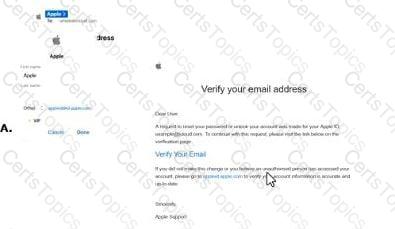
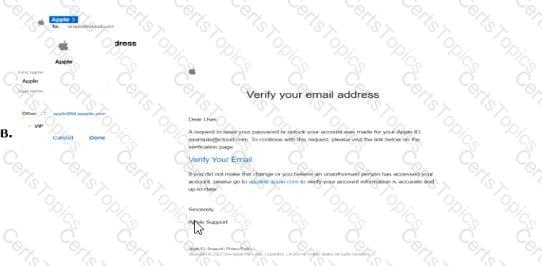
The screenshot shows an email labeled "B" with the subject "Verify your email address" purportedly from Apple. To determine if this is a phishing email, we need to analyze its content and characteristics against common phishing indicators as outlined in CNSP documentation. Since option A is not provided in the screenshot, we will evaluate email B and infer the context for A.
Analysis of Email B:
Sender and Branding:The email claims to be from "Apple Support" and includes an Apple logo, which is a common tactic to establish trust. However, phishing emails often impersonate legitimate brands like Apple to deceive users.
Subject and Content:The subject "Verify your email address" and the body requesting the user to verify their email by clicking a link ("Verify Your Email") are typical of phishing attempts. Legitimate companies like Apple may send verification emails, but the tone and context here raise suspicion.
Link Presence:The email contains a clickable link ("Verify Your Email") that is purportedly for email verification. The screenshot does not show the URL, but phishing emails often include malicious links that lead to fake login pages to steal credentials. CNSP emphasizes that unsolicited requests to click links for verification are a red flag.
Urgency and Vague Instructions:The email includes a statement, "If you did not make this change or believe an unauthorized person has accessed your account, click here to cancel and secure your account." This creates a sense of urgency, a common phishing tactic to prompt immediate action without critical thinking.
Generic Greeting:The email starts with "Dear User," a generic greeting often used in phishing emails. Legitimate companies like Apple typically personalize emails with the user’s name.
Suspicious Elements:The email mentions "your Apple ID (example@icloud.com)," which is a placeholder rather than a specific email address, further indicating a mass phishing campaign rather than a targeted, legitimate communication.
Phishing Indicators (per CNSP):CNSP documentation on phishing identification lists several red flags:
Unsolicited requests for verification or account updates.
Generic greetings (e.g., "Dear User" instead of a personalized name).
Presence of links that may lead to malicious sites (not verifiable in the screenshot but implied).
Urgency or threats (e.g., "click here to cancel and secure your account").
Impersonation of trusted brands (e.g., Apple).Email B exhibits multiple indicators: the generic greeting, unsolicited verification request, urgent call to action, and impersonation of Apple.
Option A Context:Since the screenshot only shows email B, and the correct answer is "Only B," we can infer that email A (not shown) does not exhibit phishing characteristics. For example, A might be a legitimate email from Apple with proper personalization, no suspicious links, or a different context (e.g., a purchase confirmation rather than a verification request).
Evaluation of Options:
1. Only A:Incorrect, as email A is not shown, and the correct answer indicates B asthe phishing email.
2. Only B:Correct. Email B shows clear phishing characteristics, such as impersonation, a generic greeting, an unsolicited verification link, and urgency, aligning with CNSP’s phishing criteria.
3. Both A and B:Incorrect, as A is implied to be non-phishing based on the correct answer.
4. None of the above:Incorrect, as B is a phishing email.