of the following is the BEST way to detect software license violations?
Implementing a corporate policy on copyright infringements and software use.
Requiring that all PCs be diskless workstations.
Installing metering software on the LAN so applications can be accessed through the metered software.
Regularly scanning PCs in use to ensure that unauthorized copies of software have not been loaded on the PC.
The best way to prevent and detect software license violations is to regularly scan used PCs, either from the LAN or directly, to ensure that unauthorized copies of software have not been loaded on the PC.
Other options are not detective.
A corporate policy is not necessarily enforced and followed by all employees.
Software can be installed from other means than floppies or CD-ROMs (from a LAN or even downloaded from the Internet) and software metering only concerns applications that are registered.
Source: Information Systems Audit and Control Association, Certified Information Systems Auditor 2002 review manual, Chapter 3: Technical Infrastructure and Operational Practices (page 108).
Which of the following is an issue with signature-based intrusion detection systems?
Only previously identified attack signatures are detected.
Signature databases must be augmented with inferential elements.
It runs only on the windows operating system
Hackers can circumvent signature evaluations.
An issue with signature-based ID is that only attack signatures that are stored in their database are detected.
New attacks without a signature would not be reported. They do require constant updates in order to maintain their effectiveness.
Reference used for this question:
KRUTZ, Ronald L. & VINES, Russel D., The CISSP Prep Guide: Mastering the Ten Domains of Computer Security, 2001, John Wiley & Sons, Page 49.
Several analysis methods can be employed by an IDS, each with its own strengths and weaknesses, and their applicability to any given situation should be carefully considered. There are two basic IDS analysis methods that exists. Which of the basic method is more prone to false positive?
Pattern Matching (also called signature analysis)
Anomaly Detection
Host-based intrusion detection
Network-based intrusion detection
Several analysis methods can be employed by an IDS, each with its own strengths and weaknesses, and their applicability to any given situation should be carefully considered.
There are two basic IDS analysis methods:
1. Pattern Matching (also called signature analysis), and
2. Anomaly detection
PATTERN MATCHING
Some of the first IDS products used signature analysis as their detection method and simply looked for known characteristics of an attack (such as specific packet sequences or text in the data stream) to produce an alert if that pattern was detected. If a new or different attack vector is used, it will not match a known signature and, thus, slip past the IDS.
ANOMALY DETECTION
Alternately, anomaly detection uses behavioral characteristics of a system’s operation or network traffic to draw conclusions on whether the traffic represents a risk to the network or host. Anomalies may include but are not limited to:
Multiple failed log-on attempts
Users logging in at strange hours
Unexplained changes to system clocks
Unusual error messages
Unexplained system shutdowns or restarts
Attempts to access restricted files
An anomaly-based IDS tends to produce more data because anything outside of the expected behavior is reported. Thus, they tend to report more false positives as expected behavior patterns change. An advantage to anomaly-based IDS is that, because they are based on behavior identification and not specific patterns of traffic, they are often able to detect new attacks that may be overlooked by a signature-based system. Often information from an anomaly-based IDS may be used to create a pattern for a signature-based IDS.
Host Based Intrusion Detection (HIDS)
HIDS is the implementation of IDS capabilities at the host level. Its most significant difference from NIDS is that related processes are limited to the boundaries of a single-host system. However, this presents advantages in effectively detecting objectionable activities because the IDS process is running directly on the host system, not just observing it from the network. This offers unfettered access to system logs, processes, system information, and device information, and virtually eliminates limits associated with encryption. The level of integration represented by HIDS increases the level of visibility and control at the disposal of the HIDS application.
Network Based Intrustion Detection (NIDS)
NIDS are usually incorporated into the network in a passive architecture, taking advantage of promiscuous mode access to the network. This means that it has visibility into every packet traversing the network segment. This allows the system to inspect packets and monitor sessions without impacting the network or the systems and applications utilizing the network.
Below you have other ways that instrusion detection can be performed:
Stateful Matching Intrusion Detection
Stateful matching takes pattern matching to the next level. It scans for attack signatures in the context of a stream of traffic or overall system behavior rather than the individual packets or discrete system activities. For example, an attacker may use a tool that sends a volley of valid packets to a targeted system. Because all the packets are valid, pattern matching is nearly useless. However, the fact that a large volume of the packets was seen may, itself, represent a known or potential attack pattern. To evade attack, then, the attacker may send the packets from multiple locations with long wait periods between each transmission to either confuse the signature detection system or exhaust its session timing window. If the IDS service is tuned to record and analyze traffic over a long period of time it may detect such an attack. Because stateful matching also uses signatures, it too must be updated regularly and, thus, has some of the same limitations as pattern matching.
Statistical Anomaly-Based Intrusion Detection
The statistical anomaly-based IDS analyzes event data by comparing it to typical, known, or predicted traffic profiles in an effort to find potential security breaches. It attempts to identify suspicious behavior by analyzing event data and identifying patterns of entries that deviate from a predicted norm. This type of detection method can be very effective and, at a very high level, begins to take on characteristics seen in IPS by establishing an expected baseline of behavior and acting on divergence from that baseline. However, there are some potential issues that may surface with a statistical IDS. Tuning the IDS can be challenging and, if not performed regularly, the system will be prone to false positives. Also, the definition of normal traffic can be open to interpretation and does not preclude an attacker from using normal activities to penetrate systems. Additionally, in a large, complex, dynamic corporate environment, it can be difficult, if not impossible, to clearly define “normal” traffic. The value of statistical analysis is that the system has the potential to detect previously unknown attacks. This is a huge departure from the limitation of matching previously known signatures. Therefore, when combined with signature matching technology, the statistical anomaly-based IDS can be very effective.
Protocol Anomaly-Based Intrusion Detection
A protocol anomaly-based IDS identifies any unacceptable deviation from expected behavior based on known network protocols. For example, if the IDS is monitoring an HTTP session and the traffic contains attributes that deviate from established HTTP session protocol standards, the IDS may view that as a malicious attempt to manipulate the protocol, penetrate a firewall, or exploit a vulnerability. The value of this method is directly related to the use of well-known or well-defined protocols within an environment. If an organization primarily uses well-known protocols (such as HTTP, FTP, or telnet) this can be an effective method of performing intrusion detection. In the face of custom or nonstandard protocols, however, the system will have more difficulty or be completely unable to determine the proper packet format. Interestingly, this type of method is prone to the same challenges faced by signature-based IDSs. For example, specific protocol analysis modules may have to be added or customized to deal with unique or new protocols or unusual use of standard protocols. Nevertheless, having an IDS that is intimately aware of valid protocol use can be very powerful when an organization employs standard implementations of common protocols.
Traffic Anomaly-Based Intrusion
Detection A traffic anomaly-based IDS identifies any unacceptable deviation from expected behavior based on actual traffic structure. When a session is established between systems, there is typically an expected pattern and behavior to the traffic transmitted in that session. That traffic can be compared to expected traffic conduct based on the understandings of traditional system interaction for that type of connection. Like the other types of anomaly-based IDS, traffic anomaly-based IDS relies on the ability to establish “normal” patterns of traffic and expected modes of behavior in systems, networks, and applications. In a highly dynamic environment it may be difficult, if not impossible, to clearly define these parameters.
Reference(s) used for this question:
Hernandez CISSP, Steven (2012-12-21). Official (ISC)2 Guide to the CISSP CBK, Third Edition ((ISC)2 Press) (Kindle Locations 3664-3686). Auerbach Publications. Kindle Edition.
and
Hernandez CISSP, Steven (2012-12-21). Official (ISC)2 Guide to the CISSP CBK, Third Edition ((ISC)2 Press) (Kindle Locations 3711-3734). Auerbach Publications. Kindle Edition.
and
Hernandez CISSP, Steven (2012-12-21). Official (ISC)2 Guide to the CISSP CBK, Third Edition ((ISC)2 Press) (Kindle Locations 3694-3711). Auerbach Publications. Kindle Edition.
Which of the following are additional terms used to describe knowledge-based IDS and behavior-based IDS?
signature-based IDS and statistical anomaly-based IDS, respectively
signature-based IDS and dynamic anomaly-based IDS, respectively
anomaly-based IDS and statistical-based IDS, respectively
signature-based IDS and motion anomaly-based IDS, respectively.
The two current conceptual approaches to Intrusion Detection methodology are knowledge-based ID systems and behavior-based ID systems, sometimes referred to as signature-based ID and statistical anomaly-based ID, respectively.
Source: KRUTZ, Ronald L. & VINES, Russel D., The CISSP Prep Guide: Mastering the Ten Domains of Computer Security, 2001, John Wiley & Sons, Page 63.
Which of the following would assist the most in Host Based intrusion detection?
audit trails.
access control lists.
security clearances
host-based authentication
To assist in Intrusion Detection you would review audit logs for access violations.
The following answers are incorrect:
access control lists. This is incorrect because access control lists determine who has access to what but do not detect intrusions.
security clearances. This is incorrect because security clearances determine who has access to what but do not detect intrusions.
host-based authentication. This is incorrect because host-based authentication determine who have been authenticated to the system but do not dectect intrusions.
Which of the following monitors network traffic in real time?
network-based IDS
host-based IDS
application-based IDS
firewall-based IDS
This type of IDS is called a network-based IDS because monitors network traffic in real time.
Source: KRUTZ, Ronald L. & VINES, Russel D., The CISSP Prep Guide: Mastering the Ten Domains of Computer Security, 2001, John Wiley & Sons, Page 48.
Which of the following is required in order to provide accountability?
Authentication
Integrity
Confidentiality
Audit trails
Accountability can actually be seen in two different ways:
1) Although audit trails are also needed for accountability, no user can be accountable for their actions unless properly authenticated.
2) Accountability is another facet of access control. Individuals on a system are responsible for their actions. This accountability property enables system activities to be traced to the proper individuals. Accountability is supported by audit trails that record events on the system and network. Audit trails can be used for intrusion detection and for the reconstruction of past events. Monitoring individual activities, such as keystroke monitoring, should be accomplished in accordance with the company policy and appropriate laws. Banners at the log-on time should notify the user of any monitoring that is being conducted.
The point is that unless you employ an appropriate auditing mechanism, you don't have accountability. Authorization only gives a user certain permissions on the network. Accountability is far more complex because it also includes intrusion detection, unauthorized actions by both unauthorized users and authorized users, and system faults. The audit trail provides the proof that unauthorized modifications by both authorized and unauthorized users took place. No proof, No accountability.
Source: KRUTZ, Ronald L. & VINES, Russel D., The CISSP Prep Guide: Mastering the Ten Domains of Computer Security, John Wiley & Sons, 2001, Page 50.
The Shon Harris AIO book, 4th Edition, on Page 243 also states:
Auditing Capabilities ensures users are accountable for their actions, verify that the secutiy policies are enforced,
and can be used as investigation tools. Accountability is tracked by recording user, system, and application activities.
This recording is done through auditing functions and mechanisms within an operating sytem or application.
Audit trail contain information about operating System activities, application events, and user actions.
As a result of a risk assessment, your security manager has determined that your organization needs to implement an intrusion detection system that can detect unknown attacks and can watch for unusual traffic behavior, such as a new service appearing on the network. What type of intrusion detection system would you select?
Protocol anomaly based
Pattern matching
Stateful matching
Traffic anomaly-based
Traffic anomaly-based is the correct choice. An anomaly based IDS can detect unknown attacks. A traffic anomaly based IDS identifies any unacceptable deviation from expected behavior based on network traffic.
Protocol anomaly based is not the best choice as while a protocol anomaly based IDS can identify unknown attacks, this type of system is more suited to identifying deviations from established protocol standards such as HTTP. This type of IDS faces problems in analyzing complex or custom protocols.
Pattern matching is not the best choice as a pattern matching IDS cannot identify unknown attacks. This type of system can only compare packets against signatures of known attacks.
Stateful matching is not the best choice as a statful matching IDS cannot identify unknown attacks. This type of system works by scanning traffic streams for patterns or signatures of attacks.
How often should a Business Continuity Plan be reviewed?
At least once a month
At least every six months
At least once a year
At least Quarterly
As stated in SP 800-34 Rev. 1:
To be effective, the plan must be maintained in a ready state that accurately reflects system requirements, procedures, organizational structure, and policies. During the Operation/Maintenance phase of the SDLC, information systems undergo frequent changes because of shifting business needs, technology upgrades, or new internal or external policies.
As a general rule, the plan should be reviewed for accuracy and completeness at an organization-defined frequency (at least once a year for the purpose of the exam) or whenever significant changes occur to any element of the plan. Certain elements, such as contact lists, will require more frequent reviews.
Remember, there could be two good answers as specified above. Either once a year or whenever significant changes occur to the plan. You will of course get only one of the two presented within you exam.
Reference(s) used for this question:
NIST SP 800-34 Revision 1
Which of the following is used to monitor network traffic or to monitor host audit logs in real time to determine violations of system security policy that have taken place?
Intrusion Detection System
Compliance Validation System
Intrusion Management System (IMS)
Compliance Monitoring System
An Intrusion Detection System (IDS) is a system that is used to monitor network traffic or to monitor host audit logs in order to determine if any violations of an organization's system security policy have taken place.
Source: KRUTZ, Ronald L. & VINES, Russel D., The CISSP Prep Guide: Mastering the Ten Domains of Computer Security, 2001, John Wiley & Sons, Page 48.
Which of the following would NOT violate the Due Diligence concept?
Security policy being outdated
Data owners not laying out the foundation of data protection
Network administrator not taking mandatory two-week vacation as planned
Latest security patches for servers being installed as per the Patch Management process
To be effective a patch management program must be in place (due diligence) and detailed procedures would specify how and when the patches are applied properly (Due Care). Remember, the question asked for NOT a violation of Due Diligence, in this case, applying patches demonstrates due care and the patch management process in place demonstrates due diligence.
Due diligence is the act of investigating and understanding the risks the company faces. A company practices by developing and implementing security policies, procedures, and standards. Detecting risks would be based on standards such as ISO 2700, Best Practices, and other published standards such as NIST standards for example.
Due Diligence is understanding the current threats and risks. Due diligence is practiced by activities that make sure that the protection mechanisms are continually maintained and operational where risks are constantly being evaluated and reviewed. The security policy being outdated would be an example of violating the due diligence concept.
Due Care is implementing countermeasures to provide protection from those threats. Due care is when the necessary steps to help protect the company and its resources from possible risks that have been identifed. If the information owner does not lay out the foundation of data protection (doing something about it) and ensure that the directives are being enforced (actually being done and kept at an acceptable level), this would violate the due care concept.
If a company does not practice due care and due diligence pertaining to the security of its assets, it can be legally charged with negligence and held accountable for any ramifications of that negligence. Liability is usually established based on Due Diligence and Due Care or the lack of either.
A good way to remember this is using the first letter of both words within Due Diligence (DD) and Due Care (DC).
Due Diligence = Due Detect
Steps you take to identify risks based on best practices and standards.
Due Care = Due Correct.
Action you take to bring the risk level down to an acceptable level and maintaining that level over time.
The Following answer were wrong:
Security policy being outdated:
While having and enforcing a security policy is the right thing to do (due care), if it is outdated, you are not doing it the right way (due diligence). This questions violates due diligence and not due care.
Data owners not laying out the foundation for data protection:
Data owners are not recognizing the "right thing" to do. They don't have a security policy.
Network administrator not taking mandatory two week vacation:
The two week vacation is the "right thing" to do, but not taking the vacation violates due diligence (not doing the right thing the right way)
Reference(s) used for this question
Shon Harris, CISSP All In One, Version 5, Chapter 3, pg 110
Which of the following questions are least likely to help in assessing controls covering audit trails?
Does the audit trail provide a trace of user actions?
Are incidents monitored and tracked until resolved?
Is access to online logs strictly controlled?
Is there separation of duties between security personnel who administer the access control function and those who administer the audit trail?
Audit trails maintain a record of system activity by system or application processes and by user activity. In conjunction with appropriate tools and procedures, audit trails can provide individual accountability, a means to reconstruct events, detect intrusions, and identify problems. Audit trail controls are considered technical controls. Monitoring and tracking of incidents is more an operational control related to incident response capability.
Reference(s) used for this question:
SWANSON, Marianne, NIST Special Publication 800-26, Security Self-Assessment Guide for Information Technology Systems, November 2001 (Pages A-50 to A-51).
NOTE: NIST SP 800-26 has been superceded By: FIPS 200, SP 800-53, SP 800-53A
You can find the new replacement at:
However, if you really wish to see the old standard, it is listed as an archived document at:
What IDS approach relies on a database of known attacks?
Signature-based intrusion detection
Statistical anomaly-based intrusion detection
Behavior-based intrusion detection
Network-based intrusion detection
A weakness of the signature-based (or knowledge-based) intrusion detection approach is that only attack signatures that are stored in a database are detected. Network-based intrusion detection can either be signature-based or statistical anomaly-based (also called behavior-based).
Source: KRUTZ, Ronald L. & VINES, Russel D., The CISSP Prep Guide: Mastering the Ten Domains of Computer Security, John Wiley & Sons, 2001, Chapter 2: Access control systems (page 49).
Which of the following statements pertaining to ethical hacking is incorrect?
An organization should use ethical hackers who do not sell auditing, hardware, software, firewall, hosting, and/or networking services.
Testing should be done remotely to simulate external threats.
Ethical hacking should not involve writing to or modifying the target systems negatively.
Ethical hackers never use tools that have the potential of affecting servers or services.
This means that many of the tools used for ethical hacking have the potential of exploiting vulnerabilities and causing disruption to IT system. It is up to the individuals performing the tests to be familiar with their use and to make sure that no such disruption can happen or at least shoudl be avoided.
The first step before sending even one single packet to the target would be to have a signed agreement with clear rules of engagement and a signed contract. The signed contract explains to the client the associated risks and the client must agree to them before you even send one packet to the target range. This way the client understand that some of the test could lead to interruption of service or even crash a server. The client signs that he is aware of such risks and willing to accept them.
The following are incorrect answers:
An organization should use ethical hackers who do not sell auditing, hardware, software, firewall, hosting, and/or networking services. An ethical hacking firm's independence can be questioned if they sell security solutions at the same time as doing testing for the same client. There has to be independance between the judge (the tester) and the accuse (the client).
