A patient was admitted 3 days ago for an overdose of acetaminophen (Tylenol). The patient is developing a decreasing level of consciousness. Which the following is the most likely finding?
A patient's blood culture report notes the presence of vancomycin resistant enterococcus. The nurse should place the patient in which type of isolation?
Which of the following is the most common prerenal cause of acute tubular necrosis?
Which of the following diagnostic procedures best pinpoints the location, size, and origin of a cerebral aneurysm?
The purpose of administering a sodium nitroprusside (Nipride) drip after a carotid endarterectomy is to
A patient has experienced significant brain damage from an anoxic episode and has been unable to be weaned from ventilator support. The patient's spouse expresses ambivalence about stopping the ventilator now that it has been started. Which of the following statements is the nurse's most appropriate response?
A patient with a history of asthma presents with acute onset of dyspnea, a non-productive cough, and tachypnea. He is very anxious, restless, and tachycardic. Which of the following is a first-line drug for these symptoms?
An older adult patient is admitted with acute exacerbation of congestive heart failure. An echocardiogram indicates that EF is unchanged at 50%. The patient is most likely experiencing
Which of the following serum laboratory results is most concerning to a nurse who is caring for a patient with a Stage Ill pressure ulcer on the coccyx?
For a patient with unstable angina, the major goal of treatment is to
A patient is experiencing lower left quadrant pain with guarding, as well as abdominal distention and rigidity. KUB reveals free air in the abdominal
cavity. Vital signs are:
BP76/40
HR130
RR32
T101.7° F (38.7°C)
A nurse would suspect
Which of the following signs is most frequently associated with meningitis?
Family members have been complaining about limited visiting hours. To facilitate a potential change in practice, a nurse should first
A patient with a sodium level of 114 mEq/L is most likely to develop
An unconscious patient in hepatic failure secondary to alcoholism becomes acutely hypoglycemic. Glucagon administration is contraindicated for this patient because glucagon
A patient is admitted for acute benzodiazepine overdose. Nursing interventions should include administration of
A patient presents with fever and chills, is diaphoretic, and reports experiencing abdominal and intermittent left shoulder pain for the past week. An
ultrasound shows an enlarged spleen. Vital signs are:
BP 106/59
HR 118
RR 23
T101.2° F (38.4° C)
When reviewing the lab report, which of the following findings is most significant to this presentation?
A patient who is confused and dyspneic is admitted with ABG values that reveal hypoxemia. Results from insertion of a pulmonary artery catheter are:
PAP 38/18 mm Hg
PAOP10 mm Hg
CI 3.5 L/min/m2
These values are most indicative of
A patient is 2 days post MI. The patient was stable until this morning, when severe chest discomfort developed. Assessment reveals:
BP70/palpable
HR122
RR38
PAOP28 mm Hg, with large V waves
CI1.6 L/min/m2
Cool, clammy skin
Inspiratory crackles throughout the lung field
Loud blowing holosystolic murmur at the apex
The patient's present clinical status is most likely a result of
Which of the following suggests acute peripheral arterial insufficiency?
A nurse admits a patient awaiting surgery for an unstable pelvic fracture following a fall in which no other injuries were sustained. The nurse should prioritize
A patient underwent bariatric surgery for weight loss 3 days ago. The patient appears anxious, restless, and reports increased abdominal pain over the last 24 hours. The nurse palpates mild subcutaneous crepitus over the neck. Vital signs are:
BP 106/64
HR 128
RR 27
T 100.4° F (38°C)
Which action should the nurse anticipate?
An older adult patient has been in the unit for 60 hours. The patient has received benzodiazepines for agitation, opioids for persistent pain, and bronchodilators. The patient reports that there is too much noise, and they cannot get peace and quiet. The nurse should evaluate for
A patient underwent a successful percutaneous coronary intervention to the left anterior descending coronary artery. The patient suddenly begins to complain of dyspnea, jaw pain, and chest tightness. The bedside monitor displays sinus tachycardia and ST segment elevation in lead V2. The patient's neck veins are flat and BP is 152/98. Which of the following is the most likely cause of the patient's symptoms?