Testing should be done remotely to simulate external threats Testing simulating a cracker from the Internet is often time one of the first test being done, this is to validate perimeter security. By performing tests remotely, the ethical hacking firm emulates the hacker's approach more realistically.
Ethical hacking should not involve writing to or modifying the target systems negatively. Even though ethical hacking should not involve negligence in writing to or modifying the target systems or reducing its response time, comprehensive penetration testing has to be performed using the most complete tools available just like a real cracker would.
Reference(s) used for this question:
KRUTZ, Ronald L. & VINES, Russel D., The CISSP Prep Guide: Mastering the Ten Domains of Computer Security, John Wiley & Sons, 2001, Appendix F: The Case for Ethical Hacking (page 520).
Who is responsible for providing reports to the senior management on the effectiveness of the security controls?
Information systems security professionals
Data owners
Data custodians
Information systems auditors
IT auditors determine whether systems are in compliance with the security policies, procedures, standards, baselines, designs, architectures, management direction and other requirements" and "provide top company management with an independent view of the controls that have been designed and their effectiveness."
"Information systems security professionals" is incorrect. Security professionals develop the security policies and supporting baselines, etc.
"Data owners" is incorrect. Data owners have overall responsibility for information assets and assign the appropriate classification for the asset as well as ensure that the asset is protected with the proper controls.
"Data custodians" is incorrect. Data custodians care for an information asset on behalf of the data owner.
References:
CBK, pp. 38 - 42.
AIO3. pp. 99 - 104
What is a characteristic of using the Electronic Code Book mode of DES encryption?
A given block of plaintext and a given key will always produce the same ciphertext.
Repetitive encryption obscures any repeated patterns that may have been present in the plaintext.
Individual characters are encoded by combining output from earlier encryption routines with plaintext.
The previous DES output is used as input.
A given message and key always produce the same ciphertext.
The following answers are incorrect:
Repetitive encryption obscures any repeated patterns that may have been present in the plaintext. Is incorrect because with Electronic Code Book a given 64 bit block of plaintext always produces the same ciphertext
Individual characters are encoded by combining output from earlier encryption routines with plaintext. This is incorrect because with Electronic Code Book processing 64 bits at a time until the end of the file was reached. This is a characteristic of Cipher Feedback. Cipher Feedback the ciphertext is run through a key-generating device to create the key for the next block of plaintext.
The previous DES output is used as input. Is incorrect because This is incorrect because with Electronic Code Book processing 64 bits at a time until the end of the file was reached . This is a characteristic of Cipher Block Chaining. Cipher Block Chaining uses the output from the previous block to encrypt the next block.
Which of the following concerning the Rijndael block cipher algorithm is false?
The design of Rijndael was strongly influenced by the design of the block cipher Square.
A total of 25 combinations of key length and block length are possible
Both block size and key length can be extended to multiples of 64 bits.
The cipher has a variable block length and key length.
The answer above is the correct answer because it is FALSE. Rijndael does not support multiples of 64 bits but multiples of 32 bits in the range of 128 bits to 256 bits. Key length could be 128, 160, 192, 224, and 256.
Both block length and key length can be extended very easily to multiples of 32 bits. For a total combination of 25 different block and key size that are possible.
The Rijndael Cipher
Rijndael is a block cipher, designed by Joan Daemen and Vincent Rijmen as a candidate algorithm for the Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) in the United States of America. The cipher has a variable block length and key length.
Rijndael can be implemented very efficiently on a wide range of processors and in hardware.
The design of Rijndael was strongly influenced by the design of the block cipher Square.
The Advanced Encryption Standard (AES)
The Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) keys are defined to be either 128, 192, or 256 bits in accordance with the requirements of the AES.
The number of rounds, or iterations of the main algorithm, can vary from 10 to 14 within the Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) and is dependent on the block size and key length. 128 bits keys uses 10 rounds or encryptions, 192 bits keys uses 12 rounds of encryption, and 256 bits keys uses 14 rounds of encryption.
The low number of rounds has been one of the main criticisms of Rijndael, but if this ever becomes a problem the number of rounds can easily be increased at little extra cost performance wise by increasing the block size and key length.
Range of key and block lengths in Rijndael and AES
Rijndael and AES differ only in the range of supported values for the block length and cipher key length.
For Rijndael, the block length and the key length can be independently specified to any multiple of 32 bits, with a minimum of 128 bits, and a maximum of 256 bits. The support for block and key lengths 160 and 224 bits was introduced in Joan Daemen and Vincent Rijmen, AES submission document on Rijndael, Version 2, September 1999 available at
AES fixes the block length to 128 bits, and supports key lengths of 128, 192 or 256 bits only.
Reference used for this question:
The Rijndael Page
and
and
FIPS PUB 197, Advanced Encryption Standard (AES), National Institute of Standards and Technology, U.S. Department of Commerce, November 2001.
Where parties do not have a shared secret and large quantities of sensitive information must be passed, the most efficient means of transferring information is to use Hybrid Encryption Methods. What does this mean?
Use of public key encryption to secure a secret key, and message encryption using the secret key.
Use of the recipient's public key for encryption and decryption based on the recipient's private key.
Use of software encryption assisted by a hardware encryption accelerator.
Use of elliptic curve encryption.
A Public Key is also known as an asymmetric algorithm and the use of a secret key would be a symmetric algorithm.
The following answers are incorrect:
Use of the recipient's public key for encryption and decryption based on the recipient's private key. Is incorrect this would be known as an asymmetric algorithm.
Use of software encryption assisted by a hardware encryption accelerator. This is incorrect, it is a distractor.
Use of Elliptic Curve Encryption. Is incorrect this would use an asymmetric algorithm.
What uses a key of the same length as the message where each bit or character from the plaintext is encrypted by a modular addition?
Running key cipher
One-time pad
Steganography
Cipher block chaining
In cryptography, the one-time pad (OTP) is a type of encryption that is impossible to crack if used correctly. Each bit or character from the plaintext is encrypted by a modular addition with a bit or character from a secret random key (or pad) of the same length as the plaintext, resulting in a ciphertext. If the key is truly random, at least as long as the plaintext, never reused in whole or part, and kept secret, the ciphertext will be impossible to decrypt or break without knowing the key. It has also been proven that any cipher with the perfect secrecy property must use keys with effectively the same requirements as OTP keys. However, practical problems have prevented one-time pads from being widely used.
First described by Frank Miller in 1882, the one-time pad was re-invented in 1917 and patented a couple of years later. It is derived from the Vernam cipher, named after Gilbert Vernam, one of its inventors. Vernam's system was a cipher that combined a message with a key read from a punched tape. In its original form, Vernam's system was vulnerable because the key tape was a loop, which was reused whenever the loop made a full cycle. One-time use came a little later when Joseph Mauborgne recognized that if the key tape were totally random, cryptanalysis would be impossible.
The "pad" part of the name comes from early implementations where the key material was distributed as a pad of paper, so the top sheet could be easily torn off and destroyed after use. For easy concealment, the pad was sometimes reduced to such a small size that a powerful magnifying glass was required to use it. Photos show captured KGB pads that fit in the palm of one's hand, or in a walnut shell. To increase security, one-time pads were sometimes printed onto sheets of highly flammable nitrocellulose so they could be quickly burned.
The following are incorrect answers:
A running key cipher uses articles in the physical world rather than an electronic algorithm. In classical cryptography, the running key cipher is a type of polyalphabetic substitution cipher in which a text, typically from a book, is used to provide a very long keystream. Usually, the book to be used would be agreed ahead of time, while the passage to use would be chosen randomly for each message and secretly indicated somewhere in the message.
The Running Key cipher has the same internal workings as the Vigenere cipher. The difference lies in how the key is chosen; the Vigenere cipher uses a short key that repeats, whereas the running key cipher uses a long key such as an excerpt from a book. This means the key does not repeat, making cryptanalysis more difficult. The cipher can still be broken though, as there are statistical patterns in both the key and the plaintext which can be exploited.
Steganography is a method where the very existence of the message is concealed. It is the art and science of encoding hidden messages in such a way that no one, apart from the sender and intended recipient, suspects the existence of the message. it is sometimes referred to as Hiding in Plain Sight.
Cipher block chaining is a DES operating mode. IBM invented the cipher-block chaining (CBC) mode of operation in 1976. In CBC mode, each block of plaintext is XORed with the previous ciphertext block before being encrypted. This way, each ciphertext block depends on all plaintext blocks processed up to that point. To make each message unique, an initialization vector must be used in the first block.
Reference(s) used for this question:
HARRIS, Shon, All-In-One CISSP Certification Exam Guide, McGraw-Hill/Osborne, 2002, chapter 8: Cryptography (page 555).
and
In a hierarchical PKI the highest CA is regularly called Root CA, it is also referred to by which one of the following term?
Subordinate CA
Top Level CA
Big CA
Master CA
Which of the following algorithms does NOT provide hashing?
SHA-1
MD2
RC4
MD5
As it is an algorithm used for encryption and does not provide hashing functions , it is also commonly implemented ' Stream Ciphers '.
The other answers are incorrect because :
SHA-1 was designed by NIST and NSA to be used with the Digital Signature Standard (DSS). SHA was designed to be used in digital signatures and was developed when a more secure hashing algorithm was required for U.S. government applications.
MD2 is a one-way hash function designed by Ron Rivest that creates a 128-bit message digest value. It is not necessarily any weaker than the other algorithms in the "MD" family, but it is much slower.
MD5 was also created by Ron Rivest and is the newer version of MD4. It still produces a 128-bit hash, but the algorithm is more complex, which makes it harder to break.
Reference : Shon Harris , AIO v3 , Chapter - 8 : Cryptography , Page : 644 - 645
When we encrypt or decrypt data there is a basic operation involving ones and zeros where they are compared in a process that looks something like this:
0101 0001 Plain text
0111 0011 Key stream
0010 0010 Output
What is this cryptographic operation called?
Exclusive-OR
Bit Swapping
Logical-NOR
Decryption
When we encrypt data we are basically taking the plaintext information and applying some key material or keystream and conducting something called an XOR or Exclusive-OR operation.
The symbol used for XOR is the following: ⊕ This is a type of cipher known as a stream cipher.
The operation looks like this:
0101 0001 Plain text
0111 0011 Key stream
0010 0010 Output (ciphertext)
As you can see, it's not simple addition and the XOR Operation uses something called a truth table that explains why 0+1=1 and 1+1=0.
The rules are simples, if both bits are the same the result is zero, if both bits are not the same the result is one.
The following answers are incorrect:
- Bit Swapping: Incorrect. This isn't a known cryptographic operations.
- Logical NOR: Sorry, this isn't correct but is where only 0+0=1. All other combinations of 1+1, 1+0 equals 0. More on NOR here.
- Decryption: Sorry, this is the opposite of the process of encryption or, the process of applying the keystream to the plaintext to get the resulting encrypted text.
The following reference(s) was used to create this question:
For more details on XOR and all other QUESTION NO: s of cryptography. Subscribe to our holistic Security+ CBT tutorial at
and
and
Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) uses asymmetric key encryption between parties. The originator encrypts information using the intended recipient's "public" key in order to get confidentiality of the data being sent. The recipients use their own "private" key to decrypt the information. The "Infrastructure" of this methodology ensures that:
The sender and recipient have reached a mutual agreement on the encryption key exchange that they will use.
The channels through which the information flows are secure.
The recipient's identity can be positively verified by the sender.
The sender of the message is the only other person with access to the recipient's private key.
Through the use of Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) the recipient's identity can be positively verified by the sender.
The sender of the message knows he is using a Public Key that belongs to a specific user. He can validate through the Certification Authority (CA) that a public key is in fact the valid public key of the receiver and the receiver is really who he claims to be. By using the public key of the recipient, only the recipient using the matching private key will be able to decrypt the message. When you wish to achieve confidentiality, you encrypt the message with the recipient public key.
If the sender would wish to prove to the recipient that he is really who he claims to be then the sender would apply a digital signature on the message before encrypting it with the public key of the receiver. This would provide Confidentiality and Authenticity of the message.
A PKI (Public Key Infrastructure) enables users of an insecure public network, such as the Internet, to securely and privately exchange data through the use of public key-pairs that are obtained and shared through a trusted authority, usually referred to as a Certificate Authority.
The PKI provides for digital certificates that can vouch for the identity of individuals or organizations, and for directory services that can store, and when necessary, revoke those digital certificates. A PKI is the underlying technology that addresses the issue of trust in a normally untrusted environment.
The following answers are incorrect:
The sender and recipient have reached a mutual agreement on the encryption key exchange that they will use. Is incorrect because through the use of Public Key Infrastructure (PKI), the parties do not have to have a mutual agreement. They have a trusted 3rd party Certificate Authority to perform the verification of the sender.
The channels through which the information flows are secure. Is incorrect because the use of Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) does nothing to secure the channels.
The sender of the message is the only other person with access to the recipient's private key. Is incorrect because the sender does not have access to the recipient's private key though Public Key Infrastructure (PKI).
Reference(s) used for this question:
OIG CBK Cryptography (pages 253 - 254)
Which of the following terms can be described as the process to conceal data into another file or media in a practice known as security through obscurity?
Steganography
ADS - Alternate Data Streams
Encryption
NTFS ADS
It is the art and science of encoding hidden messages in such a way that no one, apart from the sender and intended recipient, suspects the existence of the message or could claim there is a message.
It is a form of security through obscurity.
The word steganography is of Greek origin and means "concealed writing." It combines the Greek words steganos (στεγανός), meaning "covered or protected," and graphei (γραφή) meaning "writing."
The first recorded use of the term was in 1499 by Johannes Trithemius in his Steganographia, a treatise on cryptography and steganography, disguised as a book on magic. Generally, the hidden messages will appear to be (or be part of) something else: images, articles, shopping lists, or some other cover text. For example, the hidden message may be in invisible ink between the visible lines of a private letter.
The advantage of steganography over cryptography alone is that the intended secret message does not attract attention to itself as an object of scrutiny. Plainly visible encrypted messages, no matter how unbreakable, will arouse interest, and may in themselves be incriminating in countries where encryption is illegal. Thus, whereas cryptography is the practice of protecting the contents of a message alone, steganography is concerned with concealing the fact that a secret message is being sent, as well as concealing the contents of the message.
It is sometimes referred to as Hiding in Plain Sight. This image of trees blow contains in it another image of a cat using Steganography.
ADS Tree with Cat inside

This image below is hidden in the picture of the trees above:

Hidden Kitty
As explained here the image is hidden by removing all but the two least significant bits of each color component and subsequent normalization.
ABOUT MSF and LSF
One of the common method to perform steganography is by hiding bits within the Least Significant Bits of a media (LSB) or what is sometimes referred to as Slack Space. By modifying only the least significant bit, it is not possible to tell if there is an hidden message or not looking at the picture or the media. If you would change the Most Significant Bits (MSB) then it would be possible to view or detect the changes just by looking at the picture. A person can perceive only up to 6 bits of depth, bit that are changed past the first sixth bit of the color code would be undetectable to a human eye.
If we make use of a high quality digital picture, we could hide six bits of data within each of the pixel of the image. You have a color code for each pixel composed of a Red, Green, and Blue value. The color code is 3 sets of 8 bits each for each of the color. You could change the last two bit to hide your data. See below a color code for one pixel in binary format. The bits below are not real they are just example for illustration purpose:
RED GREEN BLUE
0101 0101 1100 1011 1110 0011
MSB LSB MSB LSB MSB LSB
Let's say that I would like to hide the letter A uppercase within the pixels of the picture. If we convert the letter "A" uppercase to a decimal value it would be number 65 within the ASCII table , in binary format the value 65 would translet to 01000001
You can break the 8 bits of character A uppercase in group of two bits as follow: 01 00 00 01
Using the pixel above we will hide those bits within the last two bits of each of the color as follow:
RED GREEN BLUE
0101 0101 1100 1000 1110 0000
MSB LSB MSB LSB MSB LSB
As you can see above, the last two bits of RED was already set to the proper value of 01, then we move to the GREEN value and we changed the last two bit from 11 to 00, and finally we changed the last two bits of blue to 00. One pixel allowed us to hide 6 bits of data. We would have to use another pixel to hide the remaining two bits.
The following answers are incorrect:
- ADS - Alternate Data Streams: This is almost correct but ADS is different from steganography in that ADS hides data in streams of communications or files while Steganography hides data in a single file.
- Encryption: This is almost correct but Steganography isn't exactly encryption as much as using space in a file to store another file.
- NTFS ADS: This is also almost correct in that you're hiding data where you have space to do so. NTFS, or New Technology File System common on Windows computers has a feature where you can hide files where they're not viewable under normal conditions. Tools are required to uncover the ADS-hidden files.
The following reference(s) was used to create this question:
The CCCure Security+ Holistic Tutorial at
and
Steganography tool
and
What size is an MD5 message digest (hash)?
128 bits
160 bits
256 bits
128 bytes
MD5 is a one-way hash function producing a 128-bit message digest from the input message, through 4 rounds of transformation. MD5 is specified as an Internet Standard (RFC1312).
Reference(s) used for this question:
TIPTON, Hal, (ISC)2, Introduction to the CISSP Exam presentation.
Which of the following is NOT an asymmetric key algorithm?
RSA
Elliptic Curve Cryptosystem (ECC)
El Gamal
Data Encryption System (DES)
Data Encryption Standard (DES) is a symmetric key algorithm. Originally developed by IBM, under project name Lucifer, this 128-bit algorithm was accepted by the NIST in 1974, but the key size was reduced to 56 bits, plus 8 bits for parity. It somehow became a national cryptographic standard in 1977, and an American National Standard Institute (ANSI) standard in 1978. DES was later replaced by the Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) by the NIST. All other options are asymmetric algorithms.
Source: HARRIS, Shon, All-In-One CISSP Certification Exam Guide, McGraw-Hill/Osborne, 2002, chapter 8: Cryptography (page 525).
What is the maximum number of different keys that can be used when encrypting with Triple DES?
1
2
3
4
Triple DES encrypts a message three times. This encryption can be accomplished in several ways. The most secure form of triple DES is when the three encryptions are performed with three different keys.
Source: KRUTZ, Ronald L. & VINES, Russel D., The CISSP Prep Guide: Mastering the Ten Domains of Computer Security, John Wiley & Sons, 2001, Chapter 4: Cryptography (page 152).
What kind of certificate is used to validate a user identity?
Public key certificate
Attribute certificate
Root certificate
Code signing certificate
In cryptography, a public key certificate (or identity certificate) is an electronic document which incorporates a digital signature to bind together a public key with an identity — information such as the name of a person or an organization, their address, and so forth. The certificate can be used to verify that a public key belongs to an individual.
In a typical public key infrastructure (PKI) scheme, the signature will be of a certificate authority (CA). In a web of trust scheme, the signature is of either the user (a self-signed certificate) or other users ("endorsements"). In either case, the signatures on a certificate are attestations by the certificate signer that the identity information and the public key belong together.
In computer security, an authorization certificate (also known as an attribute certificate) is a digital document that describes a written permission from the issuer to use a service or a resource that the issuer controls or has access to use. The permission can be delegated.
Some people constantly confuse PKCs and ACs. An analogy may make the distinction clear. A PKC can be considered to be like a passport: it identifies the holder, tends to last for a long time, and should not be trivial to obtain. An AC is more like an entry visa: it is typically issued by a different authority and does not last for as long a time. As acquiring an entry visa typically requires presenting a passport, getting a visa can be a simpler process.
A real life example of this can be found in the mobile software deployments by large service providers and are typically applied to platforms such as Microsoft Smartphone (and related), Symbian OS, J2ME, and others.
In each of these systems a mobile communications service provider may customize the mobile terminal client distribution (ie. the mobile phone operating system or application environment) to include one or more root certificates each associated with a set of capabilities or permissions such as "update firmware", "access address book", "use radio interface", and the most basic one, "install and execute". When a developer wishes to enable distribution and execution in one of these controlled environments they must acquire a certificate from an appropriate CA, typically a large commercial CA, and in the process they usually have their identity verified using out-of-band mechanisms such as a combination of phone call, validation of their legal entity through government and commercial databases, etc., similar to the high assurance SSL certificate vetting process, though often there are additional specific requirements imposed on would-be developers/publishers.
Once the identity has been validated they are issued an identity certificate they can use to sign their software; generally the software signed by the developer or publisher's identity certificate is not distributed but rather it is submitted to processor to possibly test or profile the content before generating an authorization certificate which is unique to the particular software release. That certificate is then used with an ephemeral asymmetric key-pair to sign the software as the last step of preparation for distribution. There are many advantages to separating the identity and authorization certificates especially relating to risk mitigation of new content being accepted into the system and key management as well as recovery from errant software which can be used as attack vectors.
References:
HARRIS, Shon, All-In-One CISSP Certification Exam Guide, 2001, McGraw-Hill/Osborne, page 540.
Which of the following is less likely to be used today in creating a Virtual Private Network?
L2TP
PPTP
IPSec
L2F
L2F (Layer 2 Forwarding) provides no authentication or encryption. It is a Protocol that supports the creation of secure virtual private dial-up networks over the Internet.
At one point L2F was merged with PPTP to produce L2TP to be used on networks and not only on dial up links.
IPSec is now considered the best VPN solution for IP environments.
Source: HARRIS, Shon, All-In-One CISSP Certification Exam Guide, McGraw-Hill/Osborne, 2002, Chapter 8: Cryptography (page 507).
The RSA algorithm is an example of what type of cryptography?
Asymmetric Key.
Symmetric Key.
Secret Key.
Private Key.
The following answers are incorrect.
Symmetric Key. Is incorrect because RSA is a Public Key or a Asymmetric Key cryptographic system and not a Symmetric Key or a Secret Key cryptographic system.
Secret Key. Is incorrect because RSA is a Public Key or a Asymmetric Key cryptographic system and not a Secret Key or a Symmetric Key cryptographic system.
Private Key. Is incorrect because Private Key is just one part if an Asymmetric Key cryptographic system, a Private Key used alone is also called a Symmetric Key cryptographic system.
The Data Encryption Algorithm performs how many rounds of substitution and permutation?
4
16
54
64
Source: TIPTON, Hal, (ISC)2, Introduction to the CISSP Exam presentation.
What is the name for a substitution cipher that shifts the alphabet by 13 places?
Caesar cipher
Polyalphabetic cipher
ROT13 cipher
Transposition cipher
An extremely simple example of conventional cryptography is a substitution cipher.
A substitution cipher substitutes one piece of information for another. This is most frequently done by offsetting letters of the alphabet. Two examples are Captain Midnight's Secret Decoder Ring, which you may have owned when you were a kid, and Julius Caesar's cipher. In both cases, the algorithm is to offset the alphabet and the key is the number of characters to offset it. So the offset could be one, two, or any number you wish. ROT-13 is an example where it is shifted 13 spaces. The Ceaser Cipher is another example where it is shifted 3 letters to the left.
ROT13 ("rotate by 13 places", sometimes hyphenated ROT-13) is a simple letter substitution cipher that replaces a letter with the letter 13 letters after it in the alphabet. ROT13 is an example of the Caesar cipher, developed in ancient Rome.
In the basic Latin alphabet, ROT13 is its own inverse; that is, to undo ROT13, the same algorithm is applied, so the same action can be used for encoding and decoding. The algorithm provides virtually no cryptographic security, and is often cited as a canonical example of weak encryption.
ROT13 is used in online forums as a means of hiding spoilers, puzzle solutions, and offensive materials from the casual glance. ROT13 has been described as the "Usenet equivalent of a magazine printing the answer to a quiz upside down". ROT13 has inspired a variety of letter and word games on-line, and is frequently mentioned in newsgroup conversations. See diagram Below:
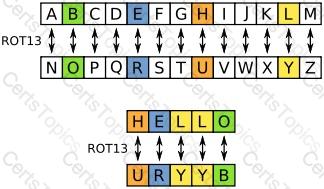
Rot 13 Cipher
The following are incorrect:
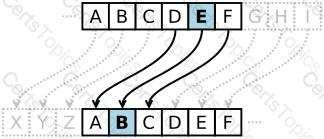
The Caesar cipher is a simple substitution cipher that involves shifting the alphabet three positions to the right. In cryptography, a Caesar cipher, also known as Caesar's cipher, the shift cipher, Caesar's code or Caesar shift, is one of the simplest and most widely known encryption techniques. It is a type of substitution cipher in which each letter in the plaintext is replaced by a letter some fixed number of positions down the alphabet. For example, with a left shift of 3, D would be replaced by A, E would become B, and so on. The method is named after Julius Caesar, who used it in his private correspondence.
Caesar Cipher
Polyalphabetic cipher refers to using multiple alphabets at a time. A polyalphabetic cipher is any cipher based on substitution, using multiple substitution alphabets. The Vigenère cipher is probably the best-known example of a polyalphabetic cipher, though it is a simplified special case.

Viginere Cipher
Transposition cipher is a different type of cipher. In cryptography, a transposition cipher is a method of encryption by which the positions held by units of plaintext (which are commonly characters or groups of characters) are shifted according to a regular system, so that the ciphertext constitutes a permutation of the plaintext. That is, the order of the units is changed. See the reference below for multiple examples of Transpositio Ciphers.
An exemple of Transposition cipher could be columnar transposition, the message is written out in rows of a fixed length, and then read out again column by column, and the columns are chosen in some scrambled order. Both the width of the rows and the permutation of the columns are usually defined by a keyword. For example, the word ZEBRAS is of length 6 (so the rows are of length 6), and the permutation is defined by the alphabetical order of the letters in the keyword. In this case, the order would be "6 3 2 4 1 5".
In a regular columnar transposition cipher, any spare spaces are filled with nulls; in an irregular columnar transposition cipher, the spaces are left blank. Finally, the message is read off in columns, in the order specified by the keyword. For example, suppose we use the keyword ZEBRAS and the message WE ARE DISCOVERED. FLEE AT ONCE. In a regular columnar transposition, we write this into the grid as Follows:

Transposition Cipher
Providing five nulls (QKJEU) at the end. The ciphertext is then read off as:
EVLNE ACDTK ESEAQ ROFOJ DEECU WIREE
Reference(s) used for this question:
Which of the following would best define a digital envelope?
A message that is encrypted and signed with a digital certificate.
A message that is signed with a secret key and encrypted with the sender's private key.
A message encrypted with a secret key attached with the message. The secret key is encrypted with the public key of the receiver.
A message that is encrypted with the recipient's public key and signed with the sender's private key.
A digital envelope for a recipient is a combination of encrypted data and its encryption key in an encrypted form that has been prepared for use of the recipient.
It consists of a hybrid encryption scheme in sealing a message, by encrypting the data and sending both it and a protected form of the key to the intended recipient, so that one else can open the message.
In PKCS #7, it means first encrypting the data using a symmetric encryption algorithm and a secret key, and then encrypting the secret key using an asymmetric encryption algorithm and the public key of the intended recipient.
Source: SHIREY, Robert W., RFC2828: Internet Security Glossary, may 2000.
Which of the following is NOT a property of a one-way hash function?
It converts a message of a fixed length into a message digest of arbitrary length.
It is computationally infeasible to construct two different messages with the same digest.
It converts a message of arbitrary length into a message digest of a fixed length.
Given a digest value, it is computationally infeasible to find the corresponding message.
An algorithm that turns messages or text into a fixed string of digits, usually for security or data management purposes. The "one way" means that it's nearly impossible to derive the original text from the string.
A one-way hash function is used to create digital signatures, which in turn identify and authenticate the sender and message of a digitally distributed message.
A cryptographic hash function is a deterministic procedure that takes an arbitrary block of data and returns a fixed-size bit string, the (cryptographic) hash value, such that an accidental or intentional change to the data will change the hash value. The data to be encoded is often called the "message," and the hash value is sometimes called the message digest or simply digest.
The ideal cryptographic hash function has four main or significant properties:
it is easy (but not necessarily quick) to compute the hash value for any given message
it is infeasible to generate a message that has a given hash
it is infeasible to modify a message without changing the hash
it is infeasible to find two different messages with the same hash
Cryptographic hash functions have many information security applications, notably in digital signatures, message authentication codes (MACs), and other forms of authentication. They can also be used as ordinary hash functions, to index data in hash tables, for fingerprinting, to detect duplicate data or uniquely identify files, and as checksums to detect accidental data corruption. Indeed, in information security contexts, cryptographic hash values are sometimes called (digital) fingerprints, checksums, or just hash values, even though all these terms stand for functions with rather different properties and purposes.
Source:
TIPTON, Hal, (ISC)2, Introduction to the CISSP Exam presentation.
and
Which of the following can best be defined as a key distribution protocol that uses hybrid encryption to convey session keys. This protocol establishes a long-term key once, and then requires no prior communication in order to establish or exchange keys on a session-by-session basis?
Internet Security Association and Key Management Protocol (ISAKMP)
Simple Key-management for Internet Protocols (SKIP)
Diffie-Hellman Key Distribution Protocol
IPsec Key exchange (IKE)
RFC 2828 (Internet Security Glossary) defines Simple Key Management for Internet Protocols (SKIP) as:
A key distribution protocol that uses hybrid encryption to convey session keys that are used to encrypt data in IP packets.
SKIP is an hybrid Key distribution protocol similar to SSL, except that it establishes a long-term key once, and then requires no prior communication in order to establish or exchange keys on a session-by-session basis. Therefore, no connection setup overhead exists and new keys values are not continually generated. SKIP uses the knowledge of its own secret key or private component and the destination's public component to calculate a unique key that can only be used between them.
IKE stand for Internet Key Exchange, it makes use of ISAKMP and OAKLEY internally.
Internet Key Exchange (IKE or IKEv2) is the protocol used to set up a security association (SA) in the IPsec protocol suite. IKE builds upon the Oakley protocol and ISAKMP. IKE uses X.509 certificates for authentication and a Diffie–Hellman key exchange to set up a shared session secret from which cryptographic keys are derived.
The following are incorrect answers:
ISAKMP is an Internet IPsec protocol to negotiate, establish, modify, and delete security associations, and to exchange key generation and authentication data, independent of the details of any specific key generation technique, key establishment protocol, encryption algorithm, or authentication mechanism.
IKE is an Internet, IPsec, key-establishment protocol (partly based on OAKLEY) that is intended for putting in place authenticated keying material for use with ISAKMP and for other security associations, such as in AH and ESP.
IPsec Key exchange (IKE) is only a detracto.
Reference(s) used for this question:
SHIREY, Robert W., RFC2828: Internet Security Glossary, may 2000.
and
and
Which type of algorithm is considered to have the highest strength per bit of key length of any of the asymmetric algorithms?
Rivest, Shamir, Adleman (RSA)
El Gamal
Elliptic Curve Cryptography (ECC)
Advanced Encryption Standard (AES)
The other answers are not correct because:
"Rivest, Shamir, Adleman (RSA)" is incorrect because RSA is a "traditional" asymmetric algorithm. While it is reasonably strong, it is not considered to be as strong as ECC based systems.
"El Gamal" is incorrect because it is also a "traditional" asymmetric algorithm and not considered as strong as ECC based systems.
"Advanced Encryption Standard (AES)" is incorrect because the question asks specifically about asymmetric algorithms and AES is a symmetric algorithm.
References:
Official ISC2 Guide page: 258
All in One Third Edition page: 638
The RSA Crypto FAQ:
PGP uses which of the following to encrypt data?
An asymmetric encryption algorithm
A symmetric encryption algorithm
A symmetric key distribution system
An X.509 digital certificate
Notice that the question specifically asks what PGP uses to encrypt For this, PGP uses an symmetric key algorithm. PGP then uses an asymmetric key algorithm to encrypt the session key and then send it securely to the receiver. It is an hybrid system where both types of ciphers are being used for different purposes.
Whenever a question talks about the bulk of the data to be sent, Symmetric is always best to choice to use because of the inherent speed within Symmetric Ciphers. Asymmetric ciphers are 100 to 1000 times slower than Symmetric Ciphers.
The other answers are not correct because:
"An asymmetric encryption algorithm" is incorrect because PGP uses a symmetric algorithm to encrypt data.
"A symmetric key distribution system" is incorrect because PGP uses an asymmetric algorithm for the distribution of the session keys used for the bulk of the data.
"An X.509 digital certificate" is incorrect because PGP does not use X.509 digital certificates to encrypt the data, it uses a session key to encrypt the data.
References:
Official ISC2 Guide page: 275
All in One Third Edition page: 664 - 665
The Clipper Chip utilizes which concept in public key cryptography?
Substitution
Key Escrow
An undefined algorithm
Super strong encryption
The Clipper chip is a chipset that was developed and promoted by the U.S. Government as an encryption device to be adopted by telecommunications companies for voice transmission. It was announced in 1993 and by 1996 was entirely defunct.
The heart of the concept was key escrow. In the factory, any new telephone or other device with a Clipper chip would be given a "cryptographic key", that would then be provided to the government in "escrow". If government agencies "established their authority" to listen to a communication, then the password would be given to those government agencies, who could then decrypt all data transmitted by that particular telephone.
The CISSP Prep Guide states, "The idea is to divide the key into two parts, and to escrow two portions of the key with two separate 'trusted' organizations. Then, law enforcement officals, after obtaining a court order, can retreive the two pieces of the key from the organizations and decrypt the message."
References:
and
Source: KRUTZ, Ronald L. & VINES, Russel D., The CISSP Prep Guide: Mastering the Ten Domains of Computer Security, John Wiley & Sons, 2001, page 166.
Controls provide accountability for individuals who are accessing sensitive information. This accountability is accomplished:
through access control mechanisms that require identification and authentication and through the audit function.
through logical or technical controls involving the restriction of access to systems and the protection of information.
through logical or technical controls but not involving the restriction of access to systems and the protection of information.
through access control mechanisms that do not require identification and authentication and do not operate through the audit function.
Controls provide accountability for individuals who are accessing sensitive information. This accountability is accomplished through access control mechanisms that require identification and authentication and through the audit function. These controls must be in accordance with and accurately represent the organization's security policy. Assurance procedures ensure that the control mechanisms correctly implement the security policy for the entire life cycle of an information system.
Source: KRUTZ, Ronald L. & VINES, Russel D., The CISSP Prep Guide: Mastering the Ten Domains of Computer Security, 2001, John Wiley & Sons, Page 33.
Organizations should consider which of the following first before allowing external access to their LANs via the Internet?
plan for implementing workstation locking mechanisms.
plan for protecting the modem pool.
plan for providing the user with his account usage information.
plan for considering proper authentication options.
Before a LAN is connected to the Internet, you need to determine what the access controls mechanisms are to be used, this would include how you are going to authenticate individuals that may access your network externally through access control.
The following answers are incorrect:
plan for implementing workstation locking mechanisms. This is incorrect because locking the workstations have no impact on the LAN or Internet access.
plan for protecting the modem pool. This is incorrect because protecting the modem pool has no impact on the LAN or Internet access, it just protects the modem.
plan for providing the user with his account usage information. This is incorrect because the question asks what should be done first. While important your primary concern should be focused on security.
In biometrics, "one-to-many" search against database of stored biometric images is done in:
Authentication
Identification
Identities
Identity-based access control
In biometrics, identification is a "one-to-many" search of an individual's characteristics from a database of stored images.
Source: KRUTZ, Ronald L. & VINES, Russel D., The CISSP Prep Guide: Mastering the Ten Domains of Computer Security, 2001, John Wiley & Sons, Page 38.
Which of the following remote access authentication systems is the most robust?
TACACS+
RADIUS
PAP
TACACS
TACACS+ is a proprietary Cisco enhancement to TACACS and is more robust than RADIUS. PAP is not a remote access authentication system but a remote node security protocol.
Source: KRUTZ, Ronald L. & VINES, Russel D., The CISSP Prep Guide: Mastering the Ten Domains of Computer Security, John Wiley & Sons, 2001, Chapter 3: Telecommunications and Network Security (page 122).