A patient who underwent bowel resection surgery due to small bowel rupture is tachycardic and hypotensive. A nurse calls the on-call surgical resident and reports the findings. No new orders are received. The nurse should continue to monitor the patient and
A nurse has responded to a rapid response call on a medical-surgical floor in the hospital. The nurse finds the patient with the following data:
BP72/30
HR132
RR24
T102.3° F (39.0° C)
SpO295%
Ph7.13
PaCO234 mm Hg
PaO288 mm Hg
HCO3 14 mEq/L
Na+ 142 mEq/L
The nurse should anticipate an order to administer which of the following?
A patient who recently lost their spouse is admitted following an emergent cardiac catheterization. The procedure report states chest pain and ST elevation, no significant coronary artery disease, left ventricular dysfunction with apical ballooning, and an EF of 35%. These findings are consistent for
A patient who sustained acute head trauma exhibited intermittent unconsciousness prior to admission. The patient is disoriented initially and exhibits rapid deterioration in neurological status shortly after admission. X-rays reveal a right temporal bone fracture, and a diagnosis of epidural hematoma is made. The deterioration in the patient's condition is most likely associated with
A patient with cardiogenic shock for several days has been managed aggressively with vasopressor and inotrope therapies. Which of the following indicates organ dysfunction from hypoperfusion?
Following a splenectomy, a patient is most at risk for
A patient admitted with a diagnosis of pneumonia has a temperature of 103.2° F (39.5° C) and copious pulmonary secretions. ABG results drawn on room air are:

The nurse should expect that hemoglobin's affinity for oxygen in this patient to be
A physician tries three times to insert a central line, then says, "I think I can get it this time." A nurse should
A patient admits to a nurse that he has struggled with depression and feelings of isolation and abandonment since moving into a nursing home last year,
but he has recently started taking an anti-depressant. The patient states, "Sometimes it takes everything I've got just to go on each day." Which of the
following is the nurse's best initial response?
A patient with a history of alcohol abuse has been admitted for progressive dyspnea and leg swelling. Assessment findings include:
BP155/90
HR85
CVP12 mm Hg
Which of the following tests will provide the most definitive diagnosis?
Treatment of cerebral vasospasm includes administration of
The first priority in management of an acute GI hemorrhage is
Which of the following is a sign of brain death?
A patient post-surgical externalized ventricular drain placement has treatment orders that include continuous cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) drainage at 10 mm
Hg. Which of the following should the nurse anticipate with an increase in the ICP above 25 mm Hg?
A patient lying on the left side in Trendelenburg position is in the correct position for postural drainage of which of the following lobes of the lungs?
A patient who experienced a blunt chest trauma in an automobile crash is admitted with multiple rib fractures. The patient is dyspneic and hypotensive and is reporting left shoulder pain. On auscultation, a nurse notes that bowel sounds can be heard over the lower left thorax. These findings are consistent with
An unconscious patient presents with the following laboratory values:
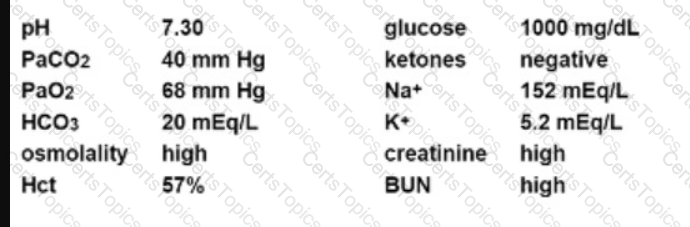
Appropriate management of this patient should include
A patient is admitted with anaphylactic shock secondary to a blood transfusion. The patient's spouse asks the nurse to explain how blood can cause a low blood pressure. The nurse responds that with anaphylactic shock the
Appropriate outcomes for a patient with status asthmaticus include
A patient's IV with norepinephrine (Levophed) infusing is red, swollen, and the IV pump is alarming. A nurse should anticipate
A patient reported to have smoked crack cocaine is brought to the hospital by paramedics and admitted in an agitated state. On the way to the hospital, the patient had a generalized seizure. The toxicology screen is positive for cocaine. Which of the following is most appropriate to administer?