The control measures that are intended to reveal the violations of security policy using software and hardware are associated with:
Preventive/physical
Detective/technical
Detective/physical
Detective/administrative
The detective/technical control measures are intended to reveal the violations of security policy using technical means.
Source: KRUTZ, Ronald L. & VINES, Russel D., The CISSP Prep Guide: Mastering the Ten Domains of Computer Security, 2001, John Wiley & Sons, Page 35.
Almost all types of detection permit a system's sensitivity to be increased or decreased during an inspection process. If the system's sensitivity is increased, such as in a biometric authentication system, the system becomes increasingly selective and has the possibility of generating:
Lower False Rejection Rate (FRR)
Higher False Rejection Rate (FRR)
Higher False Acceptance Rate (FAR)
It will not affect either FAR or FRR
Almost all types of detection permit a system's sensitivity to be increased or decreased during an inspection process. If the system's sensitivity is increased, such as in a biometric authentication system, the system becomes increasingly selective and has a higher False Rejection Rate (FRR).
Conversely, if the sensitivity is decreased, the False Acceptance Rate (FRR) will increase. Thus, to have a valid measure of the system performance, the Cross Over Error (CER) rate is used. The Crossover Error Rate (CER) is the point at which the false rejection rates and the false acceptance rates are equal. The lower the value of the CER, the more accurate the system.
There are three categories of biometric accuracy measurement (all represented as percentages):
False Reject Rate (a Type I Error): When authorized users are falsely rejected as unidentified or unverified.
False Accept Rate (a Type II Error): When unauthorized persons or imposters are falsely accepted as authentic.
Crossover Error Rate (CER): The point at which the false rejection rates and the false acceptance rates are equal. The smaller the value of the CER, the more accurate the system.
NOTE:
Within the ISC2 book they make use of the term Accept or Acceptance and also Reject or Rejection when referring to the type of errors within biometrics. Below we make use of Acceptance and Rejection throughout the text for conistency. However, on the real exam you could see either of the terms.
Performance of biometrics
Different metrics can be used to rate the performance of a biometric factor, solution or application. The most common performance metrics are the False Acceptance Rate FAR and the False Rejection Rate FRR.
When using a biometric application for the first time the user needs to enroll to the system. The system requests fingerprints, a voice recording or another biometric factor from the operator, this input is registered in the database as a template which is linked internally to a user ID. The next time when the user wants to authenticate or identify himself, the biometric input provided by the user is compared to the template(s) in the database by a matching algorithm which responds with acceptance (match) or rejection (no match).
FAR and FRR
The FAR or False Acceptance rate is the probability that the system incorrectly authorizes a non-authorized person, due to incorrectly matching the biometric input with a valid template. The FAR is normally expressed as a percentage, following the FAR definition this is the percentage of invalid inputs which are incorrectly accepted.
The FRR or False Rejection Rate is the probability that the system incorrectly rejects access to an authorized person, due to failing to match the biometric input provided by the user with a stored template. The FRR is normally expressed as a percentage, following the FRR definition this is the percentage of valid inputs which are incorrectly rejected.
FAR and FRR are very much dependent on the biometric factor that is used and on the technical implementation of the biometric solution. Furthermore the FRR is strongly person dependent, a personal FRR can be determined for each individual.
Take this into account when determining the FRR of a biometric solution, one person is insufficient to establish an overall FRR for a solution. Also FRR might increase due to environmental conditions or incorrect use, for example when using dirty fingers on a fingerprint reader. Mostly the FRR lowers when a user gains more experience in how to use the biometric device or software.
FAR and FRR are key metrics for biometric solutions, some biometric devices or software even allow to tune them so that the system more quickly matches or rejects. Both FRR and FAR are important, but for most applications one of them is considered most important. Two examples to illustrate this:
When biometrics are used for logical or physical access control, the objective of the application is to disallow access to unauthorized individuals under all circumstances. It is clear that a very low FAR is needed for such an application, even if it comes at the price of a higher FRR.
When surveillance cameras are used to screen a crowd of people for missing children, the objective of the application is to identify any missing children that come up on the screen. When the identification of those children is automated using a face recognition software, this software has to be set up with a low FRR. As such a higher number of matches will be false positives, but these can be reviewed quickly by surveillance personnel.
False Acceptance Rate is also called False Match Rate, and False Rejection Rate is sometimes referred to as False Non-Match Rate.
crossover error rate
Above see a graphical representation of FAR and FRR errors on a graph, indicating the CER
CER
The Crossover Error Rate or CER is illustrated on the graph above. It is the rate where both FAR and FRR are equal.
The matching algorithm in a biometric software or device uses a (configurable) threshold which determines how close to a template the input must be for it to be considered a match. This threshold value is in some cases referred to as sensitivity, it is marked on the X axis of the plot. When you reduce this threshold there will be more false acceptance errors (higher FAR) and less false rejection errors (lower FRR), a higher threshold will lead to lower FAR and higher FRR.
Speed
Most manufacturers of biometric devices and softwares can give clear numbers on the time it takes to enroll as well on the time for an individual to be authenticated or identified using their application. If speed is important then take your time to consider this, 5 seconds might seem a short time on paper or when testing a device but if hundreds of people will use the device multiple times a day the cumulative loss of time might be significant.
Reference(s) used for this question:
Hernandez CISSP, Steven (2012-12-21). Official (ISC)2 Guide to the CISSP CBK, Third Edition ((ISC)2 Press) (Kindle Locations 2723-2731). Auerbach Publications. Kindle Edition.
and
KRUTZ, Ronald L. & VINES, Russel D., The CISSP Prep Guide: Mastering the Ten Domains of Computer Security, 2001, John Wiley & Sons, Page 37.
and
Which of the following are not Remote Access concerns?
Justification for remote access
Auditing of activities
Regular review of access privileges
Access badges
Access badges are more relevant to physical security rather than remote access.
"Justification for remote access" is incorrect. Justification for remote access is a relevant concern.
"Auditing of activities" is incorrect. Auditing of activites is an imporant aspect to assure that malicious or unauthorized activities are not occuring.
"Regular review of access privileges" is incorrect. Regular review of remote accept privileges is an important management responsibility.
References:
AIO3, pp. 547 - 548
Which of the following statements pertaining to Kerberos is TRUE?
Kerberos does not address availability
Kerberos does not address integrity
Kerberos does not make use of Symmetric Keys
Kerberos cannot address confidentiality of information
The question was asking for a TRUE statement and the only correct statement is "Kerberos does not address availability".
Kerberos addresses the confidentiality and integrity of information. It does not directly address availability.
Source: KRUTZ, Ronald L. & VINES, Russel D., The CISSP Prep Guide: Mastering the Ten Domains of Computer Security, John Wiley & Sons, 2001, Chapter 2: Access control systems (page 42).
Which of the following access control models requires security clearance for subjects?
Identity-based access control
Role-based access control
Discretionary access control
Mandatory access control
With mandatory access control (MAC), the authorization of a subject's access to an object is dependant upon labels, which indicate the subject's clearance. Identity-based access control is a type of discretionary access control. A role-based access control is a type of non-discretionary access control.
Source: KRUTZ, Ronald L. & VINES, Russel D., The CISSP Prep Guide: Mastering the Ten Domains of Computer Security, John Wiley & Sons, 2001, Chapter 2: Access control systems (page 33).
Which of the following is NOT part of the Kerberos authentication protocol?
Symmetric key cryptography
Authentication service (AS)
Principals
Public Key
There is no such component within kerberos environment. Kerberos uses only symmetric encryption and does not make use of any public key component.
The other answers are incorrect because :
Symmetric key cryptography is a part of Kerberos as the KDC holds all the users' and services' secret keys.
Authentication service (AS) : KDC (Key Distribution Center) provides an authentication service
Principals : Key Distribution Center provides services to principals , which can be users , applications or network services.
References: Shon Harris , AIO v3 , Chapter - 4: Access Control , Pages : 152-155.
Guards are appropriate whenever the function required by the security program involves which of the following?
The use of discriminating judgment
The use of physical force
The operation of access control devices
The need to detect unauthorized access
The Answer: The use of discriminating judgment, a guard can make the determinations that hardware or other automated security devices cannot make due to its ability to adjust to rapidly changing conditions, to learn and alter recognizable patterns, and to respond to various conditions in the environment. Guards are better at making value decisions at times of incidents. They are appropriate whenever immediate, discriminating judgment is required by the security entity.
The following answers are incorrect:
The use of physical force This is not the best answer. A guard provides discriminating judgment, and the ability to discern the need for physical force.
The operation of access control devices A guard is often uninvolved in the operations of an automated access control device such as a biometric reader, a smart lock, mantrap, etc.
The need to detect unauthorized access The primary function of a guard is not to detect unauthorized access, but to prevent unauthorized physical access attempts and may deter social engineering attempts.
The following reference(s) were/was used to create this question:
Source: KRUTZ, Ronald L. & VINES, Russel D., The CISSP Prep Guide: Mastering the Ten Domains of Computer Security, John Wiley & Sons, 2001, Chapter 10: Physical security (page 339).
Source: ISC2 Offical Guide to the CBK page 288-289.
What is the most critical characteristic of a biometric identifying system?
Perceived intrusiveness
Storage requirements
Accuracy
Scalability
Accuracy is the most critical characteristic of a biometric identifying verification system.
Accuracy is measured in terms of false rejection rate (FRR, or type I errors) and false acceptance rate (FAR or type II errors).
The Crossover Error Rate (CER) is the point at which the FRR equals the FAR and has become the most important measure of biometric system accuracy.
Source: TIPTON, Harold F. & KRAUSE, Micki, Information Security Management Handbook, 4th edition (volume 1), 2000, CRC Press, Chapter 1, Biometric Identification (page 9).
The Terminal Access Controller Access Control System (TACACS) employs which of the following?
a user ID and static password for network access
a user ID and dynamic password for network access
a user ID and symmetric password for network access
a user ID and asymmetric password for network access
For networked applications, the Terminal Access Controller Access Control System (TACACS) employs a user ID and a static password for network access.
Source: KRUTZ, Ronald L. & VINES, Russel D., The CISSP Prep Guide: Mastering the Ten Domains of Computer Security, 2001, John Wiley & Sons, Page 44.
This is a common security issue that is extremely hard to control in large environments. It occurs when a user has more computer rights, permissions, and access than what is required for the tasks the user needs to fulfill. What best describes this scenario?
Excessive Rights
Excessive Access
Excessive Permissions
Excessive Privileges
Even thou all 4 terms are very close to each other, the best choice is Excessive Privileges which would include the other three choices presented.
Reference(s) used for this question:
HARRIS, Shon, All-In-One CISSP Certification Exam Guide, McGraw-Hill/Osborne, 2001, Page 645.
and
In biometrics, the "one-to-one" search used to verify claim to an identity made by a person is considered:
Authentication
Identification
Auditing
Authorization
Biometric devices can be use for either IDENTIFICATION or AUTHENTICATION
ONE TO ONE is for AUTHENTICATION
This means that you as a user would provide some biometric credential such as your fingerprint. Then they will compare the template that you have provided with the one stored in the Database. If the two are exactly the same that prove that you are who you pretend to be.
ONE TO MANY is for IDENTIFICATION
A good example of this would be within airport. Many airports today have facial recognition cameras, as you walk through the airport it will take a picture of your face and then compare the template (your face) with a database full of templates and see if there is a match between your template and the ones stored in the Database. This is for IDENTIFICATION of a person.
Some additional clarification or comments that might be helpful are: Biometrics establish authentication using specific information and comparing results to expected data. It does not perform well for identification purposes such as scanning for a person's face in a moving crowd for example.
Identification methods could include: username, user ID, account number, PIN, certificate, token, smart card, biometric device or badge.
Auditing is a process of logging or tracking what was done after the identity and authentication process is completed.
Authorization is the rights the subject is given and is performed after the identity is established.
Reference OIG (2007) p148, 167
Authentication in biometrics is a "one-to-one" search to verify claim to an identity made by a person.
Source: KRUTZ, Ronald L. & VINES, Russel D., The CISSP Prep Guide: Mastering the Ten Domains of Computer Security, 2001, John Wiley & Sons, Page 38.
Which of the following is the most reliable, secure means of removing data from magnetic storage media such as a magnetic tape, or a cassette?
Degaussing
Parity Bit Manipulation
Zeroization
Buffer overflow
A "Degausser (Otherwise known as a Bulk Eraser) has the main function of reducing to near zero the magnetic flux stored in the magnetized medium. Flux density is measured in Gauss or Tesla. The operation is speedier than overwriting and done in one short operation. This is achieved by subjecting the subject in bulk to a series of fields of alternating polarity and gradually decreasing strength.
The following answers are incorrect:Parity Bit Manipulation. Parity has to do with disk lerror detection, not data removal. A bit or series of bits appended to a character or block of characters to ensure that the information received is the same as the infromation that was sent.
Zeroization. Zeroization involves overwrting data to sanitize it. It is time-consuming and not foolproof. The potential of restoration of data does exist with this method.
Buffer overflow. This is a detractor. Although many Operating Systems use a disk buffer to temporarily hold data read from disk, its primary purpose has no connection to data removal. An overflow goes outside the constraints defined for the buffer and is a method used by an attacker to attempt access to a system.
The following reference(s) were/was used to create this question:
Shon Harris AIO v3. pg 908
Which of the following would assist the most in Host Based intrusion detection?
audit trails.
access control lists.
security clearances.
host-based authentication.
To assist in Intrusion Detection you would review audit logs for access violations.
The following answers are incorrect:
access control lists. This is incorrect because access control lists determine who has access to what but do not detect intrusions.
security clearances. This is incorrect because security clearances determine who has access to what but do not detect intrusions.
host-based authentication. This is incorrect because host-based authentication determine who have been authenticated to the system but do not dectect intrusions.
Which of the following is NOT a compensating measure for access violations?
Backups
Business continuity planning
Insurance
Security awareness
Security awareness is a preventive measure, not a compensating measure for access violations.
Source: KRUTZ, Ronald L. & VINES, Russel D., The CISSP Prep Guide: Mastering the Ten Domains of Computer Security, John Wiley & Sons, 2001, Chapter 2: Access control systems (page 50).
The Orange Book is founded upon which security policy model?
The Biba Model
The Bell LaPadula Model
Clark-Wilson Model
TEMPEST
From the glossary of Computer Security Basics:
The Bell-LaPadula model is the security policy model on which the Orange Book requirements are based. From the Orange Book definition, "A formal state transition model of computer security policy that describes a set of access control rules. In this formal model, the entities in a computer system are divided into abstract sets of subjects and objects. The notion of secure state is defined and it is proven that each state transition preserves security by moving from secure state to secure state; thus, inductively proving the system is secure. A system state is defined to be 'secure' if the only permitted access modes of subjects to objects are in accordance with a specific security policy. In order to determine whether or not a specific access mode is allowed, the clearance of a subject is compared to the classification of the object and a determination is made as to whether the subject is authorized for the specific access mode."
The Biba Model is an integrity model of computer security policy that describes a set of rules. In this model, a subject may not depend on any object or other subject that is less trusted than itself.
The Clark Wilson Model is an integrity model for computer security policy designed for a commercial environment. It addresses such concepts as nondiscretionary access control, privilege separation, and least privilege. TEMPEST is a government program that prevents the compromising electrical and electromagnetic signals that emanate from computers and related equipment from being intercepted and deciphered.
Source: RUSSEL, Deborah & GANGEMI, G.T. Sr., Computer Security Basics, O'Reilly, 1991.
Also: U.S. Department of Defense, Trusted Computer System Evaluation Criteria (Orange Book), DOD 5200.28-STD. December 1985 (also available here).
Which of the following is addressed by Kerberos?
Confidentiality and Integrity
Authentication and Availability
Validation and Integrity
Auditability and Integrity
Kerberos addresses the confidentiality and integrity of information.
It also addresses primarily authentication but does not directly address availability.
Reference(s) used for this question:
KRUTZ, Ronald L. & VINES, Russel D., The CISSP Prep Guide: Mastering the Ten Domains of Computer Security, 2001, John Wiley & Sons, Page 42.
and
and
What is called the type of access control where there are pairs of elements that have the least upper bound of values and greatest lower bound of values?
Mandatory model
Discretionary model
Lattice model
Rule model
In a lattice model, there are pairs of elements that have the least upper bound of values and greatest lower bound of values.
Reference(s) used for this question:
KRUTZ, Ronald L. & VINES, Russel D., The CISSP Prep Guide: Mastering the Ten Domains of Computer Security, 2001, John Wiley & Sons, Page 34.
Which of the following protection devices is used for spot protection within a few inches of the object, rather than for overall room security monitoring?
Wave pattern motion detectors
Capacitance detectors
Field-powered devices
Audio detectors
Capacitance detectors monitor an electrical field surrounding the object being monitored. They are used for spot protection within a few inches of the object, rather than for overall room security monitoring used by wave detectors. Penetration of this field changes the electrical capacitance of the field enough to generate and alarm. Wave pattern motion detectors generate a frequency wave pattern and send an alarm if the pattern is disturbed as it is reflected back to its receiver. Field-powered devices are a type of personnel access control devices. Audio detectors simply monitor a room for any abnormal sound wave generation and trigger an alarm.
Source: KRUTZ, Ronald L. & VINES, Russel D., The CISSP Prep Guide: Mastering the Ten Domains of Computer Security, John Wiley & Sons, 2001, Chapter 10: Physical security (page 344).
Which access control model enables the OWNER of the resource to specify what subjects can access specific resources based on their identity?
Discretionary Access Control
Mandatory Access Control
Sensitive Access Control
Role-based Access Control
Data owners decide who has access to resources based only on the identity of the person accessing the resource.
The following answers are incorrect :
Mandatory Access Control : users and data owners do not have as much freedom to determine who can access files. The operating system makes the final decision and can override the users' wishes and access decisions are based on security labels.
Sensitive Access Control : There is no such access control in the context of the above question.
Role-based Access Control : uses a centrally administered set of controls to determine how subjects and objects interact , also called as non discretionary access control.
In a mandatory access control (MAC) model, users and data owners do not have as much freedom to determine who can access files. The operating system makes the final decision and can override the users’ wishes. This model is much more structured and strict and is based on a security label system. Users are given a security clearance (secret, top secret, confidential, and so on), and data is classified in the same way. The clearance and classification data is stored in the security labels, which are bound to the specific subjects and objects. When the system makes a decision about fulfilling a request to access an object, it is based on the clearance of the subject, the classification of the object, and the security policy of the system. The rules for how subjects access objects are made by the security officer, configured by the administrator, enforced by the operating system, and supported by security technologies
Reference : Shon Harris , AIO v3 , Chapter-4 : Access Control , Page : 163-165
Which of the following is an IP address that is private (i.e. reserved for internal networks, and not a valid address to use on the Internet)?
192.168.42.5
192.166.42.5
192.175.42.5
192.1.42.5
This is a valid Class C reserved address. For Class C, the reserved addresses are 192.168.0.0 - 192.168.255.255.
The private IP address ranges are defined within RFC 1918:
RFC 1918 private ip address range
The following answers are incorrect:
192.166.42.5 Is incorrect because it is not a Class C reserved address.
192.175.42.5 Is incorrect because it is not a Class C reserved address.
192.1.42.5 Is incorrect because it is not a Class C reserved address.
What is defined as the manner in which the network devices are organized to facilitate communications?
LAN transmission methods
LAN topologies
LAN transmission protocols
LAN media access methods
A network topology defines the manner in which the network devices are organized to facilitate communications. Common LAN technologies are:
bus
ring
star
meshed
LAN transmission methods refer to the way packets are sent on the network and are:
unicast
multicast
broadcast
LAN transmission protocols are the rules for communicating between computers on a LAN. Common LAN transmission protocols are:
CSMA/CD
polling
token-passing
LAN media access methods control the use of a network (physical and data link layers). They can be:
Ethernet
ARCnet
Token ring
FDDI
Source: KRUTZ, Ronald L. & VINES, Russel D., The CISSP Prep Guide: Mastering the Ten Domains of Computer Security, John Wiley & Sons, 2001, Chapter 3: Telecommunications and Network Security (page 105).
Which of the following standards is concerned with message handling?
X.400
X.500
X.509
X.800
X.400 is used in e-mail as a message handling protocol. X.500 is used in directory services. X.509 is used in digital certificates and X.800 is used a network security standard.
Which of the following statements pertaining to Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM) is false?
It can be used for voice
it can be used for data
It carries various sizes of packets
It can be used for video
ATM is an example of a fast packet-switching network that can be used for either data, voice or video, but packets are of fixed size.
Source: HARRIS, Shon, All-In-One CISSP Certification Exam Guide, McGraw-Hill/Osborne, 2002, chapter 7: Telecommunications and Network Security (page 455).
Which type of attack consists of modifying the length and fragmentation offset fields in sequential IP packets?
Teardrop attack
Smurf attack
SYN attack
Buffer overflow attack
A teardrop attack consists of modifying the length and fragmentation offset fields in sequential IP packets so the target system becomes confused and crashes after it receives contradictory instructions on how the fragments are offset on these packets. A SYN attack is when an attacker floods a system with connection requests but does not respond when the target system replies to those requests. A smurf attack is an attack where the attacker spoofs the source IP address in an ICMP ECHO broadcast packet so it seems to have originated at the victim's system, in order to flood it with REPLY packets. A buffer overflow attack occurs when a process receives much more data than expected.
Source: KRUTZ, Ronald L. & VINES, Russel D., The CISSP Prep Guide: Mastering the Ten Domains of Computer Security, John Wiley & Sons, 2001, Chapter 3: Telecommunications and Network Security (page 76).
Which of the following is NOT a defined ISO basic task related to network management?
Fault management
Accounting resources
Security management
Communications management
ISO has defined five basic tasks related to network management :
Fault management: Detects the devices that present some kind of fault.
Configuration management: Allows users to know, define and change remotely the configuration of any device.
Accounting resources: Holds the records of the resource usage in the WAN.
Performance management: Monitors usage levels and sets alarms when a threshold has been surpassed.
Security management: Detects suspicious traffic or users and generates alarms accordingly.
Source: Information Systems Audit and Control Association, Certified Information Systems Auditor 2002 review manual, Chapter 3: Technical Infrastructure and Operational Practices (page 137).
Which of the following transmission media would NOT be affected by cross talk or interference?
Copper cable
Radio System
Satellite radiolink
Fiber optic cables
Only fiber optic cables are not affected by crosstalk or interference.
For your exam you should know the information about transmission media:
Copper Cable
Copper cable is very simple to install and easy to tap. It is used mostly for short distance and supports voice and data.
Copper has been used in electric wiring since the invention of the electromagnet and the telegraph in the 1820s.The invention of the telephone in 1876 created further demand for copper wire as an electrical conductor.
Copper is the electrical conductor in many categories of electrical wiring. Copper wire is used in power generation, power transmission, power distribution, telecommunications, electronics circuitry, and countless types of electrical equipment. Copper and its alloys are also used to make electrical contacts. Electrical wiring in buildings is the most important market for the copper industry. Roughly half of all copper mined is used to manufacture electrical wire and cable conductors.
Copper Cable

Image Source -
Coaxial cable
Coaxial cable, or coax (pronounced 'ko.aks), is a type of cable that has an inner conductor surrounded by a tubular insulating layer, surrounded by a tubular conducting shield. Many coaxial cables also have an insulating outer sheath or jacket. The term coaxial comes from the inner conductor and the outer shield sharing a geometric axis. Coaxial cable was invented by English engineer and mathematician Oliver Heaviside, who patented the design in 1880.Coaxial cable differs from other shielded cable used for carrying lower-frequency signals, such as audio signals, in that the dimensions of the cable are controlled to give a precise, constant conductor spacing, which is needed for it to function efficiently as a radio frequency transmission line.
Coaxial cable are expensive and does not support many LAN's. It supports data and video
Coaxial Cable

Image Source -
Fiber optics
An optical fiber cable is a cable containing one or more optical fibers that are used to carry light. The optical fiber elements are typically individually coated with plastic layers and contained in a protective tube suitable for the environment where the cable will be deployed. Different types of cable are used for different applications, for example long distance telecommunication, or providing a high-speed data connection between different parts of a building.
Fiber optics used for long distance, hard to splice, not vulnerable to cross talk and difficult to tap. It supports voice data, image and video.
Radio System
Radio systems are used for short distance,cheap and easy to tap.
Radio is the radiation (wireless transmission) of electromagnetic signals through the atmosphere or free space.
Information, such as sound, is carried by systematically changing (modulating) some property of the radiated waves, such as their amplitude, frequency, phase, or pulse width. When radio waves strike an electrical conductor, the oscillating fields induce an alternating current in the conductor. The information in the waves can be extracted and transformed back into its original form.
Fiber Optics

Image Source -
Microwave radio system
Microwave transmission refers to the technology of transmitting information or energy by the use of radio waves whose wavelengths are conveniently measured in small numbers of centimetre; these are called microwaves.
Microwaves are widely used for point-to-point communications because their small wavelength allows conveniently-sized antennas to direct them in narrow beams, which can be pointed directly at the receiving antenna. This allows nearby microwave equipment to use the same frequencies without interfering with each other, as lower frequency radio waves do. Another advantage is that the high frequency of microwaves gives the microwave band a very large information-carrying capacity; the microwave band has a bandwidth 30 times that of all the rest of the radio spectrum below it. A disadvantage is that microwaves are limited to line of sight propagation; they cannot pass around hills or mountains as lower frequency radio waves can.
Microwave radio transmission is commonly used in point-to-point communication systems on the surface of the Earth, in satellite communications, and in deep space radio communications. Other parts of the microwave radio band are used for radars, radio navigation systems, sensor systems, and radio astronomy.
Microwave radio systems are carriers for voice data signal, cheap and easy to tap.
Microwave Radio System

Image Source -
Satellite Radio Link
Satellite radio is a radio service broadcast from satellites primarily to cars, with the signal broadcast nationwide, across a much wider geographical area than terrestrial radio stations. It is available by subscription, mostly commercial free, and offers subscribers more stations and a wider variety of programming options than terrestrial radio.
Satellite radio link uses transponder to send information and easy to tap.
The following answers are incorrect:
Copper Cable - Copper cable is very simple to install and easy to tap. It is used mostly for short distance and supports voice and data.
Radio System - Radio systems are used for short distance,cheap and easy to tap.
Satellite Radio Link - Satellite radio link uses transponder to send information and easy to tap.
The following reference(s) were/was used to create this question:
CISA review manual 2014 page number 265 &
Official ISC2 guide to CISSP CBK 3rd Edition Page number 233
Why are coaxial cables called "coaxial"?
it includes two physical channels that carries the signal surrounded (after a layer of insulation) by another concentric physical channel, both running along the same axis.
it includes one physical channel that carries the signal surrounded (after a layer of insulation) by another concentric physical channel, both running along the same axis
it includes two physical channels that carries the signal surrounded (after a layer of insulation) by another two concentric physical channels, both running along the same axis.
it includes one physical channel that carries the signal surrounded (after a layer of insulation) by another concentric physical channel, both running perpendicular and along the different axis
Coaxial cable is called "coaxial" because it includes one physical channel that carries the signal surrounded (after a layer of insulation) by another concentric physical channel, both running along the same axis.
The outer channel serves as a ground. Many of these cables or pairs of coaxial tubes can be placed in a single outer sheathing and, with repeaters, can carry information for a great distance.
Source: STEINER, Kurt, Telecommunications and Network Security, Version 1, May 2002, CISSP Open Study Group (Domain Leader: skottikus), Page 14.
What can a packet filtering firewall also be called?
a scanning router
a shielding router
a sniffing router
a screening router
While neither CBK nor AIO3 use the term "screening router," they both discuss how the packet filtering capabilities of a router can be used to block traffic much like a packet filtering firewall. Krutz and Vine use this term on p. 90.
"A scanning router" is incorrect. This is a nonsense term to distract you.
"A shielding router" is incorrect. This is a nonsense term to distract you.
"A sniffing router" is incorrect. This is a nonsense term to distract you.
References:
CBK, p. 433
AIO3, pp.484 - 485
In a stateful inspection firewall, data packets are captured by an inspection engine that is operating at the:
Network or Transport Layer.
Application Layer.
Inspection Layer.
Data Link Layer.
Most stateful packet inspection firewalls work at the network or transport layers. For the TCP/IP protcol, this allows the firewall to make decisions both on IP addresses, protocols and TCP/UDP port numbers
Application layer is incorrect. This is too high in the OSI stack for this type of firewall.
Inspection layer is incorrect. There is no such layer in the OSI stack.
"Data link layer" is incorrect. This is too low in the OSI stack for this type of firewall.
References:
CBK, p. 466
AIO3, pp. 485 - 486
What is NOT an authentication method within IKE and IPsec?
CHAP
Pre shared key
certificate based authentication
Public key authentication
CHAP is not used within IPSEC or IKE. CHAP is an authentication scheme used by Point to Point Protocol (PPP) servers to validate the identity of remote clients. CHAP periodically verifies the identity of the client by using a three-way handshake. This happens at the time of establishing the initial link (LCP), and may happen again at any time afterwards. The verification is based on a shared secret (such as the client user's password).
After the completion of the link establishment phase, the authenticator sends a "challenge" message to the peer.
The peer responds with a value calculated using a one-way hash function on the challenge and the secret combined.
The authenticator checks the response against its own calculation of the expected hash value. If the values match, the authenticator acknowledges the authentication; otherwise it should terminate the connection.
At random intervals the authenticator sends a new challenge to the peer and repeats steps 1 through 3.
The following were incorrect answers:
Pre Shared Keys
In cryptography, a pre-shared key or PSK is a shared secret which was previously shared between the two parties using some secure channel before it needs to be used. To build a key from shared secret, the key derivation function should be used. Such systems almost always use symmetric key cryptographic algorithms. The term PSK is used in WiFi encryption such as WEP or WPA, where both the wireless access points (AP) and all clients share the same key.
The characteristics of this secret or key are determined by the system which uses it; some system designs require that such keys be in a particular format. It can be a password like 'bret13i', a passphrase like 'Idaho hung gear id gene', or a hexadecimal string like '65E4 E556 8622 EEE1'. The secret is used by all systems involved in the cryptographic processes used to secure the traffic between the systems.
Certificat Based Authentication
The most common form of trusted authentication between parties in the wide world of Web commerce is the exchange of certificates. A certificate is a digital document that at a minimum includes a Distinguished Name (DN) and an associated public key.
The certificate is digitally signed by a trusted third party known as the Certificate Authority (CA). The CA vouches for the authenticity of the certificate holder. Each principal in the transaction presents certificate as its credentials. The recipient then validates the certificate’s signature against its cache of known and trusted CA certificates. A “personal
certificate” identifies an end user in a transaction; a “server certificate” identifies the service provider.
Generally, certificate formats follow the X.509 Version 3 standard. X.509 is part of the Open Systems Interconnect
(OSI) X.500 specification.
Public Key Authentication
Public key authentication is an alternative means of identifying yourself to a login server, instead of typing a password. It is more secure and more flexible, but more difficult to set up.
In conventional password authentication, you prove you are who you claim to be by proving that you know the correct password. The only way to prove you know the password is to tell the server what you think the password is. This means that if the server has been hacked, or spoofed an attacker can learn your password.
Public key authentication solves this problem. You generate a key pair, consisting of a public key (which everybody is allowed to know) and a private key (which you keep secret and do not give to anybody). The private key is able to generate signatures. A signature created using your private key cannot be forged by anybody who does not have a copy of that private key; but anybody who has your public key can verify that a particular signature is genuine.
So you generate a key pair on your own computer, and you copy the public key to the server. Then, when the server asks you to prove who you are, you can generate a signature using your private key. The server can verify that signature (since it has your public key) and allow you to log in. Now if the server is hacked or spoofed, the attacker does not gain your private key or password; they only gain one signature. And signatures cannot be re-used, so they have gained nothing.
There is a problem with this: if your private key is stored unprotected on your own computer, then anybody who gains access to your computer will be able to generate signatures as if they were you. So they will be able to log in to your server under your account. For this reason, your private key is usually encrypted when it is stored on your local machine, using a passphrase of your choice. In order to generate a signature, you must decrypt the key, so you have to type your passphrase.
References:
RFC 2409: The Internet Key Exchange (IKE); DORASWAMY, Naganand & HARKINS, Dan
Ipsec: The New Security Standard for the Internet, Intranets, and Virtual Private Networks, 1999, Prentice Hall PTR; SMITH, Richard E.
Internet Cryptography, 1997, Addison-Wesley Pub Co.; HARRIS, Shon, All-In-One CISSP Certification Exam Guide, 2001, McGraw-Hill/Osborne, page 467.
Which of the following type of traffic can easily be filtered with a stateful packet filter by enforcing the context or state of the request?
ICMP
TCP
UDP
IP
The question is explict in asking *easily*. With TCP connection establishment there is a distinct state or sequence that can be expected. Consult the references for further details.
ICMP, IP and UDP don't have any concept of a session; i.e. each packet or datagram is handled individually, with no reference to the contents of the previous one. With no sessions, these protocols usually cannot be filtered on the state of the session.
Some newer firewalls, however, simulate the concept of state for these protocols, and filter out unexpected packets based upon normal usage. Although these are commonly treated like normal stateful filters, they are more complex to program, and hence more prone to errors.
A stateful packet filter or stateful inspection inspects each packet and only allows known connection states through. So, if a SYN/ACK packet was recieved and there was not a prior SYN packet sent it would filter that packet and not let it in. The correct sequence of steps are known and if the sequence or state is incorrect then it is dropped.
The incorrect answers are:
ICMP. ICMP is basically stateless so you could not easily filter them based on the state or sequence.
UDP. UDP has no real state so you could only partially filter them based on the state or sequence. The question was explicit in asking easily. While it is possible, UDP is not the best answer.
IP. IP would refer to the Internet Protocol and as such is stateless so you would not be able to filter it out easily.
The following reference(s) were used for this question:
What layer of the ISO/OSI model do routers normally operate at?
Data link layer
Session layer
Transport layer
Network layer
Routers are switching devices that operate at the network layer (layer 3) by examining network addresses.
Source: KRUTZ, Ronald L. & VINES, Russel D., The CISSP Prep Guide: Mastering the Ten Domains of Computer Security, John Wiley & Sons, 2001, Chapter 3: Telecommunications and Network Security (page 111).
Which port does the Post Office Protocol Version 3 (POP3) make use of?
110
109
139
119
The other answers are not correct because of the following protocol/port numbers matrix:
Post Office Protocol (POP2) 109
Network News Transfer Protocol 119
NetBIOS 139
Which of the following can best eliminate dial-up access through a Remote Access Server as a hacking vector?
Using a TACACS+ server.
Installing the Remote Access Server outside the firewall and forcing legitimate users to authenticate to the firewall.
Setting modem ring count to at least 5.
Only attaching modems to non-networked hosts.
Containing the dial-up problem is conceptually easy: by installing the Remote Access Server outside the firewall and forcing legitimate users to authenticate to the firewall, any access to internal resources through the RAS can be filtered as would any other connection coming from the Internet.
The use of a TACACS+ Server by itself cannot eliminate hacking.
Setting a modem ring count to 5 may help in defeating war-dialing hackers who look for modem by dialing long series of numbers.
Attaching modems only to non-networked hosts is not practical and would not prevent these hosts from being hacked.
Source: STREBE, Matthew and PERKINS, Charles, Firewalls 24seven, Sybex 2000, Chapter 2: Hackers.
Which of the following is a token-passing scheme like token ring that also has a second ring that remains dormant until an error condition is detected on the primary ring?
Fiber Distributed Data Interface (FDDI).
Ethernet
Fast Ethernet
Broadband
FDDI is a token-passing ring scheme like a token ring, yet it also has a second ring that remains dormant until an error condition is detected on the primary ring.
Fiber Distributed Data Interface (FDDI) provides a 100 Mbit/s optical standard for data transmission in a local area network that can extend in range up to 200 kilometers (124 miles). Although FDDI logical topology is a ring-based token network, it does not use the IEEE 802.5 token ring protocol as its basis; instead, its protocol is derived from the IEEE 802.4 token bus timed token protocol. In addition to covering large geographical areas, FDDI local area networks can support thousands of users. As a standard underlying medium it uses optical fiber, although it can use copper cable, in which case it may be refer to as CDDI (Copper Distributed Data Interface). FDDI offers both a Dual-Attached Station (DAS), counter-rotating token ring topology and a Single-Attached Station (SAS), token bus passing ring topology.
Ethernet is a family of frame-based computer networking technologies for local area networks (LANs). The name came from the physical concept of the ether. It defines a number of wiring and signaling standards for the Physical Layer of the OSI networking model as well as a common addressing format and Media Access Control at the Data Link Layer.
In computer networking, Fast Ethernet is a collective term for a number of Ethernet standards that carry traffic at the nominal rate of 100 Mbit/s, against the original Ethernet speed of 10 Mbit/s. Of the fast Ethernet standards 100BASE-TX is by far the most common and is supported by the vast majority of Ethernet hardware currently produced. Fast Ethernet was introduced in 1995 and remained the fastest version of Ethernet for three years before being superseded by gigabit Ethernet.
Broadband in data can refer to broadband networks or broadband Internet and may have the same meaning as above, so that data transmission over a fiber optic cable would be referred to as broadband as compared to a telephone modem operating at 56,000 bits per second. However, a worldwide standard for what level of bandwidth and network speeds actually constitute Broadband have not been determined.[1]
Broadband in data communications is frequently used in a more technical sense to refer to data transmission where multiple pieces of data are sent simultaneously to increase the effective rate of transmission, regardless of data signaling rate. In network engineering this term is used for methods where two or more signals share a medium.[Broadband Internet access, often shortened to just broadband, is a high data rate Internet access—typically contrasted with dial-up access using a 56k modem.
Dial-up modems are limited to a bitrate of less than 56 kbit/s (kilobits per second) and require the full use of a telephone line—whereas broadband technologies supply more than double this rate and generally without disrupting telephone use.
Source:
KRUTZ, Ronald L. & VINES, Russel D., The CISSP Prep Guide: Mastering the Ten Domains of Computer Security, 2001, John Wiley & Sons, Page 72.
also see:
Which type of attack involves impersonating a user or a system?
Smurfing attack
Spoofing attack
Spamming attack
Sniffing attack
A spoofing attack is when an attempt is made to gain access to a computer system by posing as an authorized user or system. Spamming refers to sending out or posting junk advertising and unsolicited mail. A smurf attack is a type of denial-of-service attack using PING and a spoofed address. Sniffing refers to observing packets passing on a network.
Source: KRUTZ, Ronald L. & VINES, Russel D., The CISSP Prep Guide: Mastering the Ten Domains of Computer Security, John Wiley & Sons, 2001, Chapter 3: Telecommunications and Network Security (page 77).
Which of the following NAT firewall translation modes offers no protection from hacking attacks to an internal host using this functionality?
Network redundancy translation
Load balancing translation
Dynamic translation
Static translation
Static translation (also called port forwarding), assigns a fixed address to a specific internal network resource (usually a server).
Static NAT is required to make internal hosts available for connection from external hosts.
It merely replaces port information on a one-to-one basis. This affords no protection to statistically translated hosts: hacking attacks will be just as efficiently translated as any other valid connection attempt.
NOTE FROM CLEMENT:
Hiding Nat or Overloaded Nat is when you have a group of users behind a unique public IP address. This will provide you with some security through obscurity where an attacker scanning your network would see the unique IP address on the outside of the gateway but could not tell if there is one user, ten users, or hundreds of users behind that IP.
NAT was NEVER built as a security mechanism.
In the case of Static NAT used for some of your servers for example, your web server private IP is map to a valid external public IP on a one on one basis, your SMTP server private IP is mapped to a static public IP, and so on.
If an attacker scan the IP address range on the external side of the gateway he would discover every single one of your servers or any other hosts using static natting. Ports that are open, services that are listening, and all of this info could be gathered just as if the server was in fact using a public IP. It does not provide this security through obscurity mentioned above.
All of the other answer are incorrect.
Reference used for this question:
STREBE, Matthew and PERKINS, Charles, Firewalls 24seven, Sybex 2000, Chapter 7: Network Address Translation.
Which type of attack involves hijacking a session between a host and a target by predicting the target's choice of an initial TCP sequence number?
IP spoofing attack
SYN flood attack
TCP sequence number attack
Smurf attack
A TCP sequence number attack exploits the communication session which was established between the target and the trusted host that initiated the session. It involves hijacking the session between the host and the target by predicting the target's choice of an initial TCP sequence number. An IP spoofing attack is used to convince a system that it is communication with a known entity that gives an intruder access. It involves modifying the source address of a packet for a trusted source's address. A SYN attack is when an attacker floods a system with connection requests but does not respond when the target system replies to those requests. A smurf attack occurs when an attacker sends a spoofed (IP spoofing) PING (ICMP ECHO) packet to the broadcast address of a large network (the bounce site). The modified packet containing the address of the target system, all devices on its local network respond with a ICMP REPLY to the target system, which is then saturated with those replies.
Source: KRUTZ, Ronald L. & VINES, Russel D., The CISSP Prep Guide: Mastering the Ten Domains of Computer Security, John Wiley & Sons, 2001, Chapter 3: Telecommunications and Network Security (page 77).
What is the primary difference between FTP and TFTP?
Speed of negotiation
Authentication
Ability to automate
TFTP is used to transfer configuration files to and from network equipment.
TFTP (Trivial File Transfer Protocol) is sometimes used to transfer configuration files from equipments such as routers but the primary difference between FTP and TFTP is that TFTP does not require authentication. Speed and ability to automate are not important.
Both of these protocols (FTP and TFTP) can be used for transferring files across the Internet. The differences between the two protocols are explained below:
FTP is a complete, session-oriented, general purpose file transfer protocol. TFTP is used as a bare-bones special purpose file transfer protocol.
FTP can be used interactively. TFTP allows only unidirectional transfer of files.
FTP depends on TCP, is connection oriented, and provides reliable control. TFTP depends on UDP, requires less overhead, and provides virtually no control.
FTP provides user authentication. TFTP does not.
FTP uses well-known TCP port numbers: 20 for data and 21 for connection dialog. TFTP uses UDP port number 69 for its file transfer activity.
The Windows NT FTP server service does not support TFTP because TFTP does not support authentication.
Windows 95 and TCP/IP-32 for Windows for Workgroups do not include a TFTP client program.
Ref:
What ISO/OSI layer do switches primarily operate at?
Do take note that this question makes reference to a plain vanilla switch and not one of the smart switches that is available on the market today.
Physical layer
Network layer
Data link layer
Session layer
Switches primarily operate at the data link layer (layer 2), although intelligent, extremely fast Layer 3 switching techniques are being more frequently used.
Source: KRUTZ, Ronald L. & VINES, Russel D., The CISSP Prep Guide: Mastering the Ten Domains of Computer Security, John Wiley & Sons, 2001, Chapter 3: Telecommunications and Network Security (page 111).
Which of the following media is MOST resistant to EMI interference?
microwave
fiber optic
twisted pair
coaxial cable
A fiber optic cable is a physical medium that is capable of conducting modulated light trasmission. Fiber optic cable carries signals as light waves, thus creating higher trasmission speeds and greater distances due to less attenuation. This type of cabling is more difficult to tap than other cabling and is most resistant to interference, especially EMI.
Source: KRUTZ, Ronald L. & VINES, Russel D., The CISSP Prep Guide: Mastering the Ten Domains of Computer Security, John Wiley & Sons, 2001, Chapter 3: Telecommunications and Network Security (page 103).
What layer of the OSI/ISO model does Point-to-point tunnelling protocol (PPTP) work at?
Data link layer
Transport layer
Session layer
Network layer
PPTP operates at the data link layer (layer 2) of the OSI model and uses native PPP authentication and encryption services. Designed for individual client to server connections, it enables only a single point-to-point connection per session.
PPTP - Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol - extends the Point to Point Protocol (PPP) standard for traditional dial-up networking. PPTP is best suited for the remote access applications of VPNs, but it also supports LAN internetworking.
PPTP operates at Layer 2 of the OSI model.
Using PPTP
PPTP packages data within PPP packets, then encapsulates the PPP packets within IP packets (datagrams) for transmission through an Internet-based VPN tunnel. PPTP supports data encryption and compression of these packets. PPTP also uses a form of General Routing Encapsulation (GRE) to get data to and from its final destination.
Reference(s) used for this question:
KRUTZ, Ronald L. & VINES, Russel D., The CISSP Prep Guide: Mastering the Ten Domains of Computer Security, John Wiley & Sons, 2001, Chapter 3: Telecommunications and Network Security (page 95).
and
and
In an organization, an Information Technology security function should:
Be a function within the information systems function of an organization.
Report directly to a specialized business unit such as legal, corporate security or insurance.
Be lead by a Chief Security Officer and report directly to the CEO.
Be independent but report to the Information Systems function.
In order to offer more independence and get more attention from management, an IT security function should be independent from IT and report directly to the CEO. Having it report to a specialized business unit (e.g. legal) is not recommended as it promotes a low technology view of the function and leads people to believe that it is someone else's problem.
Source: HARE, Chris, Security management Practices CISSP Open Study Guide, version 1.0, april 1999.
Related to information security, integrity is the opposite of which of the following?
abstraction
alteration
accreditation
application
Integrity is the opposite of "alteration."
Source: KRUTZ, Ronald L. & VINES, Russel D., The CISSP Prep Guide: Mastering the Ten Domains of Computer Security, 2001, John Wiley & Sons, Page 59.
Which of the following embodies all the detailed actions that personnel are required to follow?
Standards
Guidelines
Procedures
Baselines
Procedures are step-by-step instructions in support of of the policies, standards, guidelines and baselines. The procedure indicates how the policy will be implemented and who does what to accomplish the tasks."
Standards is incorrect. Standards are a "Mandatory statement of minimum requirements that support some part of a policy, the standards in this case is your own company standards and not standards such as the ISO standards"
Guidelines is incorrect. "Guidelines are discretionary or optional controls used to enable individuals to make judgments with respect to security actions."
Baselines is incorrect. Baselines "are a minimum acceptable level of security. This minimum is implemented using specific rules necessary to implement the security controls in support of the policy and standards." For example, requiring a password of at leat 8 character would be an example. Requiring all users to have a minimun of an antivirus, a personal firewall, and an anti spyware tool could be another example.
References:
CBK, pp. 12 - 16. Note especially the discussion of the "hammer policy" on pp. 16-17 for the differences between policy, standard, guideline and procedure.
AIO3, pp. 88-93.
Memory management in TCSEC levels B3 and A1 operating systems may utilize "data hiding". What does this mean?
System functions are layered, and none of the functions in a given layer can access data outside that layer.
Auditing processes and their memory addresses cannot be accessed by user processes.
Only security processes are allowed to write to ring zero memory.
It is a form of strong encryption cipher.
Data Hiding is protecting data so that it is only available to higher levels this is done and is also performed by layering, when the software in each layer maintains its own global data and does not directly reference data outside its layers.
The following answers are incorrect:
Auditing processes and their memory addresses cannot be accessed by user processes. Is incorrect because this does not offer data hiding.
Only security processes are allowed to write to ring zero memory. This is incorrect, the security kernel would be responsible for this.
It is a form of strong encryption cipher. Is incorrect because this does not conform to the definition of data hiding.
Why does compiled code pose more of a security risk than interpreted code?
Because malicious code can be embedded in compiled code and be difficult to detect.
If the executed compiled code fails, there is a chance it will fail insecurely.
Because compilers are not reliable.
There is no risk difference between interpreted code and compiled code.
From a security standpoint, a compiled program is less desirable than an interpreted one because malicious code can be
resident somewhere in the compiled code, and it is difficult to detect in a very large program.
A trusted system does NOT involve which of the following?
Enforcement of a security policy.
Sufficiency and effectiveness of mechanisms to be able to enforce a security policy.
Assurance that the security policy can be enforced in an efficient and reliable manner.
Independently-verifiable evidence that the security policy-enforcing mechanisms are sufficient and effective.
A trusted system is one that meets its intended security requirements. It involves sufficiency and effectiveness, not necessarily efficiency, in enforcing a security policy. Put succinctly, trusted systems have (1) policy, (2) mechanism, and (3) assurance.
Source: HARE, Chris, Security Architecture and Models, Area 6 CISSP Open Study Guide, January 2002.
According to private sector data classification levels, how would salary levels and medical information be classified?
Public.
Internal Use Only.
Restricted.
Confidential.
Typically there are three to four levels of information classification used by most organizations:
Confidential: Information that, if released or disclosed outside of the organization, would create severe problems for the organization. For example, information that provides a competitive advantage is important to the technical or financial success (like trade secrets, intellectual property, or research designs), or protects the privacy of individuals would be considered confidential. Information may include payroll information, health records, credit information, formulas, technical designs, restricted regulatory information, senior management internal correspondence, or business strategies or plans. These may also be called top secret, privileged, personal, sensitive, or highly confidential. In other words this information is ok within a defined group in the company such as marketing or sales, but is not suited for release to anyone else in the company without permission.
The following answers are incorrect:
Public: Information that may be disclosed to the general public without concern for harming the company, employees, or business partners. No special protections are required, and information in this category is sometimes referred to as unclassified. For example, information that is posted to a company’s public Internet site, publicly released announcements, marketing materials, cafeteria menus, and any internal documents that would not present harm to the company if they were disclosed would be classified as public. While there is little concern for confidentiality, integrity and availability should be considered.
Internal Use Only: Information that could be disclosed within the company, but could harm the company if disclosed externally. Information such as customer lists, vendor pricing, organizational policies, standards and procedures, and internal organization announcements would need baseline security protections, but do not rise to the level of protection as confidential information. In other words, the information may be used freely within the company but any unapproved use outside the company can pose a chance of harm.
Restricted: Information that requires the utmost protection or, if discovered by unauthorized personnel, would cause irreparable harm to the organization would have the highest level of classification. There may be very few pieces of information like this within an organization, but data classified at this level requires all the access control and protection mechanisms available to the organization. Even when information classified at this level exists, there will be few copies of it
Reference(s) Used for this question:
Hernandez CISSP, Steven (2012-12-21). Official (ISC)2 Guide to the CISSP CBK, Third Edition ((ISC)2 Press) (Kindle Locations 952-976). Auerbach Publications. Kindle Edition.
Which of the following is the MOST important aspect relating to employee termination?
The details of employee have been removed from active payroll files.
Company property provided to the employee has been returned.
User ID and passwords of the employee have been deleted.
The appropriate company staff are notified about the termination.
Even though Logical access to information by a terminated employee is possible if the ID and password of the terminated employee has not been deleted this is only one part of the termination procedures. If user ID is not disabled or deleted, it could be possible for the employee without physical access to visit the companies networks remotely and gain access to the information.
Please note that this can also be seen in a different way: the most important thing to do could also be to inform others of the person's termination, because even if user ID's and passwords are deleted, a terminated individual could simply socially engineer their way back in by calling an individual he/she used to work with and ask them for access. He could intrude on the facility or use other weaknesses to gain access to information after he has been terminated.
By notifying the appropriate company staff about the termination, they would in turn intitiate account termination, ask the employee to return company property, and all credentials would be withdrawn for the individual concerned. This answer is more complete than simply disabling account.
It seems harsh and cold when this actually takes place , but too many companies have been hurt by vengeful employees who have lashed out at the company when their positions were revoked for one reason or another. If an employee is disgruntled in any way, or the termination is unfriendly, that employee’s accounts should be disabled right away, and all passwords on all systems changed.
For your exam you should know the information below:
Employee Termination Processes
Employees join and leave organizations every day. The reasons vary widely, due to retirement,reduction in force, layoffs, termination with or without cause, relocation to another city, careeropportunities with other employers, or involuntary transfers. Terminations may be friendly or unfriendly and will need different levels of care as a result.
Friendly Terminations
Regular termination is when there is little or no evidence or reason to believe that the termination is not agreeable to both the company and the employee. A standard set of procedures, typically maintained by the human resources department, governs the dismissal of the terminated employee to ensure that company property is returned, and all access is removed. These procedures may include exit interviews and return of keys, identification cards, badges, tokens, and cryptographic keys. Other property, such as laptops, cable locks, credit cards, and phone cards, are also collected. The user manager notifies the security department of the termination to ensure that access is revoked for all platforms and facilities. Some facilities choose to immediately delete the accounts, while others choose to disable the accounts for a policy defined period, for example, 30 days, to account for changes or extensions in the final termination date. The termination process should include a conversation with the departing associate about their continued responsibility for confidentiality of information.
Unfriendly Terminations
Unfriendly terminations may occur when the individual is fired, involuntarily transferred, laid off,or when the organization has reason to believe that the individual has the means and intention to potentially cause harm to the system. Individuals with technical skills and higher levels of access, such as the systems administrators, computer programmers, database administrators, or any individual with elevated privileges, may present higher risk to the environment. These individuals could alter files, plant logic bombs to create system file damage at a future date, or remove sensitive information. Other disgruntled users could enter erroneous data into the system that may not be discovered for several months. In these situations, immediate termination of systems access is warranted at the time of termination or prior to notifying the employee of the termination. Managing the people aspect of security, from pre-employment to postemployment, is critical to ensure that trustworthy, competent resources are employed to further the business objectives that will protect company information. Each of these actions contributes to preventive, detective, or corrective personnel controls.
The following answers are incorrect:
The other options are less important.
Following reference(s) were/was used to create this question:
CISA review manual 2014 Page number 99
Harris, Shon (2012-10-18). CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide, 6th Edition (p. 129). McGraw-Hill. Kindle Edition.
What can be described as an imaginary line that separates the trusted components of the TCB from those elements that are NOT trusted?
The security kernel
The reference monitor
The security perimeter
The reference perimeter
The security perimeter is the imaginary line that separates the trusted components of the kernel and the Trusted Computing Base (TCB) from those elements that are not trusted. The reference monitor is an abstract machine that mediates all accesses to objects by subjects. The security kernel can be software, firmware or hardware components in a trusted system and is the actual instantiation of the reference monitor. The reference perimeter is not defined and is a distracter.
Source: HARE, Chris, Security Architecture and Models, Area 6 CISSP Open Study Guide, January 2002.
Which of the following can be used as a covert channel?
Storage and timing.
Storage and low bits.
Storage and permissions.
Storage and classification.
The Orange book requires protection against two types of covert channels, Timing and Storage.
The following answers are incorrect:
Storage and low bits. Is incorrect because, low bits would not be considered a covert channel.
Storage and permissions. Is incorrect because, permissions would not be considered a covert channel.
Storage and classification. Is incorrect because, classification would not be considered a covert channel.
A Security Kernel is defined as a strict implementation of a reference monitor mechanism responsible for enforcing a security policy. To be secure, the kernel must meet three basic conditions, what are they?
Confidentiality, Integrity, and Availability
Policy, mechanism, and assurance
Isolation, layering, and abstraction
Completeness, Isolation, and Verifiability
A security kernel is responsible for enforcing a security policy. It is a strict implementation of a reference monitor mechanism. The architecture of a kernel operating system is typically layered, and the kernel should be at the lowest and most primitive level.
It is a small portion of the operating system through which all references to information and all changes to authorizations must pass. In theory, the kernel implements access control and information flow control between implemented objects according to the security policy.
To be secure, the kernel must meet three basic conditions:
completeness (all accesses to information must go through the kernel),
isolation (the kernel itself must be protected from any type of unauthorized access),
and verifiability (the kernel must be proven to meet design specifications).
The reference monitor, as noted previously, is an abstraction, but there may be a reference validator, which usually runs inside the security kernel and is responsible for performing security access checks on objects, manipulating privileges, and generating any resulting security audit messages.
A term associated with security kernels and the reference monitor is the trusted computing base (TCB). The TCB is the portion of a computer system that contains all elements of the system responsible for supporting the security policy and the isolation of objects. The security capabilities of products for use in the TCB can be verified through various evaluation criteria, such as the earlier Trusted Computer System Evaluation Criteria (TCSEC) and the current Common Criteria standard.
Many of these security terms—reference monitor, security kernel, TCB—are defined loosely by vendors for purposes of marketing literature. Thus, it is necessary for security professionals to read the small print and between the lines to fully understand what the vendor is offering in regard to security features.
TIP FOR THE EXAM:
The terms Security Kernel and Reference monitor are synonymous but at different levels.
As it was explained by Diego:
While the Reference monitor is the concept, the Security kernel is the implementation of such concept (via hardware, software and firmware means).
The two terms are the same thing, but on different levels: one is conceptual, one is "technical"
The following are incorrect answers:
Confidentiality, Integrity, and Availability
Policy, mechanism, and assurance
Isolation, layering, and abstraction
Reference(s) used for this question:
Hernandez CISSP, Steven (2012-12-21). Official (ISC)2 Guide to the CISSP CBK, Third Edition ((ISC)2 Press) (Kindle Locations 13858-13875). Auerbach Publications. Kindle Edition.
Which of the following is NOT an administrative control?
Logical access control mechanisms
Screening of personnel
Development of policies, standards, procedures and guidelines
Change control procedures
It is considered to be a technical control.
Logical is synonymous with Technical Control. That was the easy answer.
There are three broad categories of access control: Administrative, Technical, and Physical.
Each category has different access control mechanisms that can be carried out manually or automatically. All of these access control mechanisms should work in concert with each other to protect an infrastructure and its data.
Each category of access control has several components that fall within it, as shown here:
Administrative Controls
• Policy and procedures
• Personnel controls
• Supervisory structure
• Security-awareness training
• Testing
Physical Controls
Network segregation
Perimeter security
Computer controls
Work area separation
Data backups
Technical Controls
System access
Network architecture
Network access
Encryption and protocols
Control zone
Auditing
The following answers are incorrect :
Screening of personnel is considered to be an administrative control
Development of policies, standards, procedures and guidelines is considered to be an administrative control
Change control procedures is considered to be an administrative control.
Reference : Shon Harris AIO v3 , Chapter - 3 : Security Management Practices , Page : 52-54
Preservation of confidentiality within information systems requires that the information is not disclosed to:
Authorized person
Unauthorized persons or processes.
Unauthorized persons.
Authorized persons and processes
Confidentiality assures that the information is not disclosed to unauthorized persons or processes.
Source: KRUTZ, Ronald L. & VINES, Russel D., The CISSP Prep Guide: Mastering the Ten Domains of Computer Security, 2001, John Wiley & Sons, Page 31.
What can best be defined as high-level statements, beliefs, goals and objectives?
Standards
Policies
Guidelines
Procedures
Policies are high-level statements, beliefs, goals and objectives and the general means for their attainment for a specific subject area. Standards are mandatory activities, action, rules or regulations designed to provide policies with the support structure and specific direction they require to be effective. Guidelines are more general statements of how to achieve the policies objectives by providing a framework within which to implement procedures. Procedures spell out the specific steps of how the policy and supporting standards and how guidelines will be implemented.
Source: HARE, Chris, Security management Practices CISSP Open Study Guide, version 1.0, april 1999.
Making sure that the data has not been changed unintentionally, due to an accident or malice is:
Integrity.
Confidentiality.
Availability.
Auditability.
Integrity refers to the protection of information from unauthorized modification or deletion.
Confidentiality is incorrect. Confidentiality refers to the protection of information from unauthorized disclosure.
Availability is incorrect. Availability refers to the assurance that information and services will be available to authorized users in accordance with the service level objective.
Auditability is incorrect. Auditability refers to the ability to trace an action to the identity that performed it and identify the date and time at which it occurred.
References:
CBK, pp. 5 - 6
AIO3, pp. 56 - 57
A channel within a computer system or network that is designed for the authorized transfer of information is identified as a(n)?
Covert channel
Overt channel
Opened channel
Closed channel
An overt channel is a path within a computer system or network that is designed for the authorized transfer of data. The opposite would be a covert channel which is an unauthorized path.
A covert channel is a way for an entity to receive information in an unauthorized manner. It is an information flow that is not controlled by a security mechanism. This type of information path was not developed for communication; thus, the system does not properly protect this path, because the developers never envisioned information being passed in this way. Receiving information in this manner clearly violates the system’s security policy.
All of the other choices are bogus detractors.
Reference(s) used for this question:
KRUTZ, Ronald L. & VINES, Russel D., The CISSP Prep Guide: Mastering the Ten Domains of Computer Security, 2001, John Wiley & Sons, Page 219.
and
Shon Harris, CISSP All In One (AIO), 6th Edition , page 380
and
Harris, Shon (2012-10-25). CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide, 6th Edition (p. 378). McGraw-Hill. Kindle Edition.
Which of the following would best describe the difference between white-box testing and black-box testing?
White-box testing is performed by an independent programmer team.
Black-box testing uses the bottom-up approach.
White-box testing examines the program internal logical structure.
Black-box testing involves the business units
Black-box testing observes the system external behavior, while white-box testing is a detailed exam of a logical path, checking the possible conditions.
Source: Information Systems Audit and Control Association, Certified Information Systems Auditor 2002 review manual, chapter 6: Business Application System Development, Acquisition, Implementation and Maintenance (page 299).
The information security staff's participation in which of the following system development life cycle phases provides maximum benefit to the organization?
project initiation and planning phase
system design specifications phase
development and documentation phase
in parallel with every phase throughout the project
The other answers are not correct because:
You are always looking for the "best" answer. While each of the answers listed here could be considered correct in that each of them require input from the security staff, the best answer is for that input to happen at all phases of the project.
Making sure that only those who are supposed to access the data can access is which of the following?
confidentiality.
capability.
integrity.
availability.
From the published (ISC)2 goals for the Certified Information Systems Security Professional candidate, domain definition. Confidentiality is making sure that only those who are supposed to access the data can access it.
Source: KRUTZ, Ronald L. & VINES, Russel D., The CISSP Prep Guide: Mastering the Ten Domains of Computer Security, 2001, John Wiley & Sons, Page 59.
Which of the following is used in database information security to hide information?
Inheritance
Polyinstantiation
Polymorphism
Delegation
Polyinstantiation enables a relation to contain multiple tuples with the same primary keys with each instance distinguished by a security level. When this information is inserted into a database, lower-level subjects need to be restricted from this information. Instead of just restricting access, another set of data is created to fool the lower-level subjects into thinking that the information actually means something else.
Source: HARRIS, Shon, All-In-One CISSP Certification Exam Guide, McGraw-Hill/Osborne, 2002, chapter 11: Application and System Development (page 727).
Which of the following phases of a system development life-cycle is most concerned with maintaining proper authentication of users and processes to ensure appropriate access control decisions?
Development/acquisition
Implementation
Operation/Maintenance
Initiation
The operation phase of an IT system is concerned with user authentication.
Authentication is the process where a system establishes the validity of a transmission, message, or a means of verifying the eligibility of an individual, process, or machine to carry out a desired action, thereby ensuring that security is not compromised by an untrusted source.
It is essential that adequate authentication be achieved in order to implement security policies and achieve security goals. Additionally, level of trust is always an issue when dealing with cross-domain interactions. The solution is to establish an authentication policy and apply it to cross-domain interactions as required.
Source: STONEBURNER, Gary & al, National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), NIST Special Publication 800-27, Engineering Principles for Information Technology Security (A Baseline for Achieving Security), June 2001 (page 15).
As per the Orange Book, what are two types of system assurance?
Operational Assurance and Architectural Assurance.
Design Assurance and Implementation Assurance.
Architectural Assurance and Implementation Assurance.
Operational Assurance and Life-Cycle Assurance.
Are the two types of assurance mentioned in the Orange book.
The following answers are incorrect:
Operational Assurance and Architectural Assurance. Is incorrect because Architectural Assurance is not a type of assurance mentioned in the Orange book.
Design Assurance and Implementation Assurance. Is incorrect because neither are types of assurance mentioned in the Orange book.
Architectural Assurance and Implementation Assurance. Is incorrect because neither are types of assurance mentioned in the Orange book.
Which of the following test makes sure the modified or new system includes appropriate access controls and does not introduce any security holes that might compromise other systems?
Recovery testing
Security testing
Stress/volume testing
Interface testing
Security testing makes sure the modified or new system includes appropriate access controls and does not introduce any security holes that might compromise other systems.
Recovery testing checks the system's ability to recover after a software or hardware failure.
Stress/volume testing involves testing an application with large quantities of data in order to evaluate performance during peak hours.
Interface testing evaluates the connection of two or more components that pass information from one area to another.
Source: Information Systems Audit and Control Association, Certified Information Systems Auditor 2002 review manual, Chapter 6: Business Application System Development, Acquisition, Implementation and Maintenance (page 300).
Java is not:
Object-oriented.
Distributed.
Architecture Specific.
Multithreaded.
JAVA was developed so that the same program could be executed on multiple hardware and operating system platforms, it is not Architecture Specific.
The following answers are incorrect:
Object-oriented. Is not correct because JAVA is object-oriented. It should use the object-oriented programming methodology.
Distributed. Is incorrect because JAVA was developed to be able to be distrubuted, run on multiple computer systems over a network.
Multithreaded. Is incorrect because JAVA is multi-threaded that is calls to subroutines as is the case with object-oriented programming.
A virus is a program that can replicate itself on a system but not necessarily spread itself by network connections.
What best describes a scenario when an employee has been shaving off pennies from multiple accounts and depositing the funds into his own bank account?
Data fiddling
Data diddling
Salami techniques
Trojan horses
Source: HARRIS, Shon, All-In-One CISSP Certification Exam Guide, McGraw-Hill/Osborne, 2001, Page 644.
What do the ILOVEYOU and Melissa virus attacks have in common?
They are both denial-of-service (DOS) attacks.
They have nothing in common.
They are both masquerading attacks.
They are both social engineering attacks.
While a masquerading attack can be considered a type of social engineering, the Melissa and ILOVEYOU viruses are examples of masquerading attacks, even if it may cause some kind of denial of service due to the web server being flooded with messages. In this case, the receiver confidently opens a message coming from a trusted individual, only to find that the message was sent using the trusted party's identity.
Source: HARRIS, Shon, All-In-One CISSP Certification Exam Guide, McGraw-Hill/Osborne, 2002, Chapter 10: Law, Investigation, and Ethics (page 650).
In computing what is the name of a non-self-replicating type of malware program containing malicious code that appears to have some useful purpose but also contains code that has a malicious or harmful purpose imbedded in it, when executed, carries out actions that are unknown to the person installing it, typically causing loss or theft of data, and possible system harm.
virus
worm
Trojan horse.
trapdoor
A trojan horse is any code that appears to have some useful purpose but also contains code that has a malicious or harmful purpose imbedded in it. A Trojan often also includes a trapdoor as a means to gain access to a computer system bypassing security controls.
Wikipedia defines it as:
A Trojan horse, or Trojan, in computing is a non-self-replicating type of malware program containing malicious code that, when executed, carries out actions determined by the nature of the Trojan, typically causing loss or theft of data, and possible system harm. The term is derived from the story of the wooden horse used to trick defenders of Troy into taking concealed warriors into their city in ancient Greece, because computer Trojans often employ a form of social engineering, presenting themselves as routine, useful, or interesting in order to persuade victims to install them on their computers.
The following answers are incorrect:
virus. Is incorrect because a Virus is a malicious program and is does not appear to be harmless, it's sole purpose is malicious intent often doing damage to a system. A computer virus is a type of malware that, when executed, replicates by inserting copies of itself (possibly modified) into other computer programs, data files, or the boot sector of the hard drive; when this replication succeeds, the affected areas are then said to be "infected".
worm. Is incorrect because a Worm is similiar to a Virus but does not require user intervention to execute. Rather than doing damage to the system, worms tend to self-propagate and devour the resources of a system. A computer worm is a standalone malware computer program that replicates itself in order to spread to other computers. Often, it uses a computer network to spread itself, relying on security failures on the target computer to access it. Unlike a computer virus, it does not need to attach itself to an existing program. Worms almost always cause at least some harm to the network, even if only by consuming bandwidth, whereas viruses almost always corrupt or modify files on a targeted computer.
trapdoor. Is incorrect because a trapdoor is a means to bypass security by hiding an entry point into a system. Trojan Horses often have a trapdoor imbedded in them.
References:
and
and
and
What is malware that can spread itself over open network connections?
Worm
Rootkit
Adware
Logic Bomb
Computer worms are also known as Network Mobile Code, or a virus-like bit of code that can replicate itself over a network, infecting adjacent computers.
A computer worm is a standalone malware computer program that replicates itself in order to spread to other computers. Often, it uses a computer network to spread itself, relying on security failures on the target computer to access it. Unlike a computer virus, it does not need to attach itself to an existing program. Worms almost always cause at least some harm to the network, even if only by consuming bandwidth, whereas viruses almost always corrupt or modify files on a targeted computer.
A notable example is the SQL Slammer computer worm that spread globally in ten minutes on January 25, 2003. I myself came to work that day as a software tester and found all my SQL servers infected and actively trying to infect other computers on the test network.
A patch had been released a year prior by Microsoft and if systems were not patched and exposed to a 376 byte UDP packet from an infected host then system would become compromised.
Ordinarily, infected computers are not to be trusted and must be rebuilt from scratch but the vulnerability could be mitigated by replacing a single vulnerable dll called sqlsort.dll.
Replacing that with the patched version completely disabled the worm which really illustrates to us the importance of actively patching our systems against such network mobile code.
The following answers are incorrect:
- Rootkit: Sorry, this isn't correct because a rootkit isn't ordinarily classified as network mobile code like a worm is. This isn't to say that a rootkit couldn't be included in a worm, just that a rootkit isn't usually classified like a worm. A rootkit is a stealthy type of software, typically malicious, designed to hide the existence of certain processes or programs from normal methods of detection and enable continued privileged access to a computer. The term rootkit is a concatenation of "root" (the traditional name of the privileged account on Unix operating systems) and the word "kit" (which refers to the software components that implement the tool). The term "rootkit" has negative connotations through its association with malware.
- Adware: Incorrect answer. Sorry but adware isn't usually classified as a worm. Adware, or advertising-supported software, is any software package which automatically renders advertisements in order to generate revenue for its author. The advertisements may be in the user interface of the software or on a screen presented to the user during the installation process. The functions may be designed to analyze which Internet sites the user visits and to present advertising pertinent to the types of goods or services featured there. The term is sometimes used to refer to software that displays unwanted advertisements.
- Logic Bomb: Logic bombs like adware or rootkits could be spread by worms if they exploit the right service and gain root or admin access on a computer.
The following reference(s) was used to create this question:
The CCCure CompTIA Holistic Security+ Tutorial and CBT
and
and
and
The high availability of multiple all-inclusive, easy-to-use hacking tools that do NOT require much technical knowledge has brought a growth in the number of which type of attackers?
Black hats
White hats
Script kiddies
Phreakers
As script kiddies are low to moderately skilled hackers using available scripts and tools to easily launch attacks against victims.
The other answers are incorrect because :
Black hats is incorrect as they are malicious , skilled hackers.
White hats is incorrect as they are security professionals.
Phreakers is incorrect as they are telephone/PBX (private branch exchange) hackers.
Reference : Shon Harris AIO v3 , Chapter 12: Operations security , Page : 830
Virus scanning and content inspection of SMIME encrypted e-mail without doing any further processing is:
Not possible
Only possible with key recovery scheme of all user keys
It is possible only if X509 Version 3 certificates are used
It is possible only by "brute force" decryption
Content security measures presumes that the content is available in cleartext on the central mail server.
Encrypted emails have to be decrypted before it can be filtered (e.g. to detect viruses), so you need the decryption key on the central "crypto mail server".
There are several ways for such key management, e.g. by message or key recovery methods. However, that would certainly require further processing in order to achieve such goal.
Which of the following computer crime is MORE often associated with INSIDERS?
IP spoofing
Password sniffing
Data diddling
Denial of service (DOS)
It refers to the alteration of the existing data , most often seen before it is entered into an application.This type of crime is extremely common and can be prevented by using appropriate access controls and proper segregation of duties. It will more likely be perpetrated by insiders, who have access to data before it is processed.
The other answers are incorrect because :
IP Spoofing is not correct as the questions asks about the crime associated with the insiders. Spoofing is generally accomplished from the outside.
Password sniffing is also not the BEST answer as it requires a lot of technical knowledge in understanding the encryption and decryption process.
Denial of service (DOS) is also incorrect as most Denial of service attacks occur over the internet.
Reference : Shon Harris , AIO v3 , Chapter-10 : Law , Investigation & Ethics , Page : 758-760.
Which virus category has the capability of changing its own code, making it harder to detect by anti-virus software?
Stealth viruses
Polymorphic viruses
Trojan horses
Logic bombs
A polymorphic virus has the capability of changing its own code, enabling it to have many different variants, making it harder to detect by anti-virus software. The particularity of a stealth virus is that it tries to hide its presence after infecting a system. A Trojan horse is a set of unauthorized instructions that are added to or replacing a legitimate program. A logic bomb is a set of instructions that is initiated when a specific event occurs.
Source: HARRIS, Shon, All-In-One CISSP Certification Exam Guide, McGraw-Hill/Osborne, 2002, chapter 11: Application and System Development (page 786).
Crackers today are MOST often motivated by their desire to:
Help the community in securing their networks.
Seeing how far their skills will take them.
Getting recognition for their actions.
Gaining Money or Financial Gains.
A few years ago the best choice for this question would have been seeing how far their skills can take them. Today this has changed greatly, most crimes committed are financially motivated.
Profit is the most widespread motive behind all cybercrimes and, indeed, most crimes- everyone wants to make money. Hacking for money or for free services includes a smorgasbord of crimes such as embezzlement, corporate espionage and being a “hacker for hire”. Scams are easier to undertake but the likelihood of success is much lower. Money-seekers come from any lifestyle but those with persuasive skills make better con artists in the same way as those who are exceptionally tech-savvy make better “hacks for hire”.
"White hats" are the security specialists (as opposed to Black Hats) interested in helping the community in securing their networks. They will test systems and network with the owner authorization.
A Black Hat is someone who uses his skills for offensive purpose. They do not seek authorization before they attempt to comprise the security mechanisms in place.
"Grey Hats" are people who sometimes work as a White hat and other times they will work as a "Black Hat", they have not made up their mind yet as to which side they prefer to be.
The following are incorrect answers:
All the other choices could be possible reasons but the best one today is really for financial gains.
References used for this question:
and
and
Which of the following technologies is a target of XSS or CSS (Cross-Site Scripting) attacks?
Web Applications
Intrusion Detection Systems
Firewalls
DNS Servers
XSS or Cross-Site Scripting is a threat to web applications where malicious code is placed on a website that attacks the use using their existing authenticated session status.
Cross-Site Scripting attacks are a type of injection problem, in which malicious scripts are injected into the otherwise benign and trusted web sites. Cross-site scripting (XSS) attacks occur when an attacker uses a web application to send malicious code, generally in the form of a browser side script, to a different end user. Flaws that allow these attacks to succeed are quite widespread and occur anywhere a web application uses input from a user in the output it generates without validating or encoding it.
An attacker can use XSS to send a malicious script to an unsuspecting user. The end user’s browser has no way to know that the script should not be trusted, and will execute the script. Because it thinks the script came from a trusted source, the malicious script can access any cookies, session tokens, or other sensitive information retained by your browser and used with that site. These scripts can even rewrite the content of the HTML page.
Mitigation:
Configure your IPS - Intrusion Prevention System to detect and suppress this traffic.
Input Validation on the web application to normalize inputted data.
Set web apps to bind session cookies to the IP Address of the legitimate user and only permit that IP Address to use that cookie.
See the XSS (Cross Site Scripting) Prevention Cheat Sheet
See the Abridged XSS Prevention Cheat Sheet
See the DOM based XSS Prevention Cheat Sheet
See the OWASP Development Guide article on Phishing.
See the OWASP Development Guide article on Data Validation.
The following answers are incorrect:
Intrusion Detection Systems: Sorry. IDS Systems aren't usually the target of XSS attacks but a properly-configured IDS/IPS can "detect and report on malicious string and suppress the TCP connection in an attempt to mitigate the threat.
Firewalls: Sorry. Firewalls aren't usually the target of XSS attacks.
DNS Servers: Same as above, DNS Servers aren't usually targeted in XSS attacks but they play a key role in the domain name resolution in the XSS attack process.
The following reference(s) was used to create this question:
CCCure Holistic Security+ CBT and Curriculum
and
Which of the following virus types changes some of its characteristics as it spreads?
Boot Sector
Parasitic
Stealth
Polymorphic
A Polymorphic virus produces varied but operational copies of itself in hopes of evading anti-virus software.
The following answers are incorrect:
boot sector. Is incorrect because it is not the best answer. A boot sector virus attacks the boot sector of a drive. It describes the type of attack of the virus and not the characteristics of its composition.
parasitic. Is incorrect because it is not the best answer. A parasitic virus attaches itself to other files but does not change its characteristics.
stealth. Is incorrect because it is not the best answer. A stealth virus attempts to hide changes of the affected files but not itself.
Which of the following assertions is NOT true about pattern matching and anomaly detection in intrusion detection?
Anomaly detection tends to produce more data
A pattern matching IDS can only identify known attacks
Stateful matching scans for attack signatures by analyzing individual packets instead of traffic streams
An anomaly-based engine develops baselines of normal traffic activity and throughput, and alerts on deviations from these baselines
This is wrong which makes this the correct choice. This statement is not true as stateful matching scans for attack signatures by analyzing traffic streams rather than individual packets. Stateful matching intrusion detection takes pattern matching to the next level.
As networks become faster there is an emerging need for security analysis techniques that can keep up with the increased network throughput. Existing network-based intrusion detection sensors can barely keep up with bandwidths of a few hundred Mbps. Analysis tools that can deal with higher throughput are unable to maintain state between different steps of an attack or they are limited to the analysis of packet headers.
The following answers are all incorrect:
Anomaly detection tends to produce more data is true as an anomaly-based IDS produces a lot of data as any activity outside of expected behavior is recorded.
A pattern matching IDS can only identify known attacks is true as a pattern matching IDS works by comparing traffic streams against signatures. These signatures are created for known attacks.
An anomaly-based engine develops baselines of normal traffic activity and throughput, and alerts on deviations from these baselines is true as the assertion is a characteristic of a statistical anomaly-based IDS.
Which of the following is NOT a transaction redundancy implementation?
on-site mirroring
Electronic Vaulting
Remote Journaling
Database Shadowing
Three concepts are used to create a level of fault tolerance and redundancy in transaction processing.
They are Electronic vaulting, remote journaling and database shadowing provide redundancy at the transaction level.
Electronic vaulting is accomplished by backing up system data over a network. The backup location is usually at a separate geographical location known as the vault site. Vaulting can be used as a mirror or a backup mechanism using the standard incremental or differential backup cycle. Changes to the host system are sent to the vault server in real-time when the backup method is implemented as a mirror. If vaulting updates are recorded in real-time, then it will be necessary to perform regular backups at the off-site location to provide recovery services due to inadvertent or malicious alterations to user or system data.
Journaling or Remote Journaling is another technique used by database management systems to provide redundancy for their transactions. When a transaction is completed, the database management system duplicates the journal entry at a remote location. The journal provides sufficient detail for the transaction to be replayed on the remote system. This provides for database recovery in the event that the database becomes corrupted or unavailable.
There are also additional redundancy options available within application and database software platforms. For example, database shadowing may be used where a database management system updates records in multiple locations. This technique updates an entire copy of the database at a remote location.
Reference used for this question:
Hernandez CISSP, Steven (2012-12-21). Official (ISC)2 Guide to the CISSP CBK, Third Edition ((ISC)2 Press) (Kindle Locations 20403-20407). Auerbach Publications. Kindle Edition.
and
Hernandez CISSP, Steven (2012-12-21). Official (ISC)2 Guide to the CISSP CBK, Third Edition ((ISC)2 Press) (Kindle Locations 20375-20377). Auerbach Publications. Kindle Edition.
Which of the following results in the most devastating business interruptions?
Loss of Hardware/Software
Loss of Data
Loss of Communication Links
Loss of Applications
Source: Veritas eLearning CD - Introducing Disaster Recovery Planning, Chapter 1.
All of the others can be replaced or repaired. Data that is lost and was not backed up, cannot be restored.
Which of the following backup method must be made regardless of whether Differential or Incremental methods are used?
Full Backup Method.
Incremental backup method.
Supplemental backup method.
Tape backup method.
A Full Backup must be made regardless of whether Differential or Incremental methods are used.
Source: KRUTZ, Ronald L. & VINES, Russel D., The CISSP Prep Guide: Mastering the Ten Domains of Computer Security, 2001, John Wiley & Sons, Page 69.
And: HARRIS, Shon, All-In-One CISSP Certification Exam Guide, McGraw-Hill/Osborne, 2002, chapter 9: Disaster Recovery and Business continuity (pages 617-619).
Which one of the following is NOT one of the outcomes of a vulnerability assessment?
Quantative loss assessment
Qualitative loss assessment
Formal approval of BCP scope and initiation document
Defining critical support areas
When seeking to determine the security position of an organization, the security professional will eventually turn to a vulnerability assessment to help identify specific areas of weakness that need to be addressed. A vulnerability assessment is the use of various tools and analysis methodologies to determine where a particular system or process may be susceptible to attack or misuse. Most vulnerability assessments concentrate on technical vulnerabilities in systems or applications, but the assessment process is equally as effective when examining physical or administrative business processes.
The vulnerability assessment is often part of a BIA. It is similar to a Risk Assessment in that there is a quantitative (financial) section and a qualitative (operational) section. It differs in that i t is smaller than a full risk assessment and is focused on providing information that is used solely for the business continuity plan or disaster recovery plan.
A function of a vulnerability assessment is to conduct a loss impact analysis. Because there will be two parts to the assessment, a financial assessment and an operational assessment, it will be necessary to define loss criteria both quantitatively and qualitatively.
Quantitative loss criteria may be defined as follows:
Incurring financial losses from loss of revenue, capital expenditure, or personal liability resolution
The additional operational expenses incurred due to the disruptive event
Incurring financial loss from resolution of violation of contract agreements
Incurring financial loss from resolution of violation of regulatory or compliance requirements
Qualitative loss criteria may consist of the following:
The loss of competitive advantage or market share
The loss of public confidence or credibility, or incurring public mbarrassment
During the vulnerability assessment, critical support areas must be defined in order to assess the impact of a disruptive event. A critical support area is defined as a business unit or function that must be present to sustain continuity of the business processes, maintain life safety, or avoid public relations embarrassment.
Critical support areas could include the following:
Telecommunications, data communications, or information technology areas
Physical infrastructure or plant facilities, transportation services
Accounting, payroll, transaction processing, customer service, purchasing
The granular elements of these critical support areas will also need to be identified. By granular elements we mean the personnel, resources, and services the critical support areas need to maintain business continuity
Reference(s) used for this question:
Hernandez CISSP, Steven (2012-12-21). Official (ISC)2 Guide to the CISSP CBK, Third Edition ((ISC)2 Press) (Kindle Locations 4628-4632). Auerbach Publications. Kindle Edition.
KRUTZ, Ronald L. & VINES, Russel D., The CISSP Prep Guide: Mastering the Ten Domains of Computer Security, John Wiley & Sons, 2001, Page 277.
A prolonged complete loss of electric power is a:
brownout
blackout
surge
fault
A prolonged power outage is a blackout.
From: HARRIS, Shon, All-In-One CISSP Certification Exam Guide, 3rd. Edition McGraw-Hill/Osborne, 2005, page 368.
Which of the following could be BEST defined as the likelihood of a threat agent taking advantage of a vulnerability?
A risk
A residual risk
An exposure
A countermeasure
Risk is the likelihood of a threat agent taking advantage of a vulnerability and the corresponding business impact. If a firewall has several ports open , there is a higher likelihood that an intruder will use one to access the network in an unauthorized method.
The following answers are incorrect :
Residual Risk is very different from the notion of total risk. Residual Risk would be the risks that still exists after countermeasures have been implemented. Total risk is the amount of risk a company faces if it chooses not to implement any type of safeguard.
Exposure: An exposure is an instance of being exposed to losses from a threat agent.
Countermeasure: A countermeasure or a safeguard is put in place to mitigate the potential risk. Examples of countermeasures include strong password management , a security guard.
REFERENCES : SHON HARRIS ALL IN ONE 3rd EDITION
Chapter - 3: Security Management Practices , Pages : 57-59
All of the following can be considered essential business functions that should be identified when creating a Business Impact Analysis (BIA) except one. Which of the following would not be considered an essential element of the BIA but an important TOPIC to include within the BCP plan:
IT Network Support
Accounting
Public Relations
Purchasing
Public Relations, although important to a company, is not listed as an essential business function that should be identified and have loss criteria developed for.
All other entries are considered essential and should be identified and have loss criteria developed.
Source: HARRIS, Shon, All-In-One CISSP Certification Exam Guide, McGraw-Hill/Osborne, 2002, chapter 9: Disaster Recovery and Business continuity (page 598).
Which element must computer evidence have to be admissible in court?
It must be relevant.
It must be annotated.
It must be printed.
It must contain source code.
Source: TIPTON, Hal, (ISC)2, Introduction to the CISSP Exam presentation.
Which backup method only copies files that have been recently added or changed and also leaves the archive bit unchanged?
Full backup method
Incremental backup method
Fast backup method
Differential backup method
A differential backup is a partial backup that copies a selected file to tape only if the archive bit for that file is turned on, indicating that it has changed since the last full backup. A differential backup leaves the archive bits unchanged on the files it copies.
Source: KRUTZ, Ronald L. & VINES, Russel D., The CISSP Prep Guide: Mastering the Ten Domains of Computer Security, John Wiley & Sons, 2001, Chapter 3: Telecommunications and Network Security (page 69).
Also see:
Backup software can use or ignore the archive bit in determining which files to back up, and can either turn the archive bit off or leave it unchanged when the backup is complete. How the archive bit is used and manipulated determines what type of backup is done, as follows
Full backup
A full backup, which Microsoft calls a normal backup, backs up every selected file, regardless of the status of the archive bit. When the backup completes, the backup software turns off the archive bit for every file that was backed up. Note that "full" is a misnomer because a full backup backs up only the files you have selected, which may be as little as one directory or even a single file, so in that sense Microsoft's terminology is actually more accurate. Given the choice, full backup is the method to use because all files are on one tape, which makes it much easier to retrieve files from tape when necessary. Relative to partial backups, full backups also increase redundancy because all files are on all tapes. That means that if one tape fails, you may still be able to retrieve a given file from another tape.
Differential backup
A differential backup is a partial backup that copies a selected file to tape only if the archive bit for that file is turned on, indicating that it has changed since the last full backup. A differential backup leaves the archive bits unchanged on the files it copies. Accordingly, any differential backup set contains all files that have changed since the last full backup. A differential backup set run soon after a full backup will contain relatively few files. One run soon before the next full backup is due will contain many files, including those contained on all previous differential backup sets since the last full backup. When you use differential backup, a complete backup set comprises only two tapes or tape sets: the tape that contains the last full backup and the tape that contains the most recent differential backup.
Incremental backup
An incremental backup is another form of partial backup. Like differential backups, Incremental Backups copy a selected file to tape only if the archive bit for that file is turned on. Unlike the differential backup, however, the incremental backup clears the archive bits for the files it backs up. An incremental backup set therefore contains only files that have changed since the last full backup or the last incremental backup. If you run an incremental backup daily, files changed on Monday are on the Monday tape, files changed on Tuesday are on the Tuesday tape, and so forth. When you use an incremental backup scheme, a complete backup set comprises the tape that contains the last full backup and all of the tapes that contain every incremental backup done since the last normal backup. The only advantages of incremental backups are that they minimize backup time and keep multiple versions of files that change frequently. The disadvantages are that backed-up files are scattered across multiple tapes, making it difficult to locate any particular file you need to restore, and that there is no redundancy. That is, each file is stored only on one tape.
Full copy backup
A full copy backup (which Microsoft calls a copy backup) is identical to a full backup except for the last step. The full backup finishes by turning off the archive bit on all files that have been backed up. The full copy backup instead leaves the archive bits unchanged. The full copy backup is useful only if you are using a combination of full backups and incremental or differential partial backups. The full copy backup allows you to make a duplicate "full" backup—e.g., for storage offsite, without altering the state of the hard drive you are backing up, which would destroy the integrity of the partial backup rotation.
Some Microsoft backup software provides a bizarre backup method Microsoft calls a daily copy backup. This method ignores the archive bit entirely and instead depends on the date- and timestamp of files to determine which files should be backed up. The problem is, it's quite possible for software to change a file without changing the date- and timestamp, or to change the date- and timestamp without changing the contents of the file. For this reason, we regard the daily copy backup as entirely unreliable and recommend you avoid using it.
Devices that supply power when the commercial utility power system fails are called which of the following?
power conditioners
uninterruptible power supplies
power filters
power dividers
From Shon Harris AIO Fifth Edition:
Protecting power can be done in three ways: through UPSs, power line conditioners, and backup sources.
UPSs use battery packs that range in size and capacity. A UPS can be online or standby.
Online UPS systems use AC line voltage to charge a bank of batteries. When in use, the UPS has an inverter that changes the DC output from the batteries into the required AC form and that regulates the voltage as it powers computer devices.
Online UPS systems have the normal primary power passing through them day in and day out. They constantly provide power from their own inverters, even when the electric power is in proper use. Since the environment's electricity passes through this type of UPS all the time, the UPS device is able to quickly detect when a power failure takes place. An online UPS can provide the necessary electricity and picks up the load after a power failure much more quickly than a standby UPS.
Standby UPS devices stay inactive until a power line fails. The system has sensors that detect a power failure, and the load is switched to the battery pack. The switch to the battery pack is what causes the small delay in electricity being provided.
So an online UPS picks up the load much more quickly than a standby UPS, but costs more of course.
Copyright © 2021-2025 CertsTopics. All Rights Reserved

